Table of Contents
The triangular distribution in R is a probability distribution used to represent uncertain events. It is specified by three parameters: the minimum, the maximum, and the mode. In R, the function “dtriangle” is used to generate random numbers from the triangular distribution. Additionally, the “ptriangle” function can be used to calculate the probability of a specified outcome. Examples of how to use the “dtriangle” and “ptriangle” functions can be found in the R documentation.
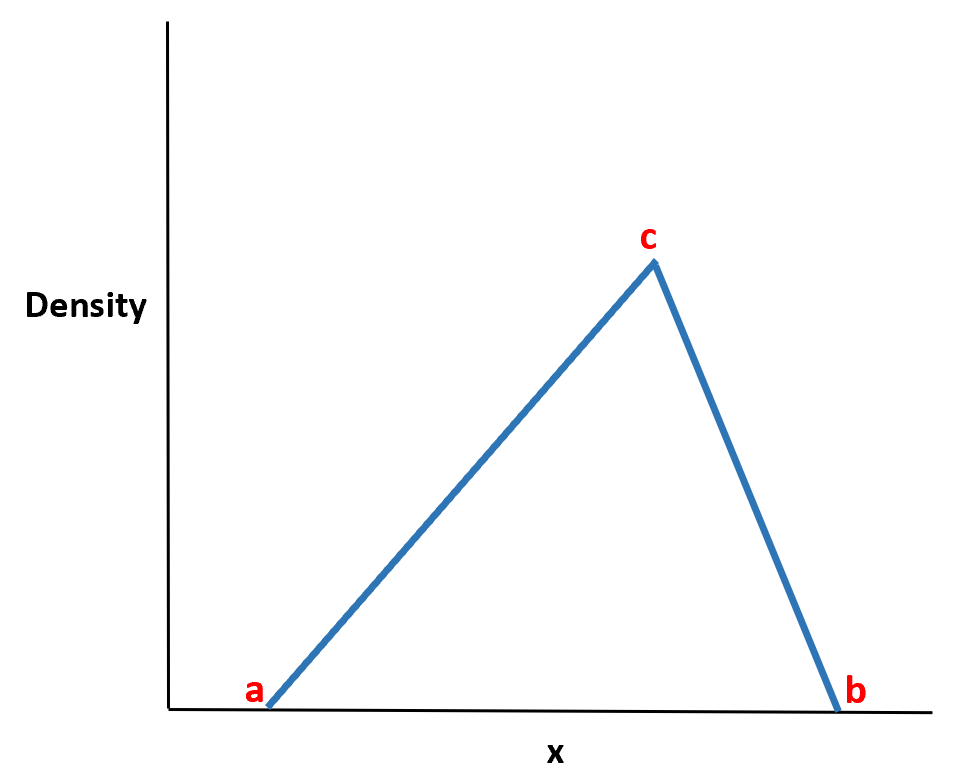
The is a continuous probability distribution with a probability density function shaped like a triangle.
It is defined by three values:
- The minimum value a
- The maximum value b
- The peak value c
To calculate probabilities for the triangular distribution in R we can use the ptri() function from the EnvStats package, which uses the following syntax:
ptri(q, min = 0, max = 1, mode = 1/2)
where:
- q: Quantile of interest
- min: The minimum value of the distribution
- max: The maximum value of the distribution
- mode: The peak value of the distribution
The following examples show how to use this function in practice in R.
Example 1: Calculating Probability Less Than Some Value
Suppose a restaurant estimates that their total sales for the upcoming week will be a minimum of $10,000, a maximum of $30,000, and most likely $25,000.
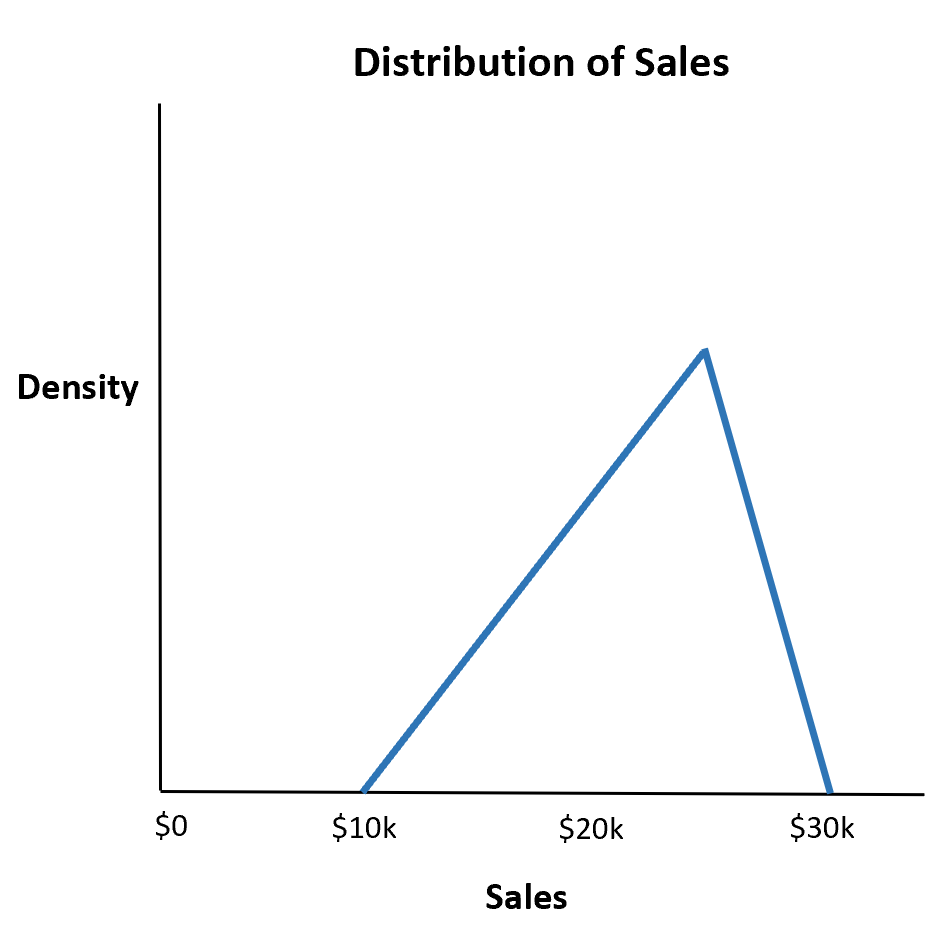
What is the probability that the restaurant makes less than $20,000 total sales?
We can use the following code to calculate this probability:
library(EnvStats) #calculate probability ptri(q = 20000, min = 10000, max = 30000, mode = 25000) [1] 0.3333333
The probability that the restaurant makes less than $20,000 total sales is .333.
Example 2: Calculating Probability Greater Than Some Value
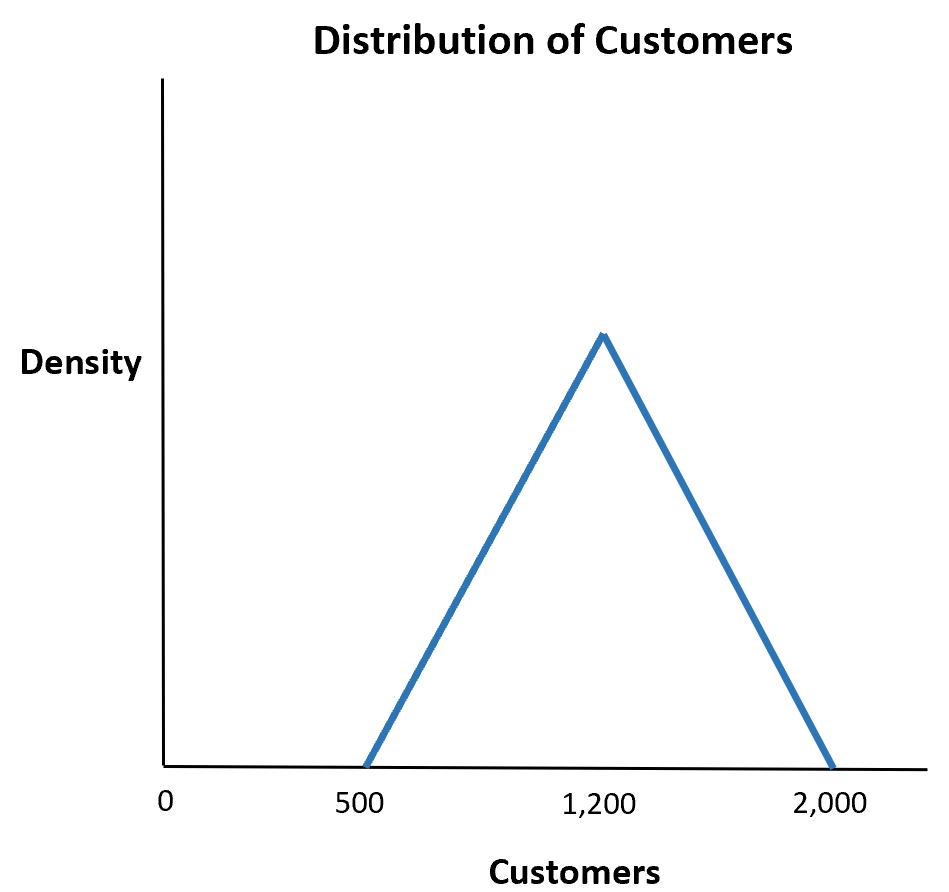
What is the probability that more than 1,500 customers enter the shop in a given week?
We can use the following code to calculate this probability:
library(EnvStats) #calculate probability 1 - ptri(q = 1500, min = 500, max = 2000, mode = 1200) [1] 0.2083333
The probability that more than 1,500 customers enter the shop is about .208.
Note: You can find the complete documentation for the ptri() function .
The following tutorials explain how to work with other probability distributions in R:
