Table of Contents
The triangular distribution in Excel can be used to model the probability of a given outcome by allowing the user to define the minimum, most likely, and maximum values for a given set of data. This is done by using the TRIMINV function in Excel, which takes in the minimum, most likely, and maximum values to generate a probability distribution. This allows the user to efficiently model the probability of an outcome to help make decisions or predictions.
The is a continuous probability distribution with a probability density function shaped like a triangle.
It is defined by three values:
- The minimum value a
- The maximum value b
- The peak value c
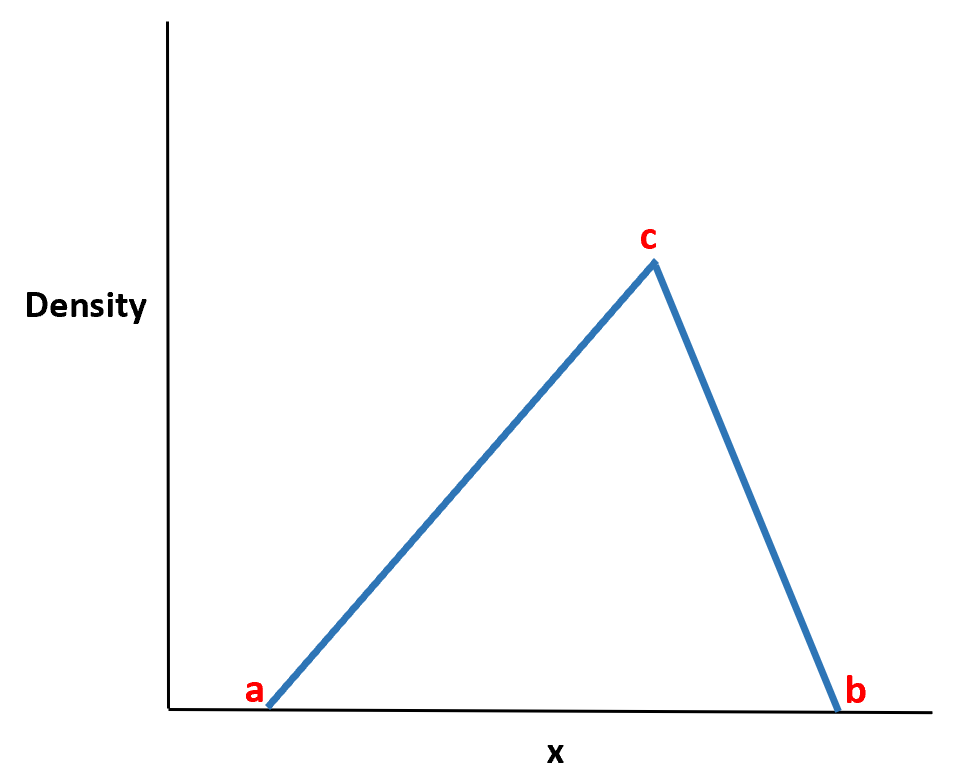
The name of the distribution comes from the fact that the probability density function is shaped like a triangle.
The triangular distribution has the following :
PDF:
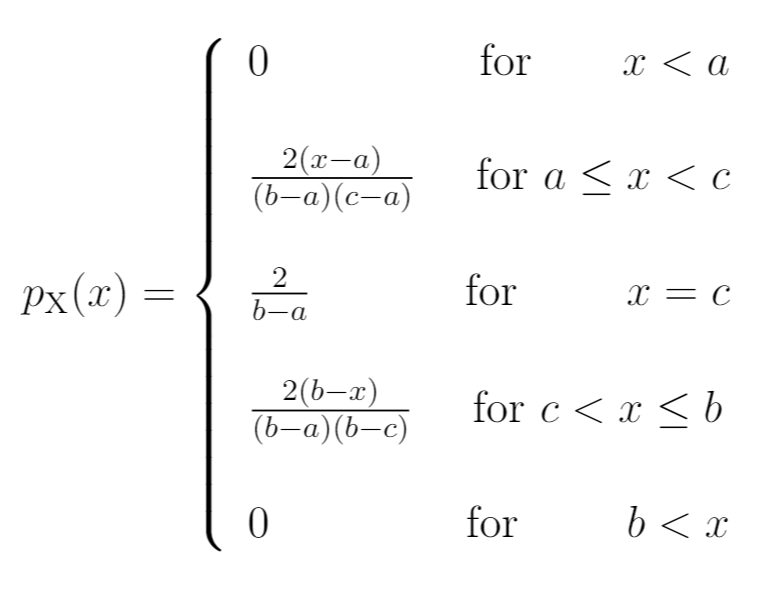
CDF:

The following examples show how to use the Triangular distribution to calculate probabilities in Excel.
Example 1: Restaurant Sales
Suppose a restaurant estimates that their total sales for the upcoming week will be a minimum of $10,000, a maximum of $30,000, and most likely $25,000.
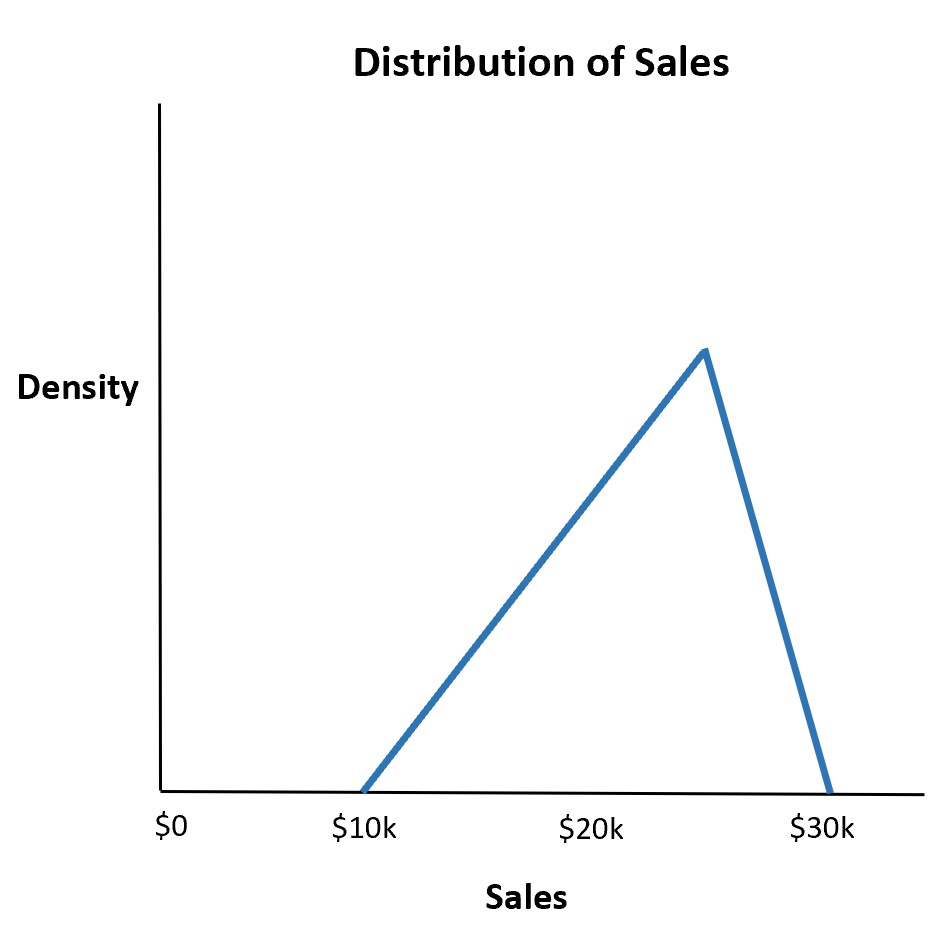
What is the probability that the restaurant makes less than $20,000 total sales?
According to the CDF, we can use the following formula to find the probability that total sales will be less than $20,000:
- P(X < x) = (x-a)2 / ((b-a)(c-a))
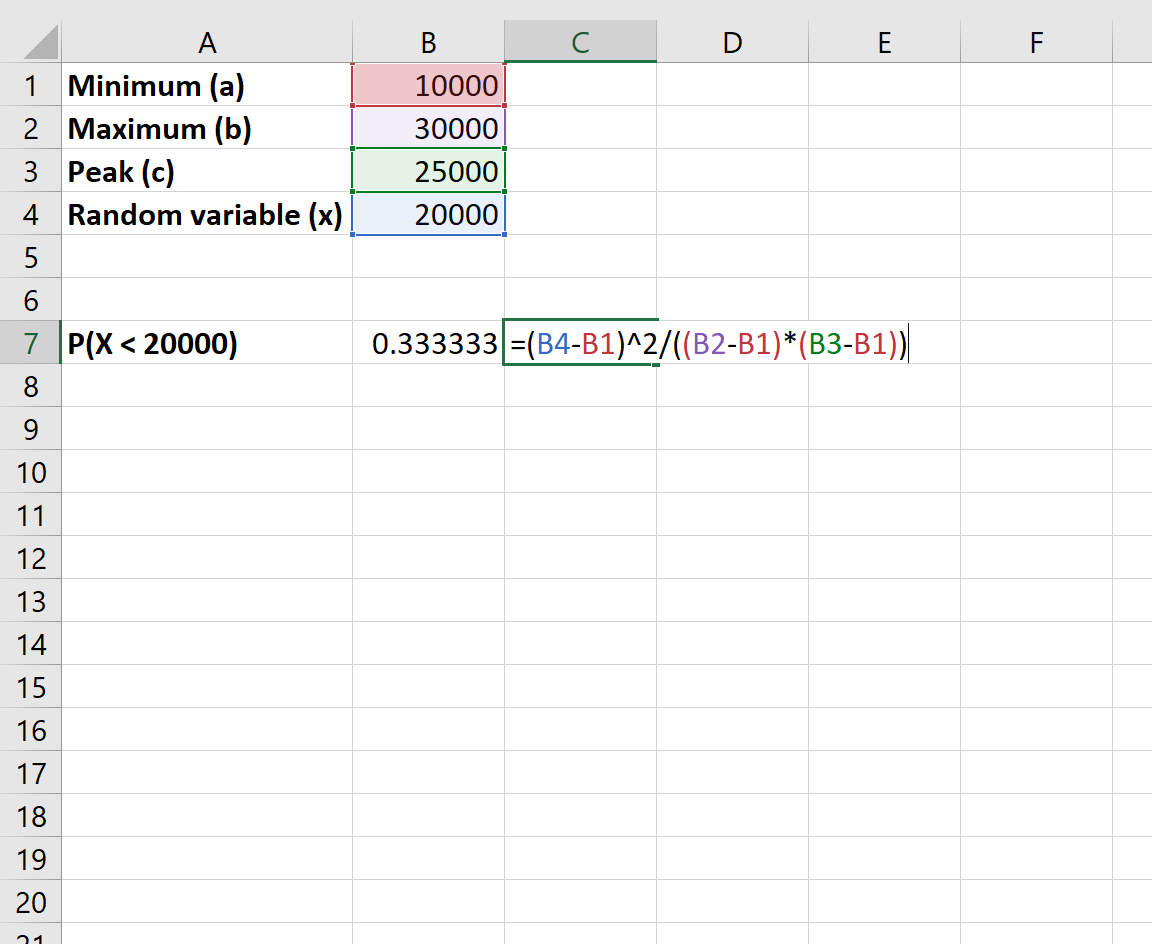
The probability that the restaurant makes less than $20,000 total sales is .333.
Example 2: Number of Customers
Suppose a shop estimates that the number of customers that will enter in a given week will be a minimum of 500, a maximum of 2,000, and most likely 1,200.
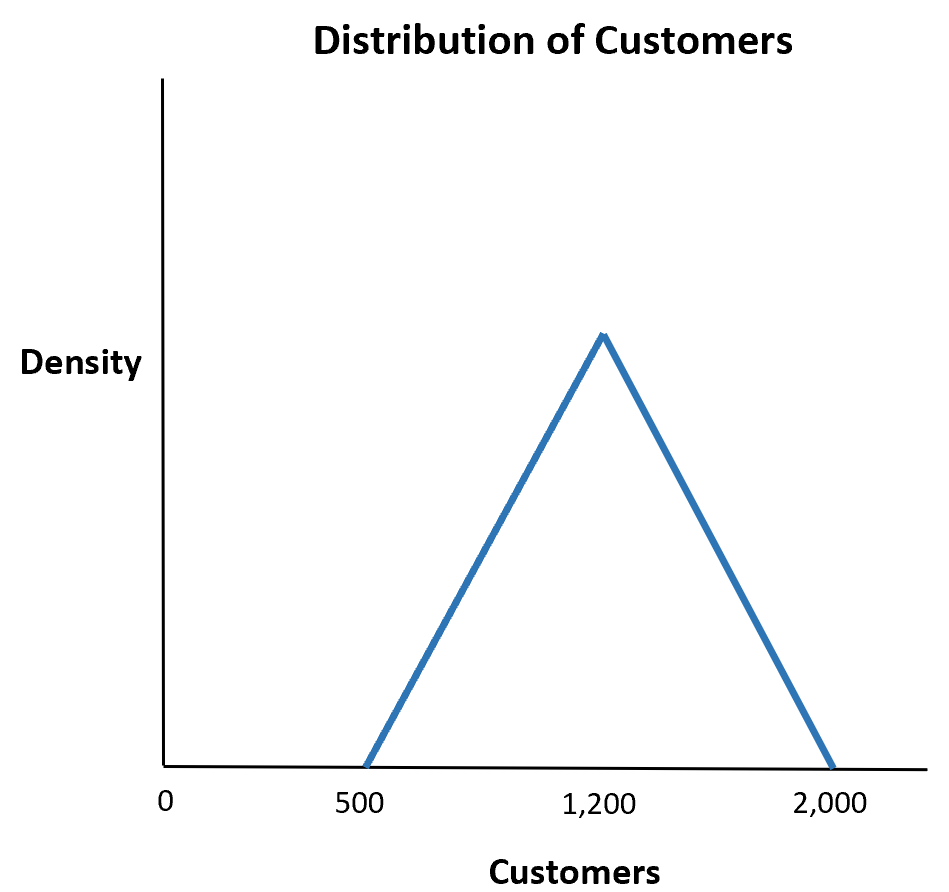
What is the probability that more than 1,500 customers enter the shop in a given week?
