Table of Contents
One way to quantify the relationship between two variables is to use the Pearson correlation coefficient which is a measure of the linear association between two variables.
It always takes on a value between -1 and 1 where:
- -1 indicates a perfectly negative linear correlation between two variables
- 0 indicates no linear correlation between two variables
- 1 indicates a perfectly positive linear correlation between two variables
To determine if a correlation coefficient is statistically significant you can perform a correlation test, which involves calculating a t-score and a corresponding p-value.
The formula to calculate the t-score is:
t = r√(n-2) / (1-r2)
where:
- r: Correlation coefficient
- n: The sample size
The p-value is calculated as the corresponding two-sided p-value for the t-distribution with n-2 degrees of freedom.
The following step-by-step example shows how to perform a correlation test in Excel.
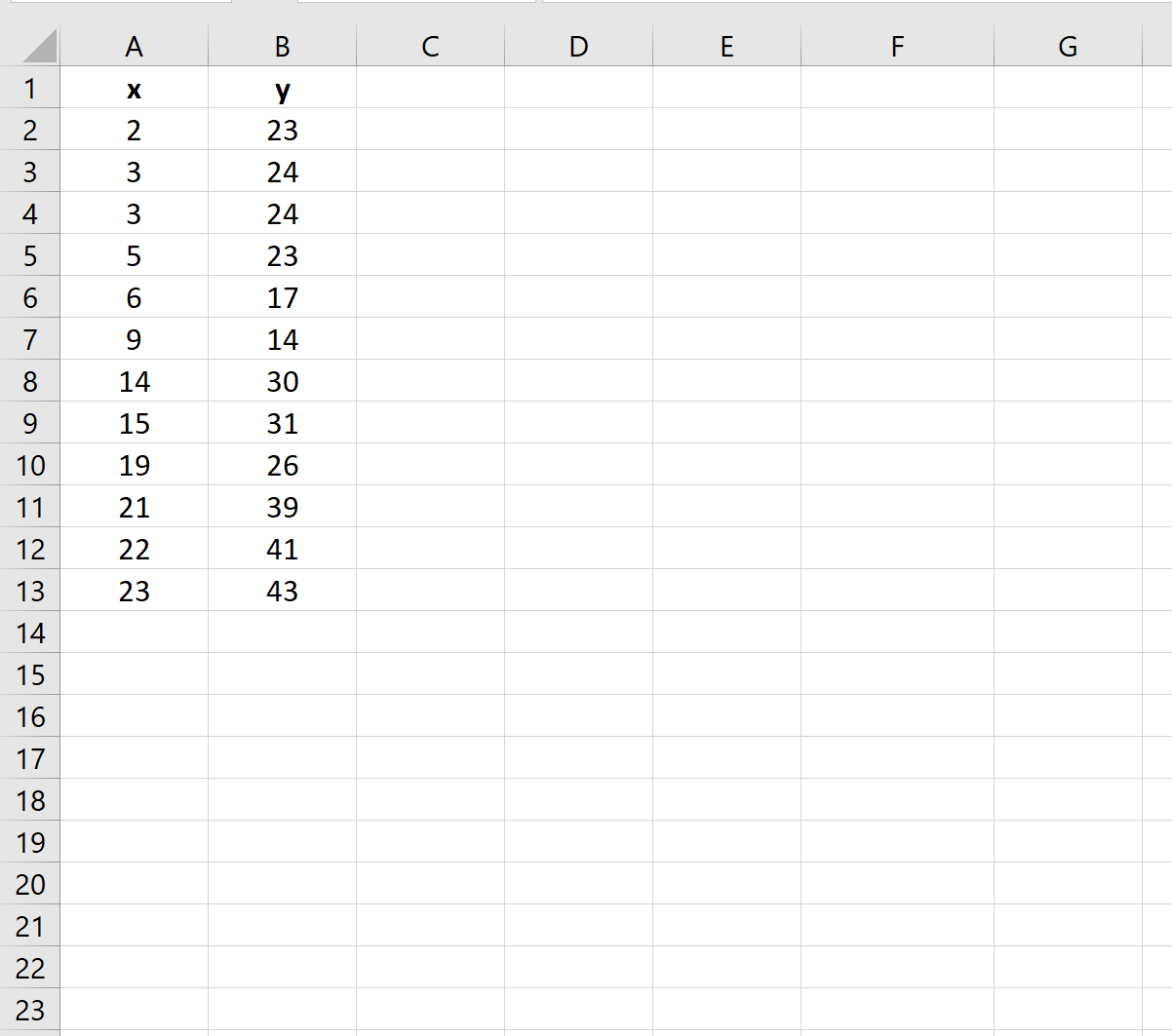
Step 1: Enter the Data
First, let’s enter some data values for two variables in Excel:
Step 2: Calculate the Correlation Coefficient
Next, we can use the CORREL() function to calculate the correlation coefficient between the two variables:
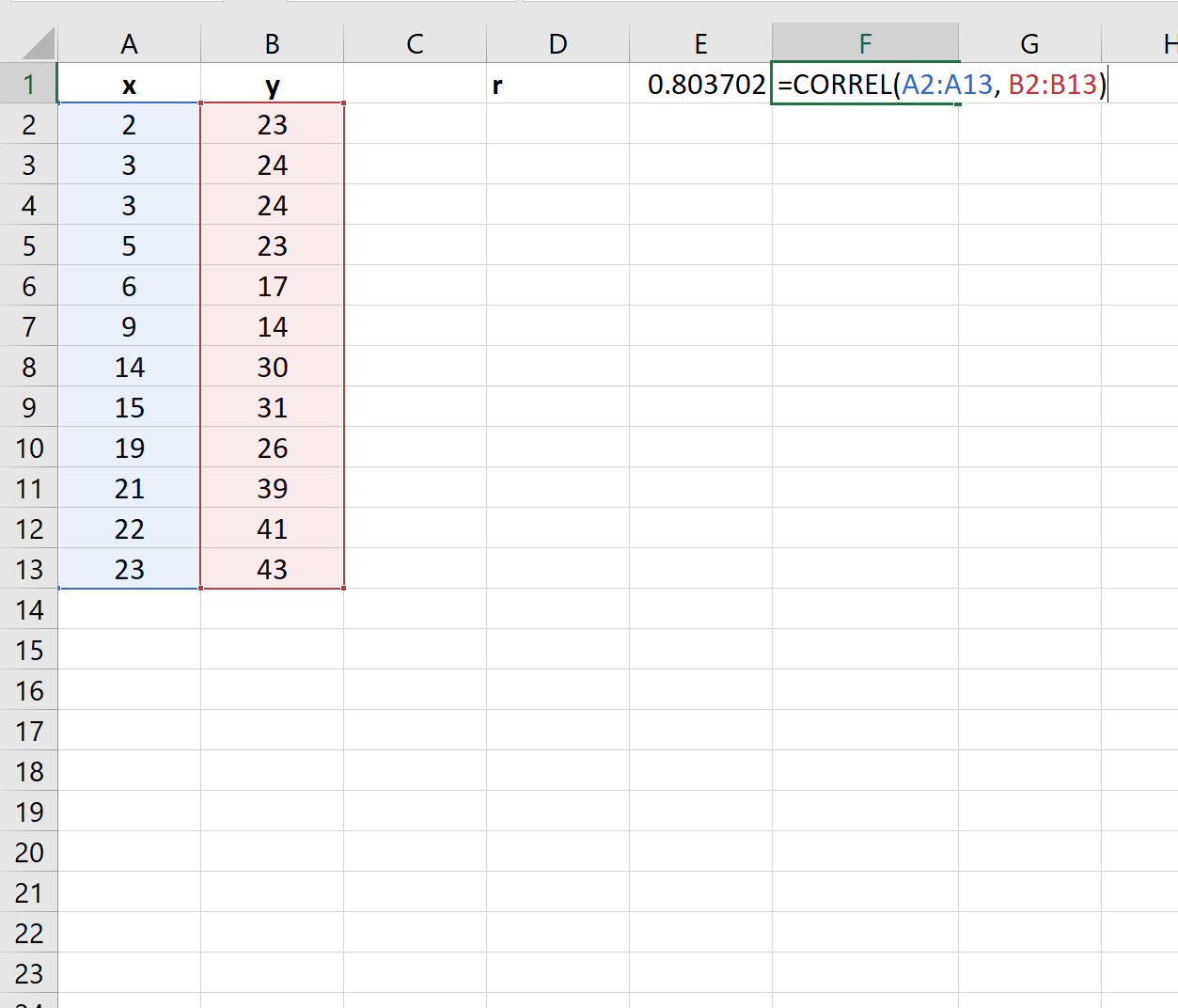
The correlation coefficient between the two variables turns out to be 0.803702.
Step 3: Calculate the Test Statistic and P-Value
Next, we can use the following formulas to calculate the test statistic and the corresponding p-value:
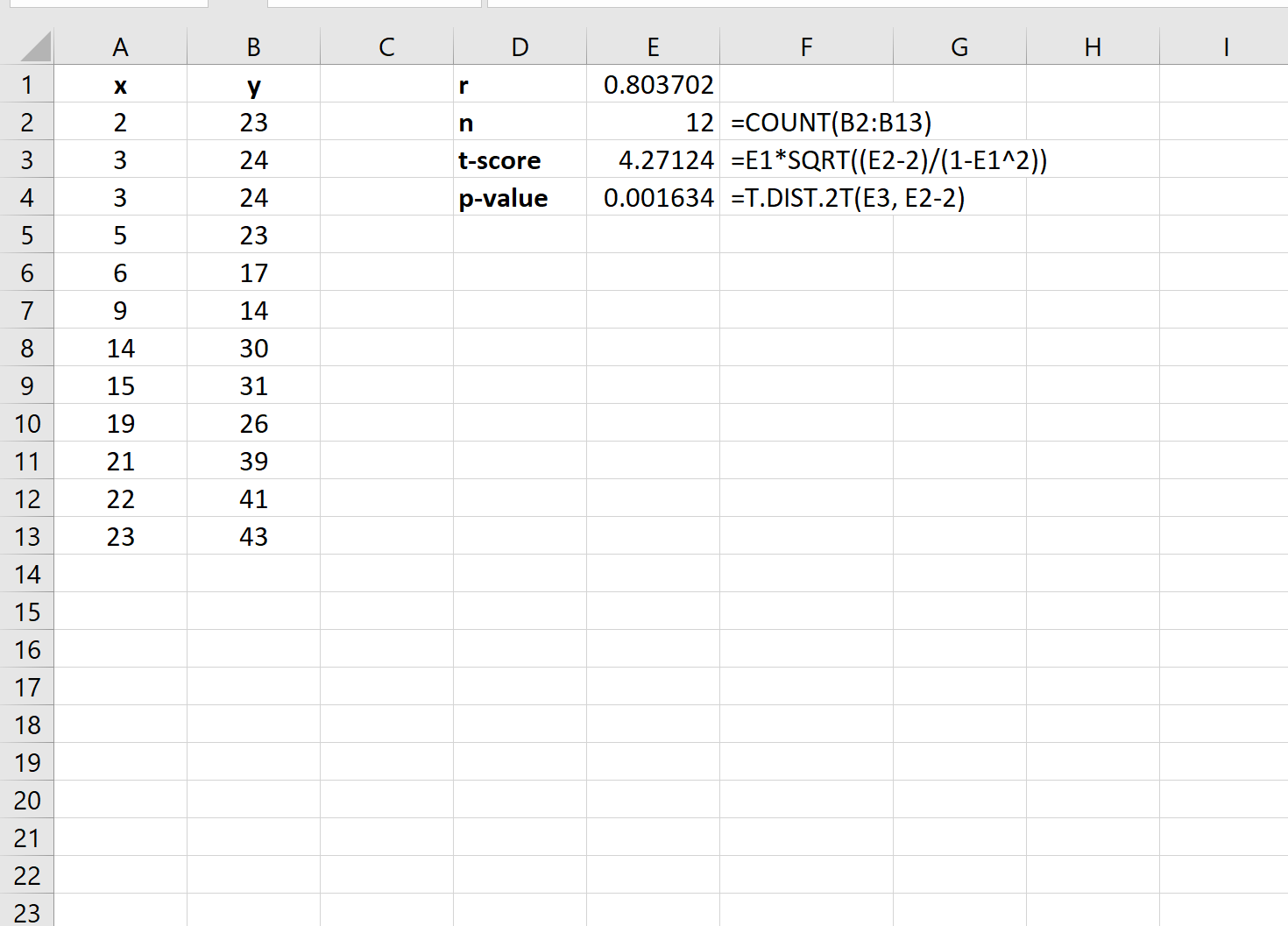
The test statistic turns out to be 4.27124 and the corresponding p-value is 0.001634.
Since this p-value is less than .05, we have sufficient evidence to say that the correlation between the two variables is statistically significant.
