Table of Contents
A Kruskal-Wallis Test is a non-parametric statistical test used to compare the medians of three or more independent groups. It is commonly used when the data does not meet the assumptions of normality required for parametric tests. In order to perform a Kruskal-Wallis Test in SPSS, the following steps can be followed:
1. Open the data set in SPSS and make sure the data is organized in a rectangular format with each group in a separate column.
2. Go to the “Analyze” tab and select “Nonparametric Tests” and then “Legacy Dialogs”.
3. From the options, select “K Independent Samples” and then “Kruskal-Wallis H”.
4. A new window will appear where you can select the variables for your analysis. Select the variables representing the groups you want to compare and move them to the “Test Variables” box.
5. Click on the “Define Range” button to specify the range of cases or observations to be included in the analysis.
6. In the “Options” tab, you can choose to include descriptive statistics and plots in your output.
7. Click on “OK” to run the analysis. The results will be displayed in the output window, including the Kruskal-Wallis test statistic, degrees of freedom, and p-value.
8. If the p-value is less than the chosen significance level, it indicates that there is a significant difference between the medians of the groups. You can further explore the differences between the groups using post-hoc tests.
In conclusion, a Kruskal-Wallis Test can be performed in SPSS by following these simple steps, allowing researchers to compare multiple groups and determine if there are significant differences between their medians.
Perform a Kruskal-Wallis Test in SPSS
A is used to determine whether or not there is a statistically significant difference between the medians of three or more independent groups. It is considered to be the non-parametric equivalent of the .
This tutorial explains how to conduct a Kruskal-Wallis Test in SPSS.
Example: Kruskal-Wallis Test in SPSS
A researcher wants to know whether or not three drugs have different effects on knee pain, so he recruits 30 individuals who all experience similar knee pain and randomly splits them up into three groups to receive either Drug 1, Drug 2, or Drug 3.
After one month of taking the drug, the researcher asks each individual to rate their knee pain on a scale of 1 to 100, with 100 indicating the most severe pain. The ratings for all 30 individuals are shown below:

Use the following steps to perform a Kruskal-Wallis Test to determine whether or not there is a difference between the reported levels of knee pain between the three groups:
Step 1: Perform a Kruskal-Wallis Test.
Click the Analyze tab, then Nonparametric Tests, then Legacy Dialogs, then K Independent Samples:

In the window that pops up, drag the variable pain into the box labelled Test Variable List and drug into the box labelled Grouping Variable. Then click Define Range and set the Minimum value to 1 and the Maximum value to 3. Then click Continue. Make sure the box is checked next to Kruskal-Wallis H and then click OK.

Step 2: Interpret the results.
Once you click OK, the results of the Kruskal-Wallis test will appear:
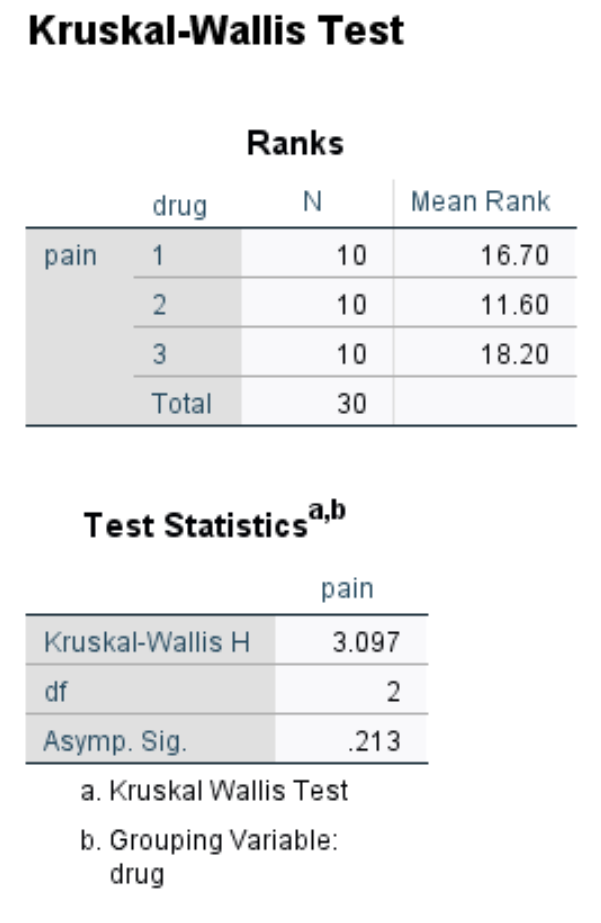
The second table in the output displays the results of the test:
- Kruskal-Wallis H: This is the X2 test statistic.
- df: This is the degrees of freedom, calculated as #groups-1 = 3-1 = 2.
- Asymp. Sig: This is the p-value associated with a X2 test statistic of 3.097 with 2 degrees of freedom. This can also be found by using the .
