Table of Contents
The “%matplotlib inline” command is used in Jupyter Notebook to display plots created with matplotlib. This command allows the output of plotting commands to be displayed directly in the notebook. It also enables the use of various GUI backends in the notebook. It is important to note that this command should be used before any plotting commands are issued, otherwise plots will not be displayed in the notebook. For example, the code below will display a simple line plot when run in a Jupyter notebook:
%matplotlib inline
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x = [1, 2, 3]
y = [2, 4, 1]
plt.plot(x, y)
You can use the following code to display and store plots within a Python Jupyter notebook:
%matplotlib inline
Here’s how this code is described within the :
“With this backend, the output of plotting commands is displayed inline within frontends like the Jupyter notebook, directly below the code cell that produced it. The resulting plots will then also be stored in the notebook document.”
The following example shows how to use this code in practice.
Example: How to Use %matplotlibe inline
Suppose we attempt to use the following code to create a Matplotlib line plot in a Jupyter notebook:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
#define x and y
x = [1, 6, 10]
y = [5, 13, 27]
#attempt to create line plot of x and y
plt.plot(x, y)
Here’s what the output looks like in the Jupyter notebook:

The code runs without any errors, but no line plot is displayed inline with the code.
To fix this, we can use the %matplotlib inline command before we create the line plot:
%matplotlib inline
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
#define x and y
x = [1, 6, 10]
y = [5, 13, 27]
#create scatter plot of x and y
plt.plot(x, y)
Here’s what the output looks like in the Jupyter notebook:
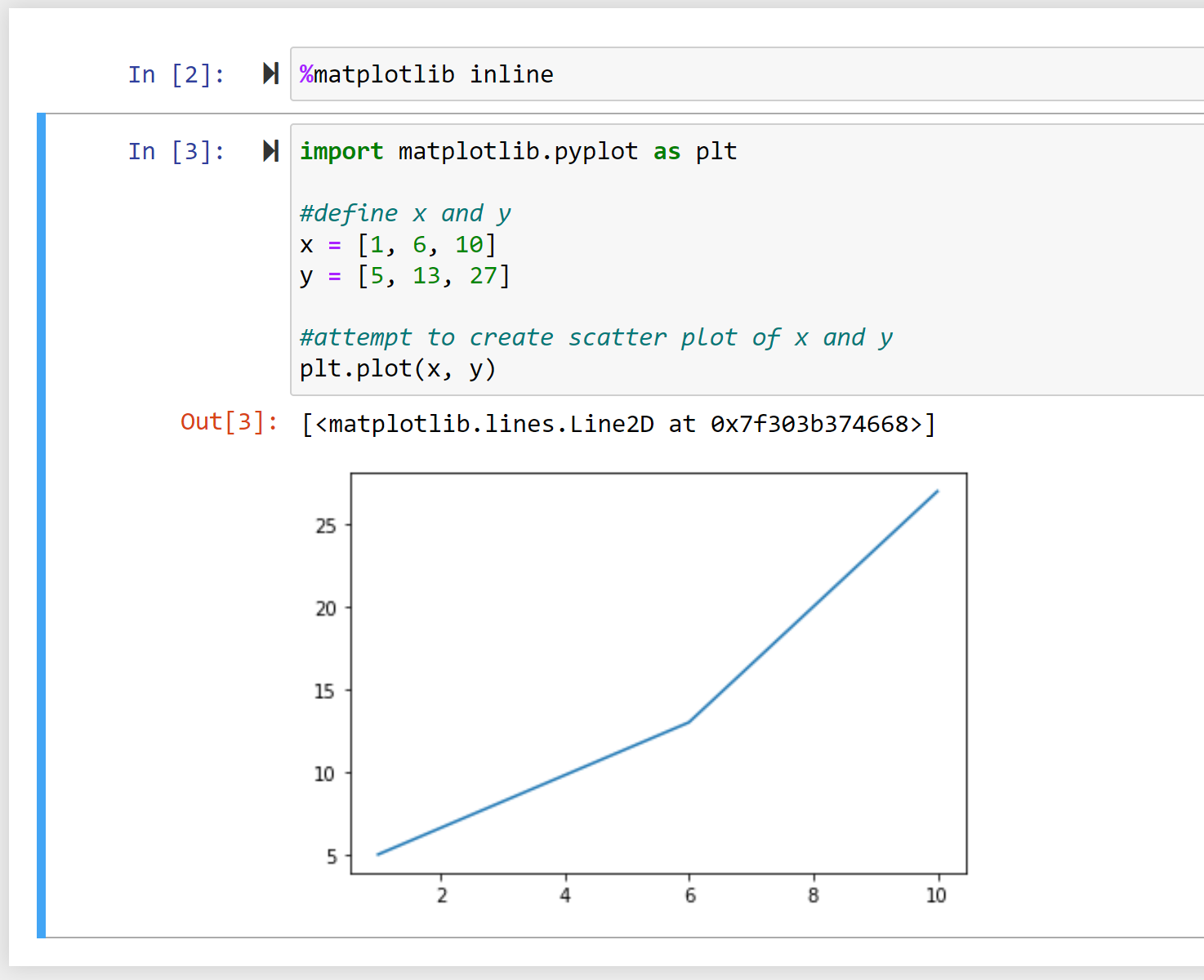
Notice that the code runs without any errors again and the plot is displayed inline in the notebook.
Note that once we’ve used %matplotlib inline, any Matplotlib plots that we create in any future cells in the notebook will also be displayed and store within the notebook.
The following tutorials explain how to perform other common operations in Python:
