Table of Contents
Overlay density plots are a visual representation of the distribution of a continuous variable in a dataset. They provide a way to compare the distribution of multiple variables on the same plot. In R, we can use the ggplot2 package to easily create overlay density plots. First, we need to load the package and import the dataset we want to use. Then, we can use the ggplot() function to specify the dataset and the variables we want to plot. Next, we add the geom_density() function to create the density plot and use the aes() function to specify the color and linetype for each variable. Finally, we can add a legend and customize the plot with labels and titles. Overall, using ggplot2 in R allows us to create visually appealing and informative overlay density plots with just a few lines of code.
Overlay Density Plots in ggplot2 (With Examples)
A density plot is a useful way to visualize the distribution of values in a dataset.
Often you may want to visualize the density plots of several variables at once. Fortunately, this is easy to do using the data visualization package in R with the following syntax:
ggplot(data, aes(x=value, fill=variable)) + geom_density(alpha=.25)
The alpha argument controls the opacity of each density plot. It’s important to set this value below 1 so that you can see each density plot when they overlay each other.
The following step-by-step example shows how to use this syntax in practice.
Step 1: Create the Data
First, let’s create a fake dataset with three variables:
#make this example reproducible set.seed(1) #create data df <- data.frame(var1=rnorm(1000, mean=0, sd=1), var2=rnorm(1000, mean=0, sd=3), var3=rnorm(1000, mean=3, sd=2)) #view first six rows of data head(df) var1 var2 var3 1 -0.6264538 3.4048953 1.2277008 2 0.1836433 3.3357955 -0.8445098 3 -0.8356286 -2.6123329 6.2394015 4 1.5952808 0.6321948 4.0385398 5 0.3295078 0.2081869 2.8883001 6 -0.8204684 -4.9879466 4.3928352
Step 2: Convert the Data from Wide to Long
Next, we need to convert the data from a wide format to a long format to make it compatible with ggplot2:
library(reshape)#convert from wide format to long format data <- melt(df) #view first six rows head(data) variable value 1 var1 -0.6264538 2 var1 0.1836433 3 var1 -0.8356286 4 var1 1.5952808 5 var1 0.3295078 6 var1 -0.8204684
Step 3: Create the Overlaying Density Plots
Lastly, we can create the overlaying density plots:
library(ggplot2) #create overlaying density plots ggplot(data, aes(x=value, fill=variable)) + geom_density(alpha=.25)
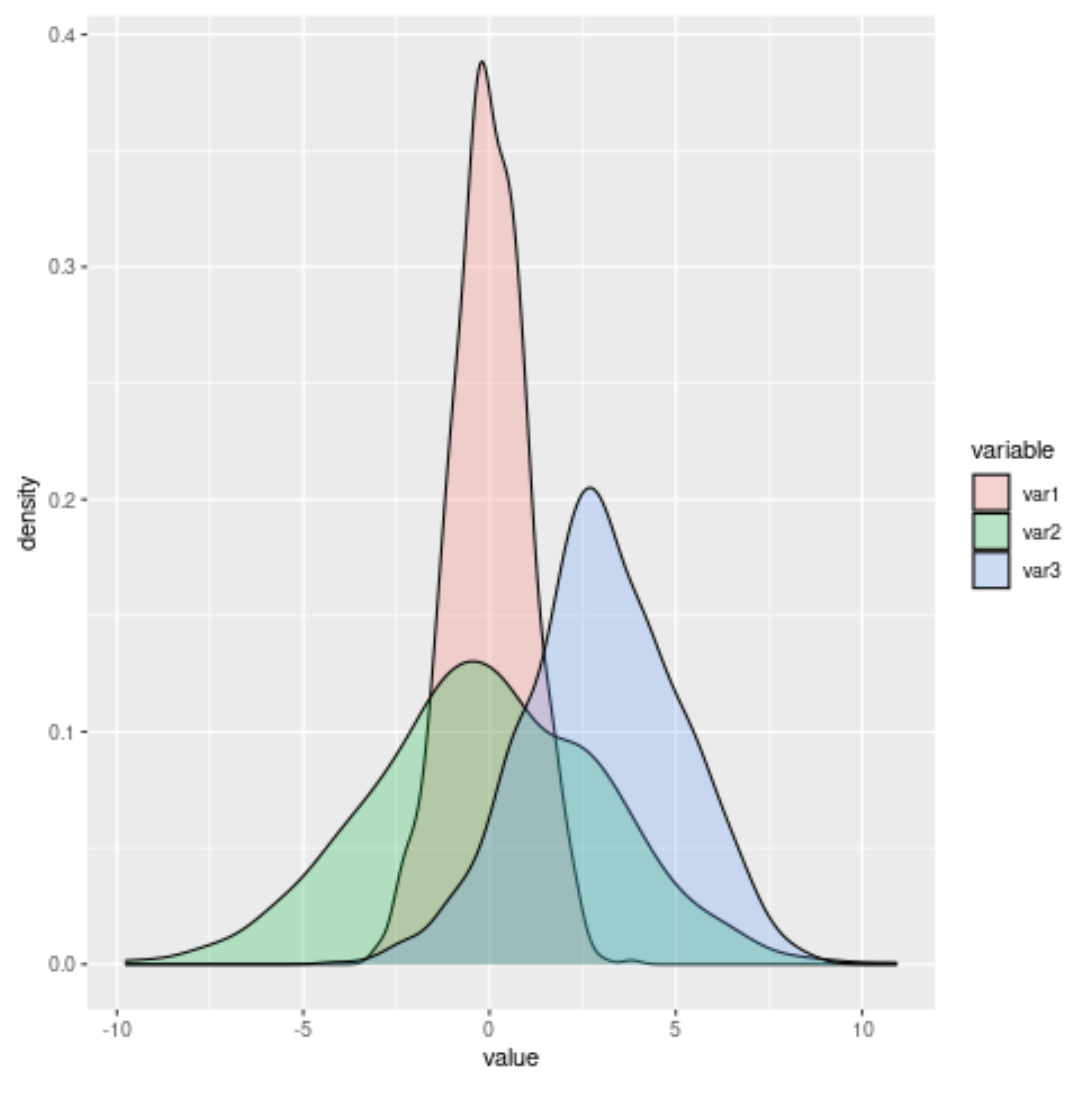
Feel free to adjust the alpha value to make the density plots more or less transparent.
For example, here’s what the plots would look like if we increased the alpha value:
library(ggplot2) #create overlaying density plots ggplot(data, aes(x=value, fill=variable)) + geom_density(alpha=.7)

