Table of Contents
Piecewise regression is a type of linear regression where the data is split into several pieces, and the best fitting regression line is found for each piece. In R, this can be accomplished by using the “segmented” package to fit a piecewise regression model to the data. This involves specifying the data, the model parameters, the number of segments to be used, and the type of cost function to be minimized. Once all of the parameters have been specified, the segmented package will then fit the piecewise regression model to the data, giving the user the final regression model and the associated coefficients.
Piecewise regression is a regression method we often use when there are clear “breakpoints” in a dataset.
The following step-by-step example shows how to perform piecewise regression in R.
Step 1: Create the Data
First, let’s create the following data frame:
#view DataFrame df <- data.frame(x=c(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16), y=c(2, 4, 5, 6, 8, 10, 12, 13, 15, 19, 24, 28, 31, 34, 39, 44)) #view first six rows of data frame head(df) x y 1 1 2 2 2 4 3 3 5 4 4 6 5 5 8 6 6 10
Step 2: Visualize the Data
Next, let’s create a scatterplot to visualize the data:
#create scatterplot of x vs. y plot(df$x, df$y, pch=16, col='steelblue')
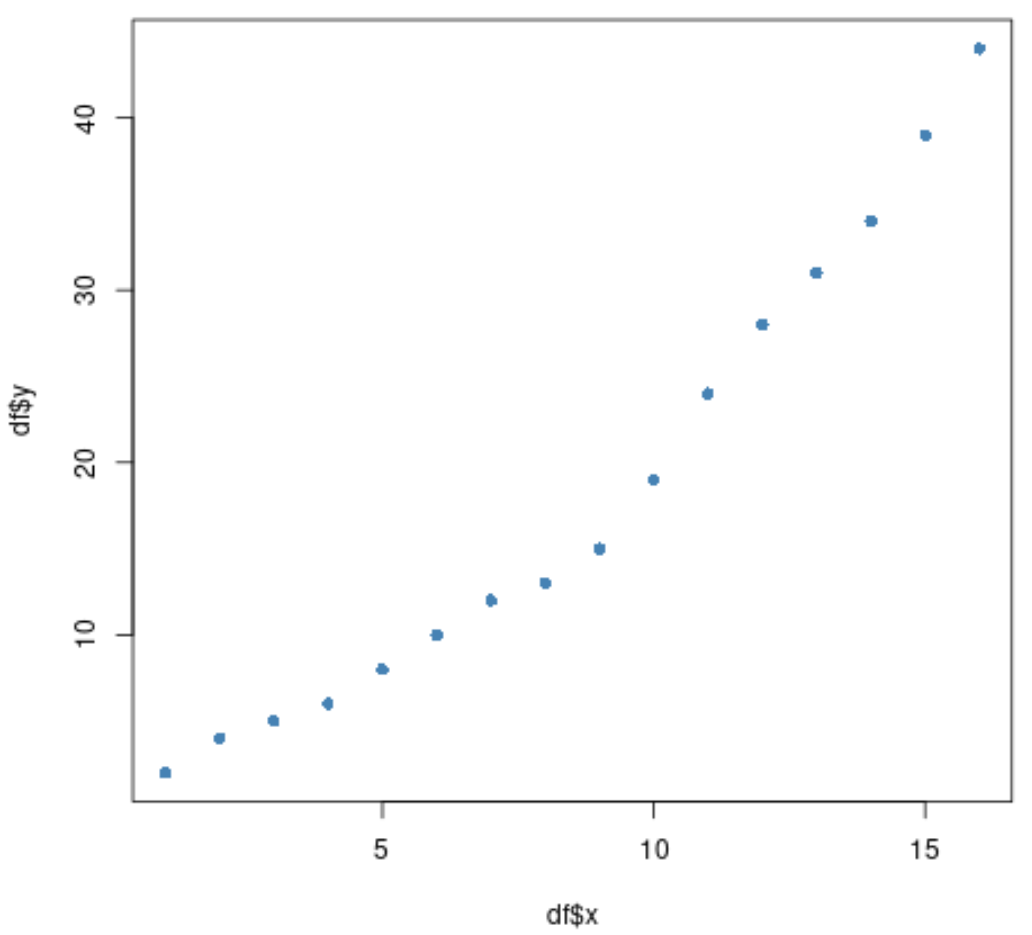
We can see that the relationship between x and y appears to abruptly change around x = 9.
Step 3: Fit the Piecewise Regression Model
We can use the segmented() function from the package in R to fit a piecewise regression model to our dataset:
library(segmented) #fit simple linear regression model fit <- lm(y ~ x, data=df) #fit piecewise regression model to original model, estimating a breakpoint at x=9 segmented.fit <- segmented(fit, seg.Z = ~x, psi=9) #view summary of segmented model summary(segmented.fit) Call: segmented.lm(obj = fit, seg.Z = ~x, psi = 9) Estimated Break-Point(s): Est. St.Err psi1.x 8.762 0.26 Meaningful coefficients of the linear terms: Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|) (Intercept) 0.32143 0.48343 0.665 0.519 x 1.59524 0.09573 16.663 1.16e-09 *** U1.x 2.40476 0.13539 17.762 NA --- Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1 Residual standard error: 0.6204 on 12 degrees of freedom Multiple R-Squared: 0.9983, Adjusted R-squared: 0.9978 Convergence attained in 2 iter. (rel. change 0)
The segmented() function detects a breakpoint at x = 8.762.
The fitted piecewise regression model is:
If x ≤ 8.762: y = .32143 + 1.59524*(x)
If x > 8.762: y = .32143 + 1.59524*(8.762) + (1.59524+2.40476)*(x-8.762)
- y = .32143 + 1.59524*(x)
- y = .32143 + 1.59524*(5)
- y = 8.297
Or suppose we have a value of x = 12. The estimated y value would be:
- y = .32143 + 1.59524*(8.762) + (1.59524+2.40476)*(12-8.762)
- y = 27.25
Step 4: Visualize the Final Piecewise Regression Model
We can use the following code to visualize the final piecewise regression model on top of our original data:
#plot original data plot(df$x, df$y, pch=16, col='steelblue') #add segmented regression model plot(segmented.fit, add=T)
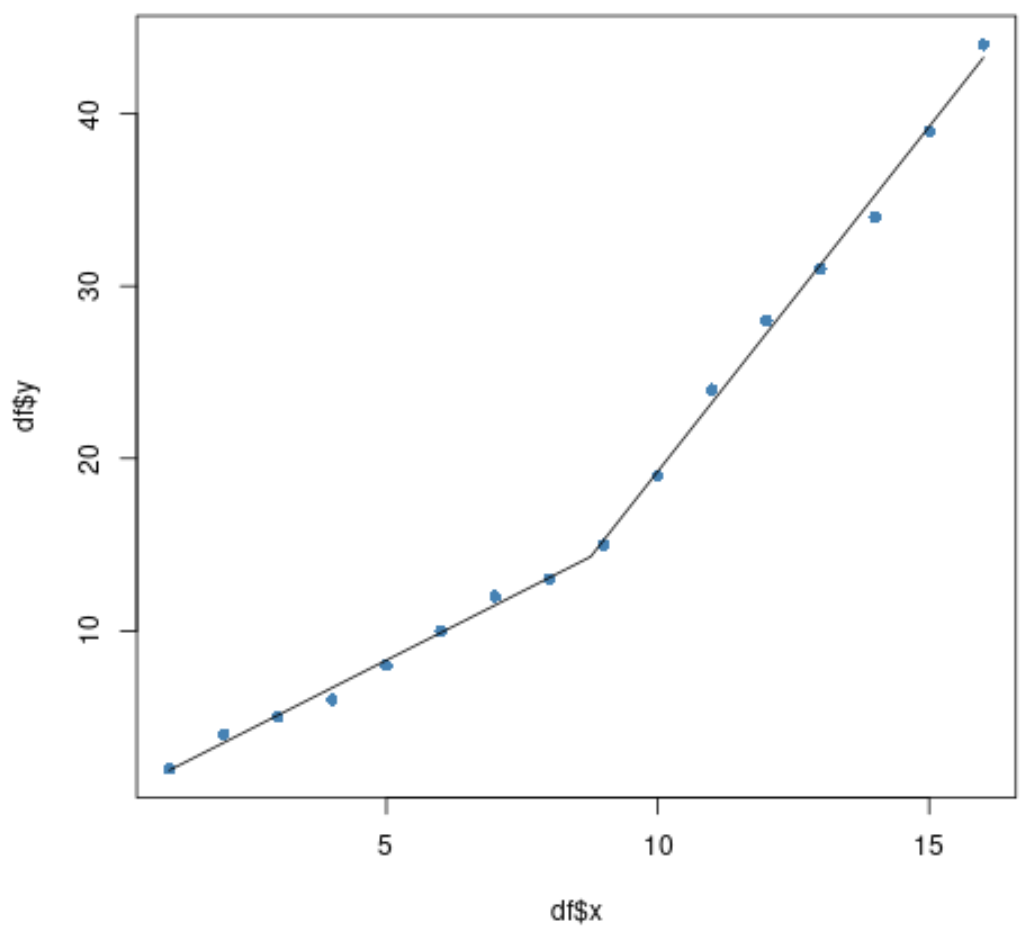
It appears that the piecewise regression model fits the data quite well.
The following tutorials provide additional information about regression models in R:
