Table of Contents
To average filtered rows in Excel, first filter out the desired data set, then select all the cells in the row range you wish to average, and press the Average function in the Home tab. An example of this could be to average the sales for a particular product across multiple regions; first filter the table to show only this product, then select the cells containing the sales figures, and press the Average function to calculate the average sales for this product.
The easiest way to take the average of a filtered range in Excel is to use the following syntax:
SUBTOTAL(101, A1:A10)
Note that the value 101 is a for taking the average of a filtered range of rows.
The following example shows how to use this function in practice.
Example: Sum Filtered Rows in Excel
Suppose we have the following dataset that shows the number of sales made during various days by a company:
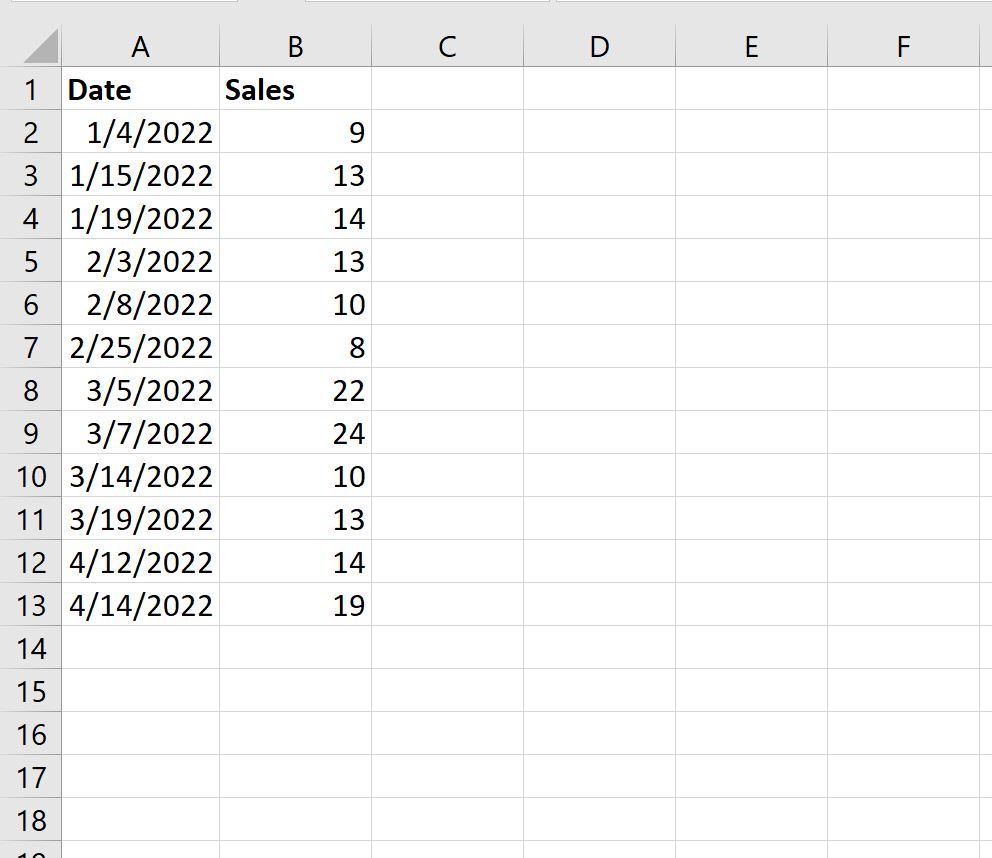
Next, let’s filter the data to only show the dates that are in January or April.
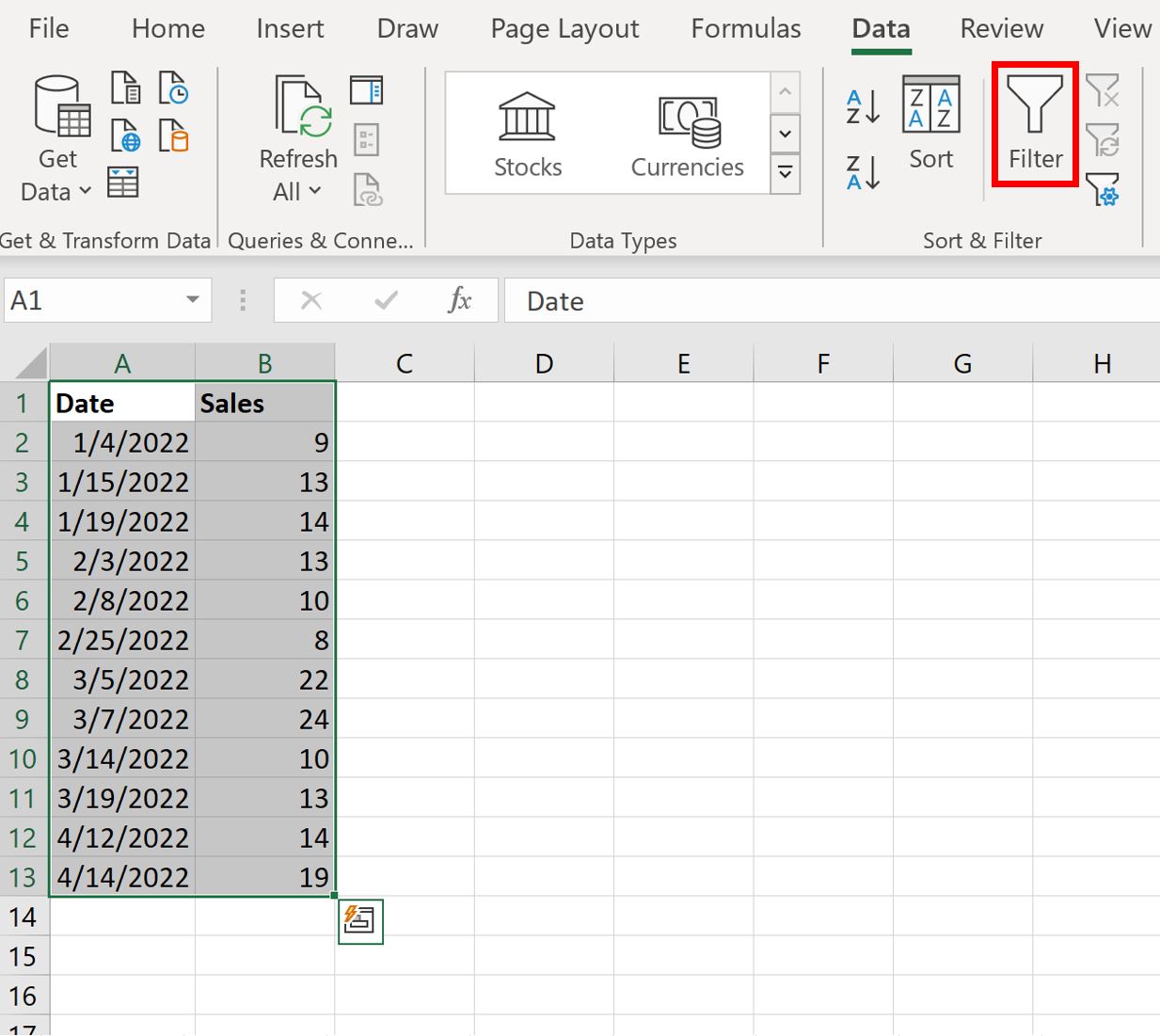
To do so, highlight the cell range A1:B13. Then click the Data tab along the top ribbon and click the Filter button.
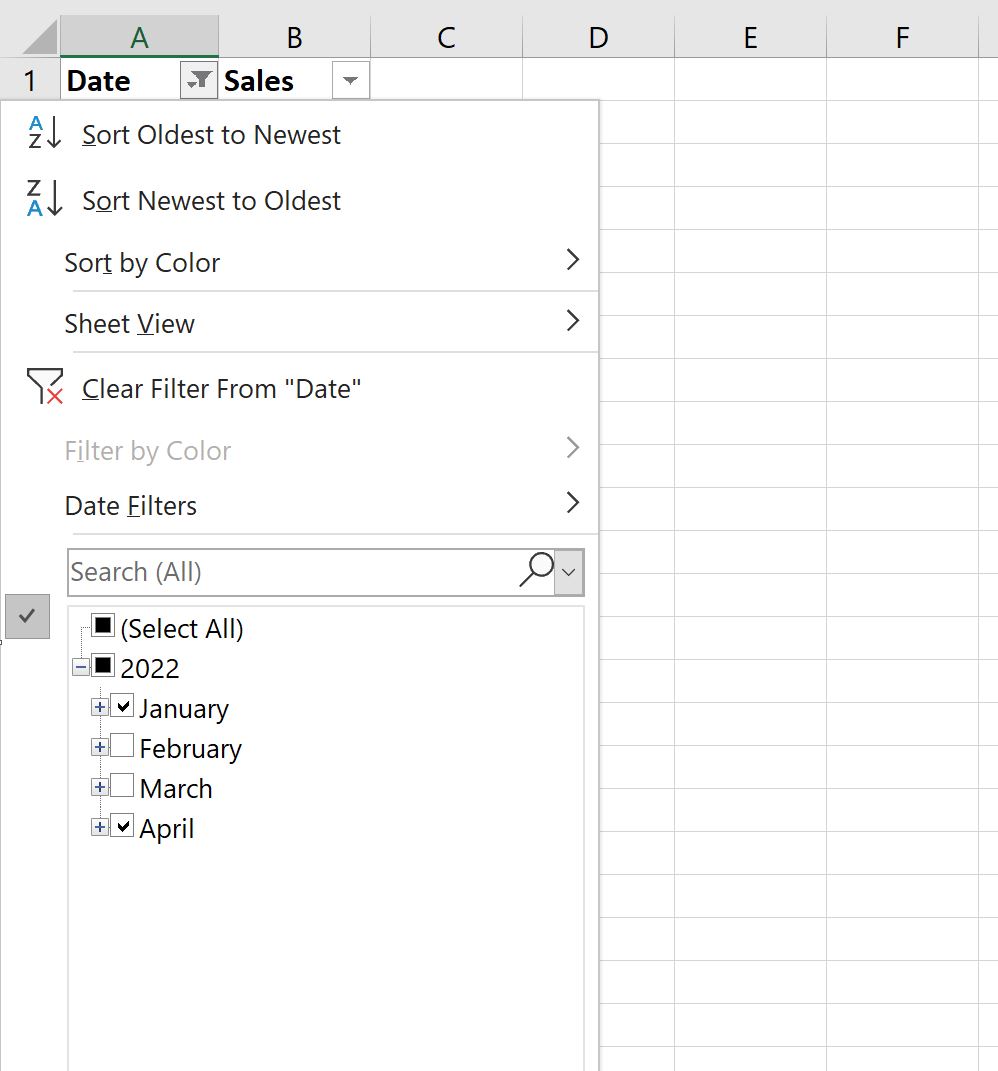
Then click the dropdown arrow next to Date and make sure that only the boxes next to January and April are checked, then click OK:
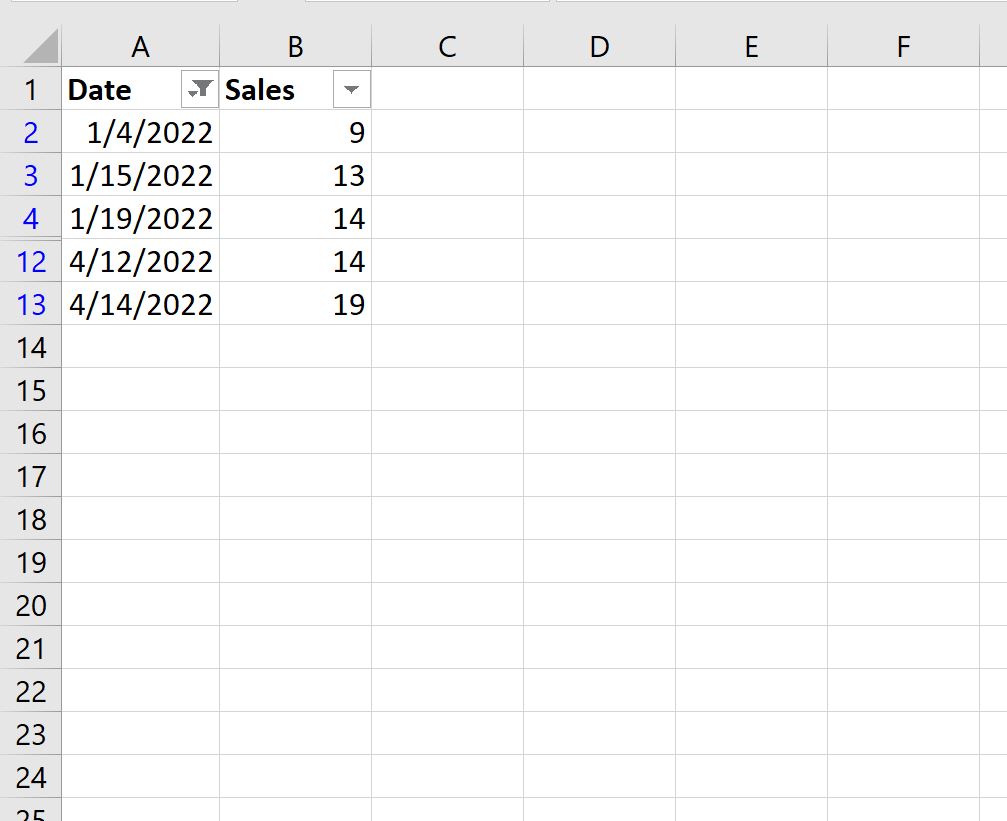
The data will automatically be filtered to only show the rows where the dates are in January or April:
If we attempt to use the AVERAGE() function to find the average value in the Sales column, it will actually return the average of all of the original values:
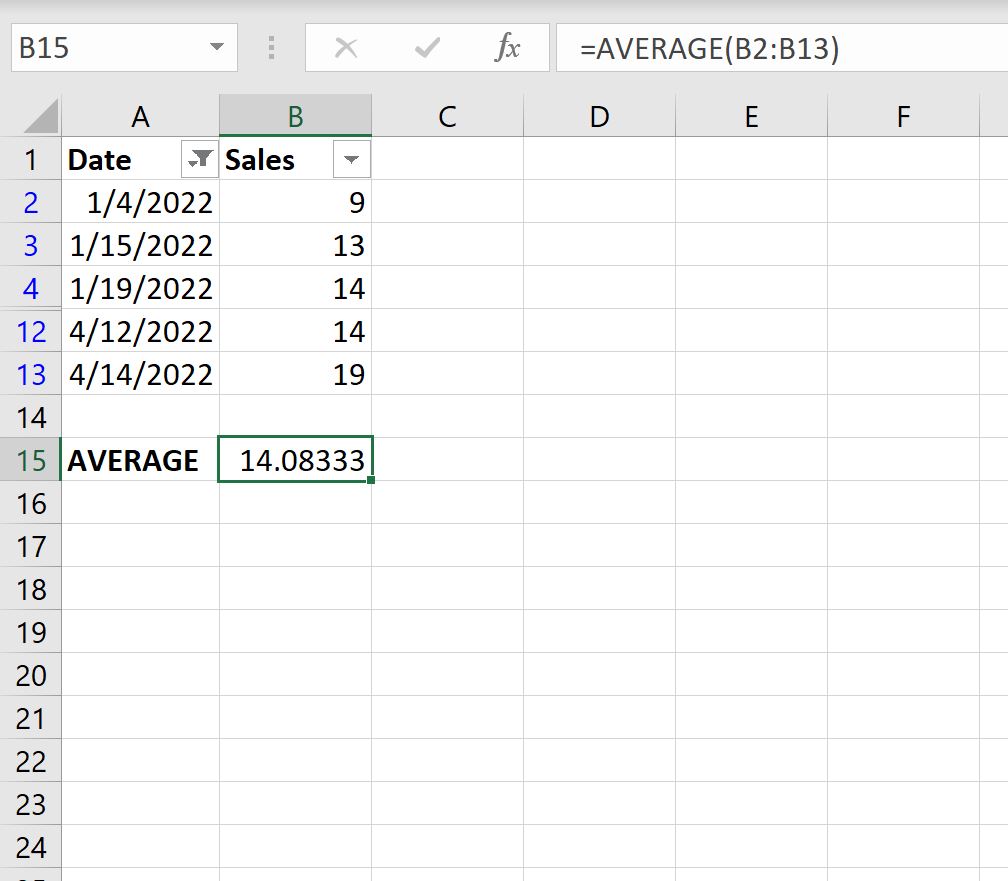
