Table of Contents
In statistics, a regressor is the name given to any variable in a regression model that is used to predict a response variable.
A regressor is also referred to as:
- An
- An
- A
- A predictor variable
- A feature
All of these terms are used interchangeably depending on the type of field you’re working in: statistics, machine learning, econometrics, biology, etc.
Note: Sometimes a response variable is called a “regressand.”
Regressors in Regression Models
Most regression models take the following form:
Y = β0 + B1x1+ B2x2 + B3x3 + ε
where:
- Y: The response variable
- βi: The coefficients for the regressors
- xi: The regressors
- ε: The error term
The whole point of building a regression model is to understand how changes in a regressor lead to changes in a response variable (or “regressand”).
Note that regression models can have one or more regressors.
When there is only one regressor, the model is referred to as a and when there are multiple regressors, the model is referred to as a to indicate that there are multiple regressors.
The following examples illustrate how to interpret regressors in different regression models.
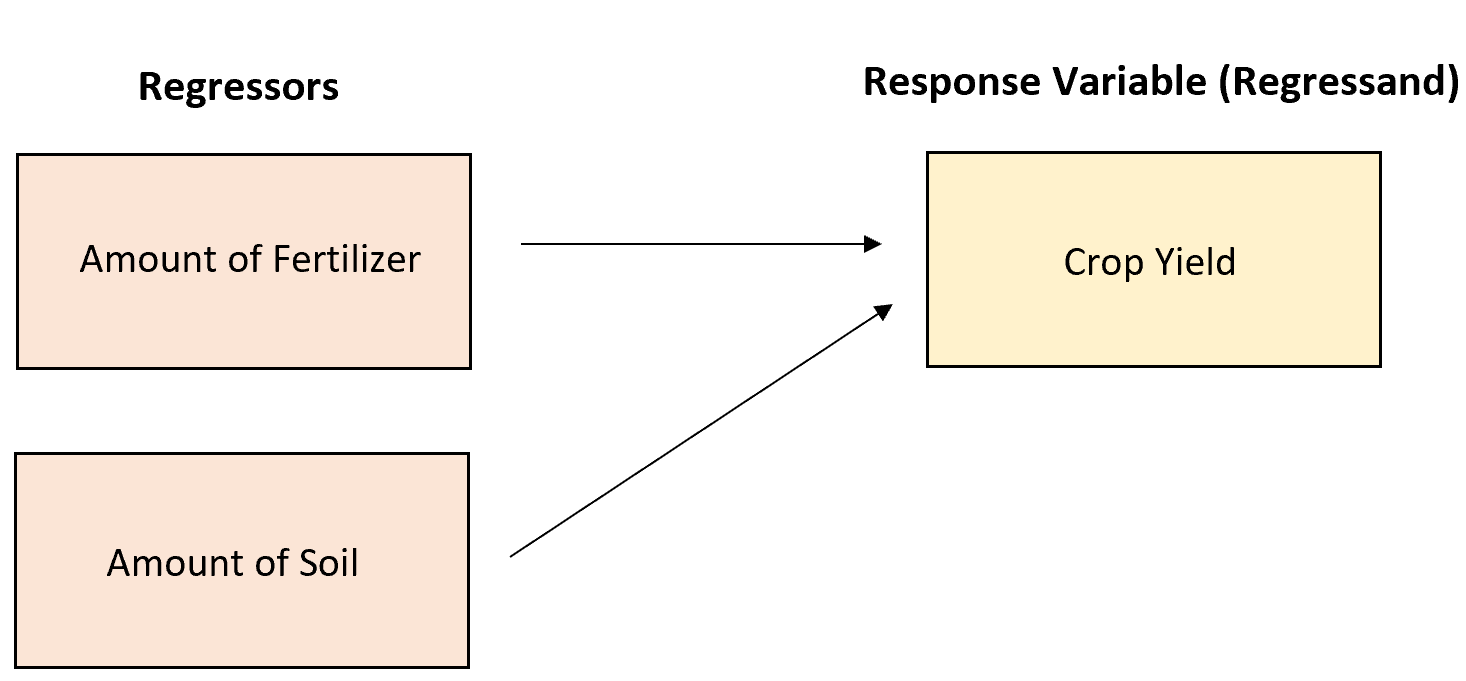
Example 1: Crop Yield
Suppose a farmer is interested in understanding the factors that affect total crop yield (in pounds). He collects data and builds the following regression model:
Crop Yield = 154.34 + 3.56*(Pounds of Fertilizer) + 1.89*(Pounds of Soil)
Here’s how to interpret these two regressors:
- Fertilizer: For each additional pound of fertilizer used, crop yield increases by an average of 3.56 pounds, assuming the amount of soil is held constant.
- Soil: For each additional pound of soil used, crop yield increases by an average of 1.89 pounds, assuming the amount of fertilizer is held constant.
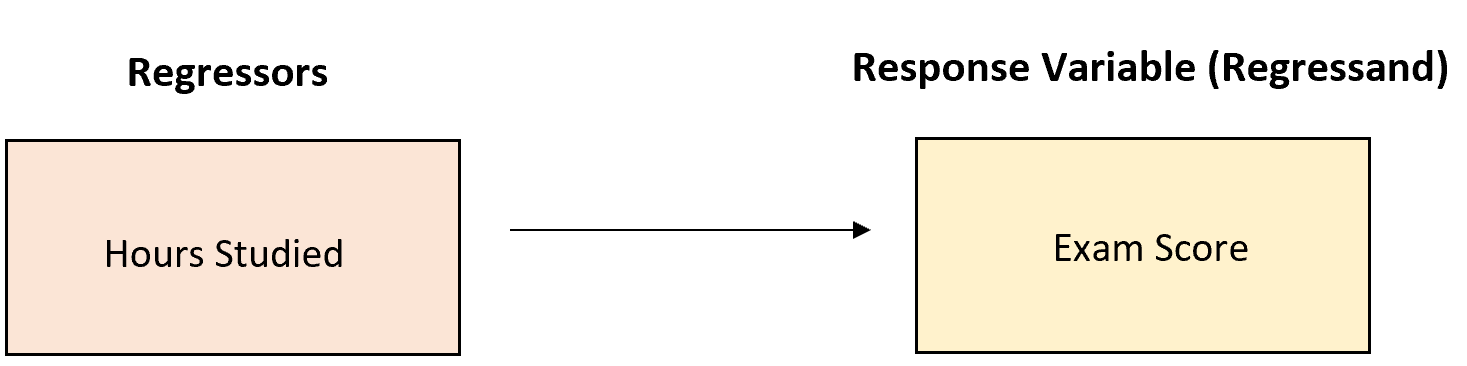
Example 2: Exam Scores
Suppose a professor is interested in understanding how the amount of hours studied affects exam scores. He collects data and builds the following regression model:
Exam Score = 68.34 + 3.44*(Hours Studied)
This model has one regressor: Hours studied. We interpret the coefficient for this regressor to mean that for each additional hour studied, exam score increases by an average of 3.44 points.