According to the CDF, we can use the following formula to find the probability that the total number of customers will be greater than 1,500:
- P(X > x) = 1 – [1 – (b-x)2 / ((b-a)(b-c))]
Here’s how to calculate this probability in Excel:
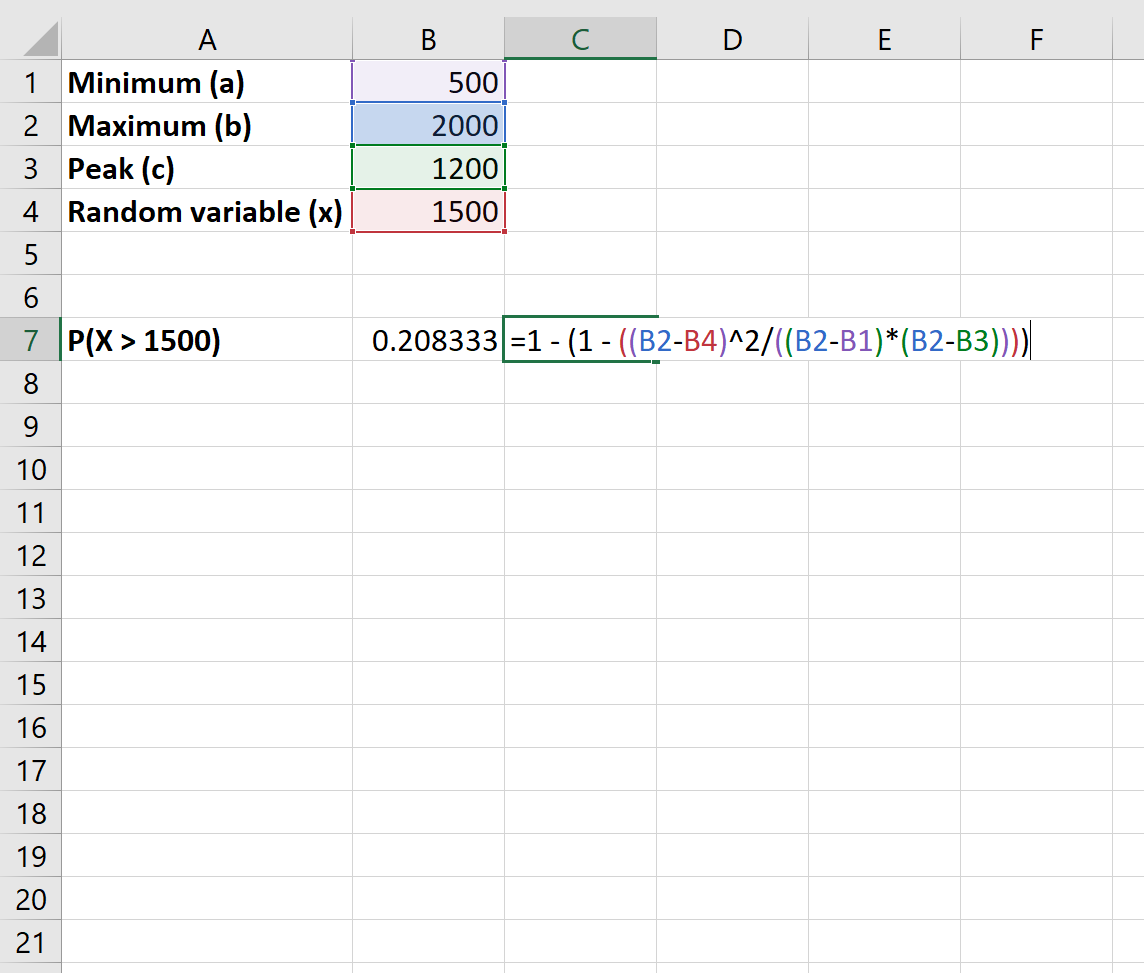
The probability that more than 1,500 customers enter the shop is .208.
The following tutorials explain how to work with other probability distributions in Excel:
