Table of Contents
The Log Rank Test in R is a statistical test that can be used to compare the survival times of two or more groups of subjects. It is performed using the survdiff() function from the survival package in R. The function takes two arguments: a survival object containing the survival times of all subjects in the study, and a vector of treatment assignments for each subject. It then returns a p-value, which can be used to assess the statistical significance of the differences in survival time between the groups.
A log rank test is the most common way to compare survival curves between two groups.
This test uses the following :
H0: There is no difference in survival between the two groups.
HA: There is a difference in survival between the two groups.
If the of the test is less than some significance level (e.g. α = .05), then we can reject the null hypothesis and conclude that there is sufficient evidence to say there is a difference in survival between the two groups.
To perform a log rank test in R, we can use the survdiff() function from the survival package, which uses the following syntax:
survdiff(Surv(time, status) ~ predictors, data)
This function returns a Chi-Squared test statistic and a corresponding p-value.
The following example shows how to use this function to perform a log rank test in R.
Example: Log Rank Test in R
For this example, we’ll use the ovarian dataset from the survival package. This dataset contains the following information about 26 patients:
- Survival time (in months) after being diagnosed with ovarian cancer
- Whether or not survival time was censored
- Type of treatment received (rx =1 or rx = 2)
The following code shows how to view the first six rows of this dataset:
library(survival) #view first six rows of dataset head(ovarian) futime fustat age resid.ds rx ecog.ps 1 59 1 72.3315 2 1 1 2 115 1 74.4932 2 1 1 3 156 1 66.4658 2 1 2 4 421 0 53.3644 2 2 1 5 431 1 50.3397 2 1 1 6 448 0 56.4301 1 1 2
The following code shows how to perform a log rank test to determine if there is a difference in survival between patients who received different treatments:
#perform log rank test
survdiff(Surv(futime, fustat) ~ rx, data=ovarian)
Call:
survdiff(formula = Surv(futime, fustat) ~ rx, data = ovarian)
N Observed Expected (O-E)^2/E (O-E)^2/V
rx=1 13 7 5.23 0.596 1.06
rx=2 13 5 6.77 0.461 1.06
Chisq= 1.1 on 1 degrees of freedom, p= 0.3
The Chi-Squared test statistic is 1.1 with 1 degree of freedom and the corresponding p-value is 0.3. Since this p-value is not less than .05, we fail to reject the null hypothesis.
We can also plot the survival curves for each group using the following syntax:
#plot survival curves for each treatment group plot(survfit(Surv(futime, fustat) ~ rx, data = ovarian), xlab = "Time", ylab = "Overall survival probability")
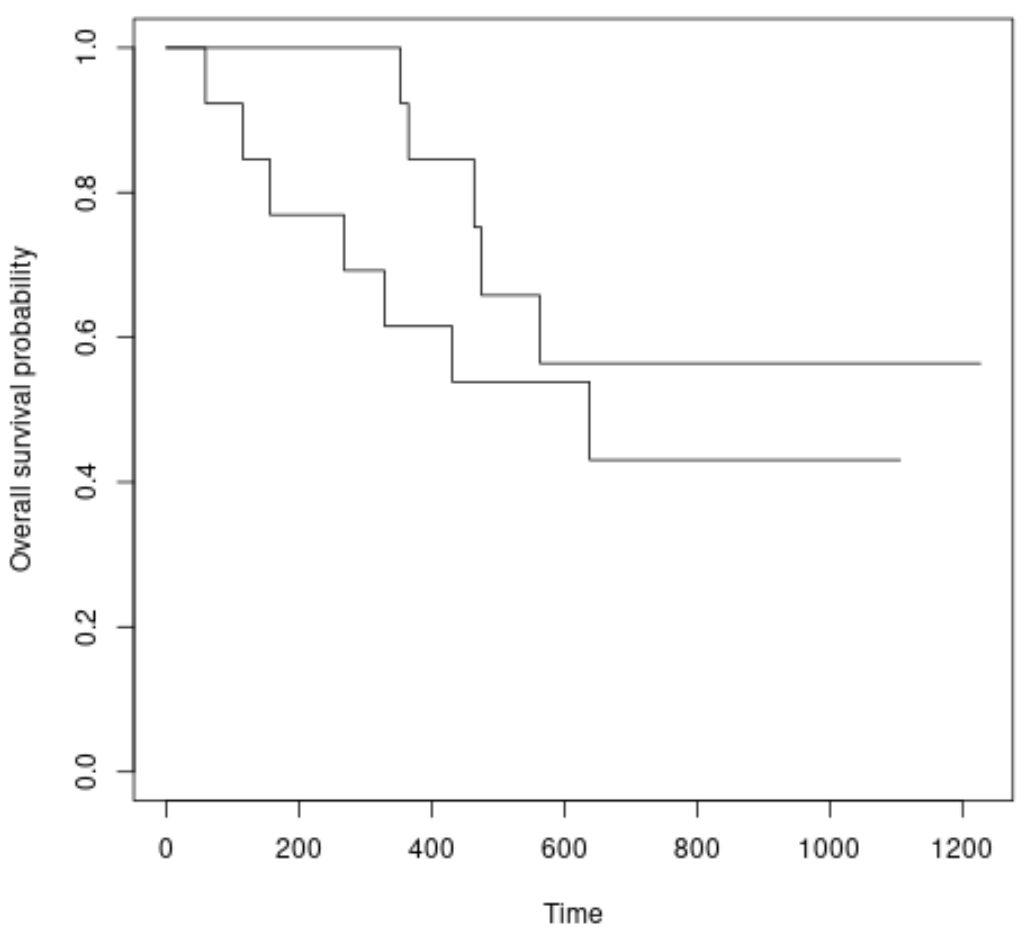
We can see that the survival curves are slightly different, but the log rank test told us that the difference is not statistically significant.
