Table of Contents
The Wilcoxon Signed Rank Test is a statistical test used to analyze paired data sets and determine if there is a significant difference between the two groups. It is a non-parametric test, meaning that it does not assume a normal distribution of the data.
To perform the Wilcoxon Signed Rank Test, the following steps are typically followed:
1. Gather the paired data sets: The first step is to collect the data from the two groups that are being compared. The data should consist of two related variables, such as pre- and post-treatment measurements.
2. Calculate the differences: Next, the differences between the two data sets should be calculated. This can be done by subtracting the values of one data set from the other.
3. Rank the differences: The differences should then be ranked from smallest to largest, ignoring the sign (+ or -).
4. Calculate the signed ranks: The signed ranks are calculated by assigning a positive sign to the ranks of the positive differences and a negative sign to the ranks of the negative differences.
5. Calculate the test statistic: The test statistic for the Wilcoxon Signed Rank Test is the sum of the signed ranks. This value is then compared to a critical value from a table or calculated using a statistical software.
6. Determine the p-value: The p-value is the probability of obtaining a test statistic as extreme as the one observed, assuming that the null hypothesis is true. This value can also be obtained from a table or calculated using a statistical software.
7. Interpret the results: If the p-value is less than the chosen significance level, typically 0.05, then the null hypothesis can be rejected and it can be concluded that there is a significant difference between the two groups.
In summary, the Wilcoxon Signed Rank Test is a useful statistical tool for analyzing paired data sets and determining if there is a significant difference between the two groups. It is a relatively simple and robust test that does not require a normal distribution of the data.
Perform the Wilcoxon Signed Rank Test
The Wilcoxon Signed Rank Test is the non-parametric version of . It is used to test whether or not there is a significant difference between two population means.
When to Use the Wilcoxon Signed Rank Test
Use the Wilcoxon Signed Rank test when you would like to use the paired t-test but the distribution of the differences between the pairs is severely .
The easiest way to determine if the differences are non-normally distributed is to create a histogram of the differences and see if they follow a somewhat normal, “bell-shaped” distribution.
Keep in mind that the paired t-test is fairly robust to departures from normality, so the deviation from a normal distribution needs to be pretty severe to justify the use of the Wilcoxon Signed Rank test.
How to Perform the Wilcoxon Signed Rank Test
The following example illustrates how to perform the Wilcoxon Signed Rank test.
A basketball coach want to know if a certain training program increases the number of free throws made by his players. To test this, he has 15 players shoot 20 free throws each before and after the training program.
Since each player can be “paired” with themselves, the coach had planned on using a paired t-test to determine if there was a significant difference between the mean number of free throws made before and after the training program.
However, the distribution of the differences turns out to be non-normal, so the coach instead uses a Wilcoxon Signed Rank Test.
The following table shows the number of free throws made (out of 20 attempts) by each of the 15 players, both before and after the training program:

Step 1: State the null and alternative hypotheses.
H0: The median difference between the two groups is zero.
HA: The median difference is negative. (e.g. the players make less free throws before participating in the training program)
Step 2: Find the difference and absolute difference for each pair.

Step 3: Order the pairs by the absolute differences and assign a rank from the smallest to largest absolute differences. Ignore pairs that have an absolute difference of “0” and assign mean ranks when there are ties.


Step 5: Reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis.
The test statistic, W, is the smaller of the absolute values of the positive ranks and negative ranks. In this case, the smaller value is 29.5. Thus, our test statistic is W = 29.5.
To determine if we should reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis, we can reference the critical value found in the that corresponds with n and our chosen alpha level.
If our test statistic, W, is less than or equal to the critical value in the table, we can reject the null hypothesis. Otherwise, we fail to reject the null hypothesis.
The critical value that corresponds to an alpha level of 0.05 and n = 13 (the total number of pairs minus the two we didn’t calculate ranks for since they had an observed difference of 0) is 17.
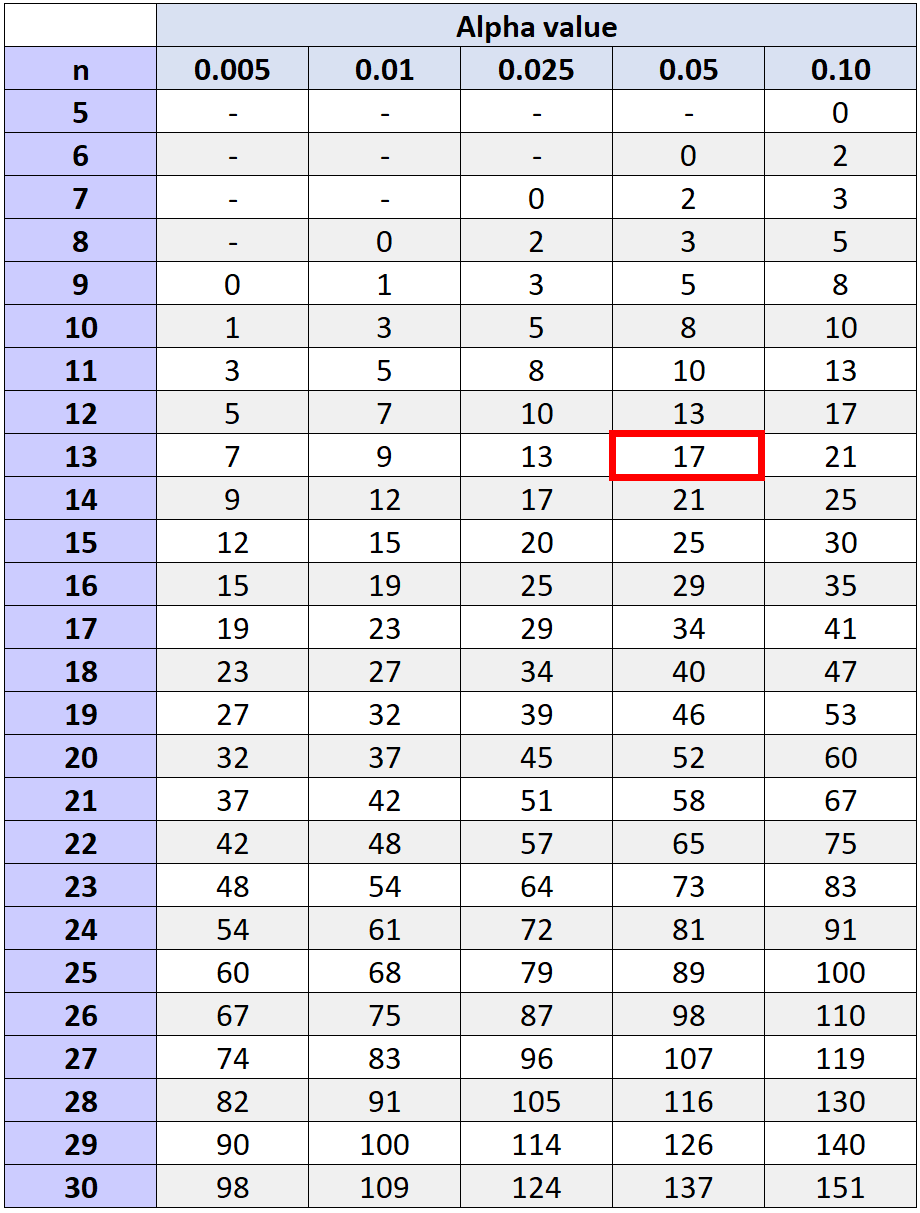
Since our test statistic (W = 29.5) is not less than or equal to 17, we fail to reject the null hypothesis. We do not have sufficient evidence to say that the training program leads to a significant increase in the number of free throws made by the players.
Note: Use the if you wish to perform the test using a calculator instead of by hand.