Instead, we can use the SUBTOTAL() function:
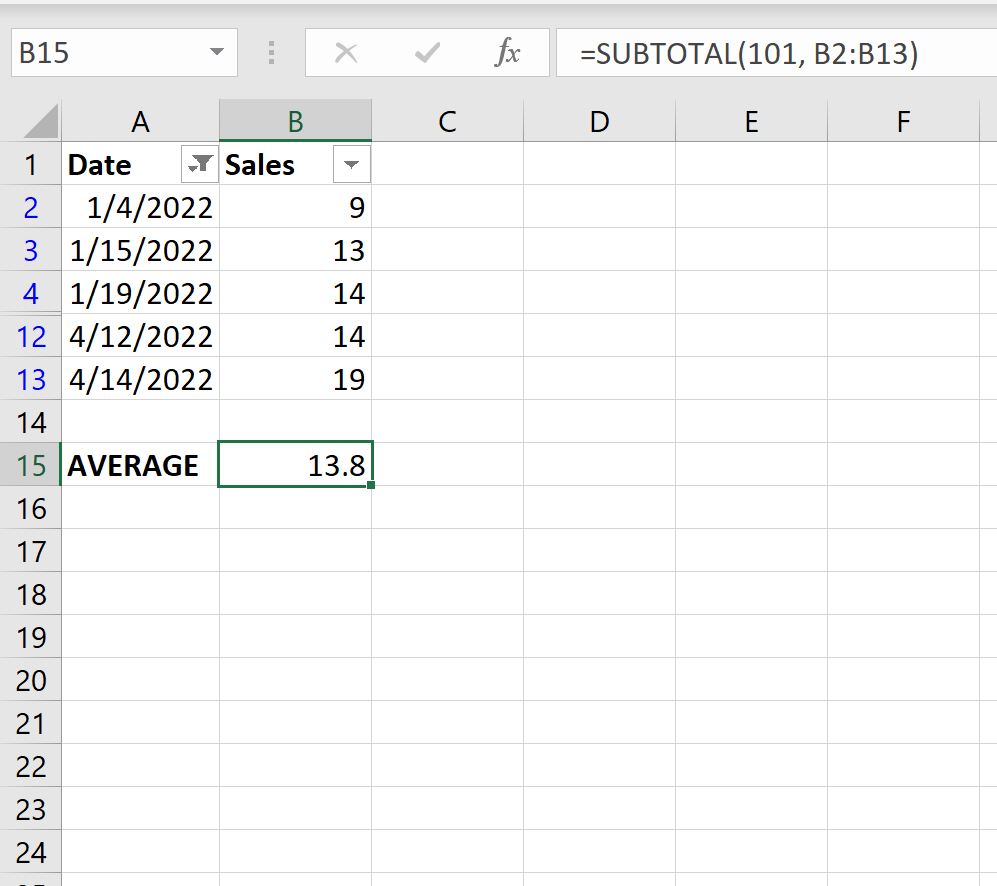
This function takes the average of only the visible rows.
We can manually verify this by taking the average of the visible rows:
Average of Sales in visible rows: (9+13+14+14+19) / 5 = 13.8.
