Table of Contents
Linear interpolation in Excel is a method of estimating a value that lies between two known values in a list or table. It can be used to fill in missing data points in a series of values, or to find an approximate value when the exact value is not known. To use linear interpolation in Excel, you will need to determine the two known values, then use the slope-intercept form of the equation of a line to calculate the value that lies between them. Finally, you will enter the equation into an Excel cell and use it to calculate the unknown value.
Interpolation is the process of estimating an unknown value of a function between two known values.
Given two known values (x1, y1) and (x2, y2), we can estimate the y-value for some point x by using the following formula:
y = y1 + (x-x1)(y2-y1)/(x2-x1)
This tutorial explains how to use linear interpolation to find some unknown y-value based on an x-value in Excel.
Example: Linear Interpolation in Excel
Suppose we have the following dataset in Excel:
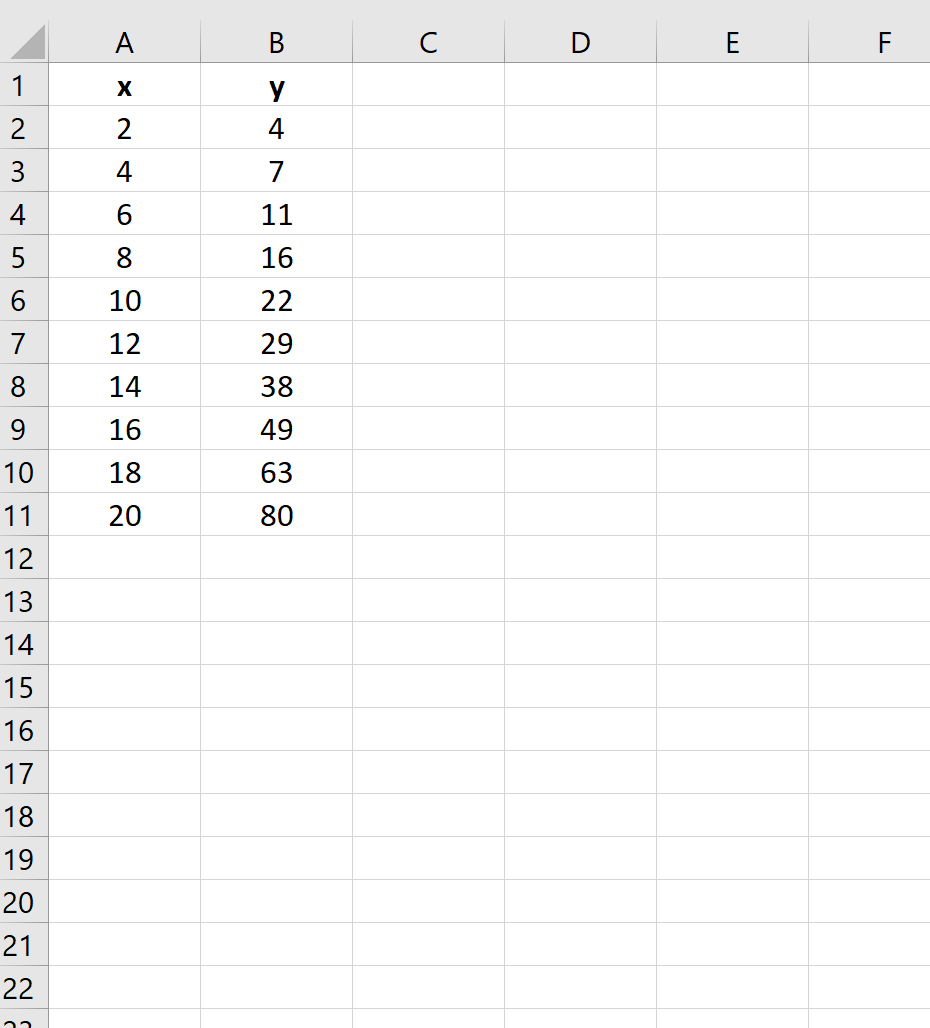
If we create a quick plot of the data, here’s what it would look like:
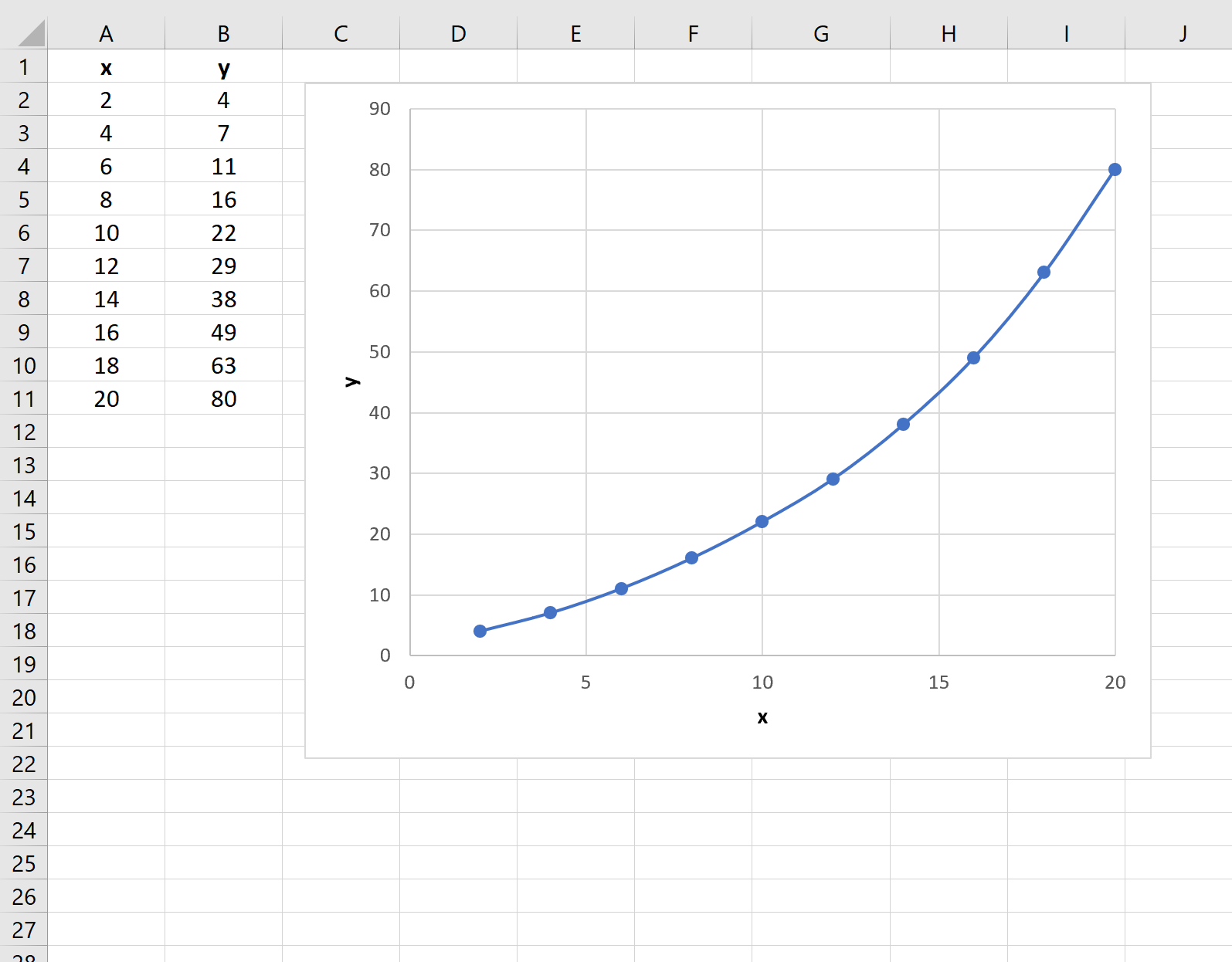
Now suppose that we’d like to find the y-value associated with a new x-value of 13. We can see that we have measured y-values for x-values of 12 and 14, but not for an x-value of 13.
We can use the following formula to perform linear interpolation in Excel to find the estimated y-value:
=FORECAST(NewX,OFFSET(KnownY,MATCH(NewX,KnownX,1)-1,0,2), OFFSET(KnownX,MATCH(NewX,KnownX,1)-1,0,2))
Here’s how to use this function to estimate the y-values associated with an x-value of 13:
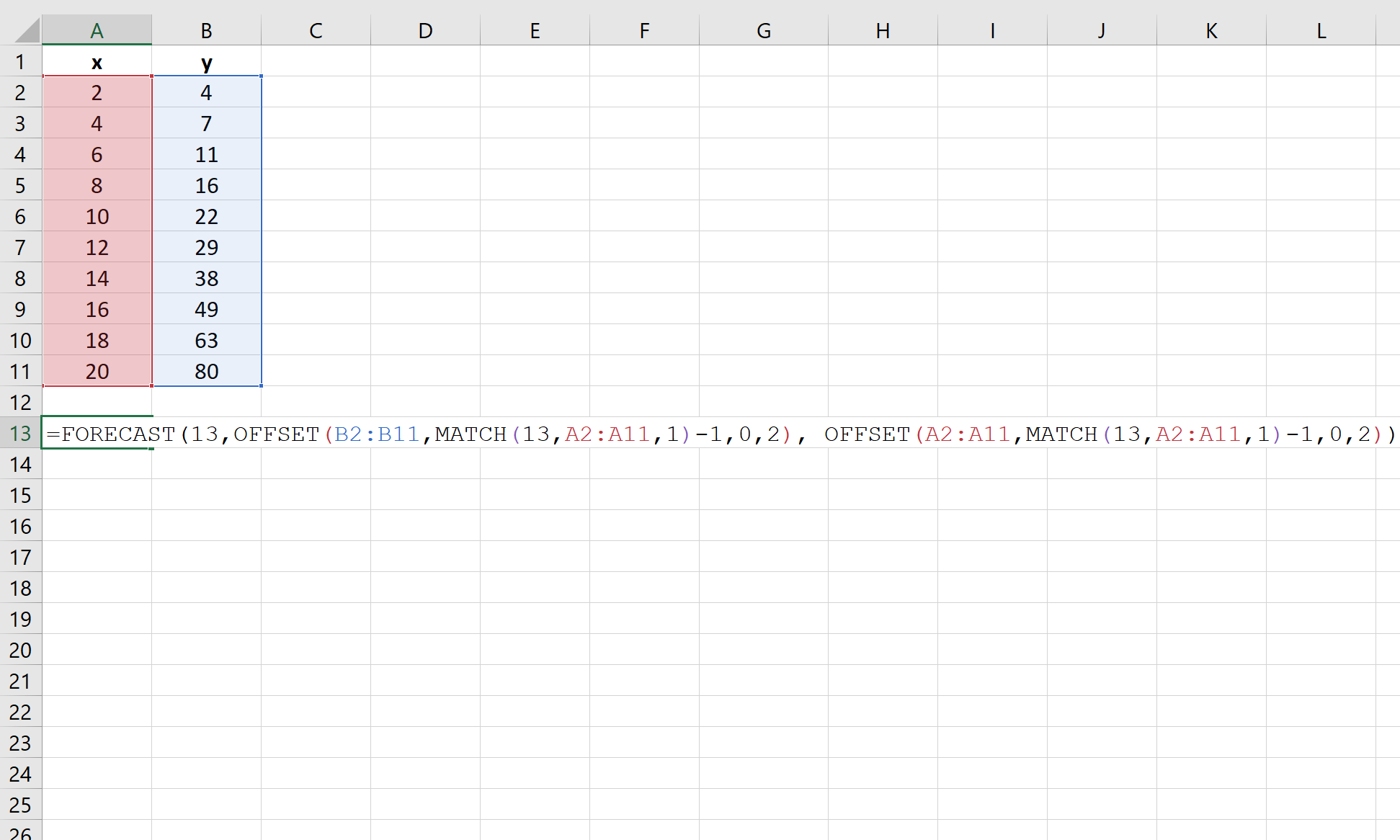
The estimated y-value turns out to be 33.5.
If we add the point (13, 33.5) to our plot, it appears to match the function quite well:
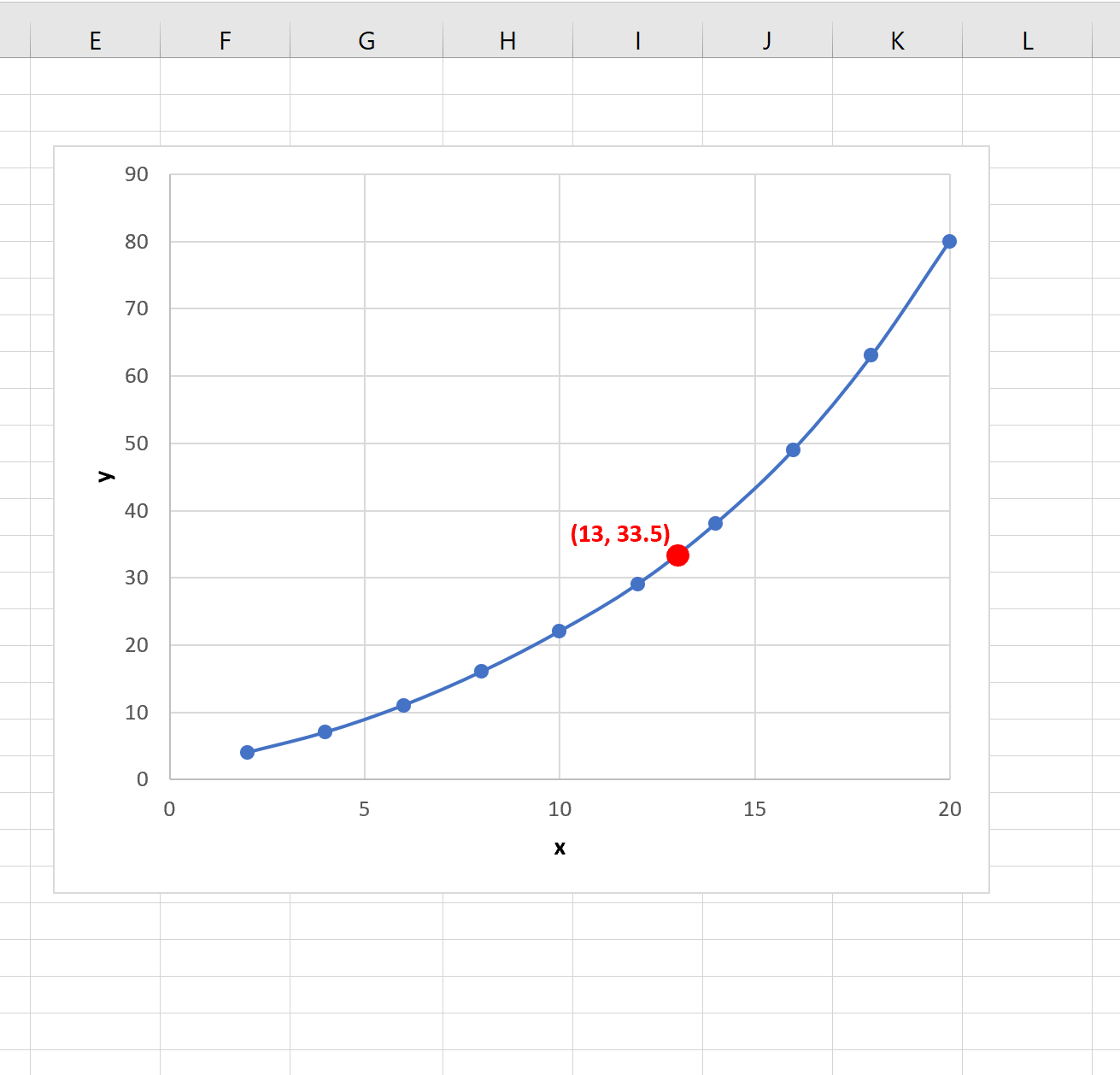
Note that in order for this function to work, the new x-value should fall within the range of the existing x-values.
You can find more Excel tutorials .
