Table of Contents
Standard deviation is a measure of how spread out the values in a data set are. It is calculated by taking the square root of the variance, which is the average of the squared differences from the mean. Standard deviation can be used to tell how much variation there is in a data set, and it is a useful tool for comparing different sets of data.
A probability distribution tells us the probability that a takes on certain values.
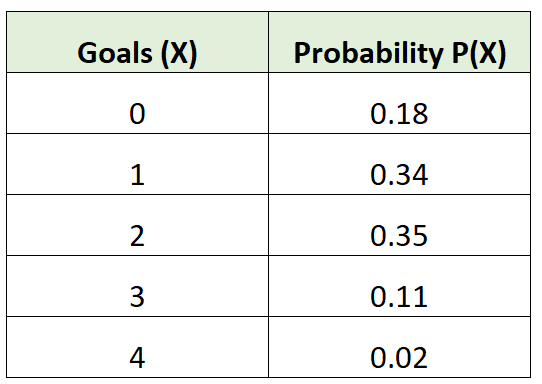
For example, the following probability distribution tells us the probability that a certain soccer team scores a certain number of goals in a given game:
To find the standard deviation of a probability distribution, we can use the following formula:
σ = √Σ(xi-μ)2 * P(xi)
where:
- xi: The ith value
- μ: The mean of the distribution
- P(xi): The probability of the ith value
For example, consider our probability distribution for the soccer team:

The mean number of goals for the soccer team would be calculated as:
μ = 0*0.18 + 1*0.34 + 2*0.35 + 3*0.11 + 4*0.02 = 1.45 goals.
We could then calculate the standard deviation as:
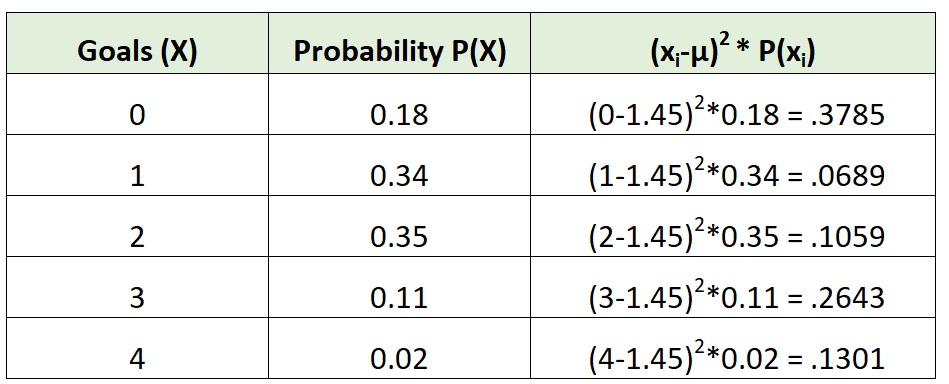
The standard deviation is the square root of the sum of the values in the third column. Thus, we would calculate it as:
Standard deviation = √(.3785 + .0689 + .1059 + .2643 + .1301) = 0.9734
The variance is simply the standard deviation squared, so:
Variance = .97342 = 0.9475
Example 1: Standard Deviation of Vehicle Failures
The following probability distribution tells us the probability that a given vehicle experiences a certain number of battery failures during a 10-year span:
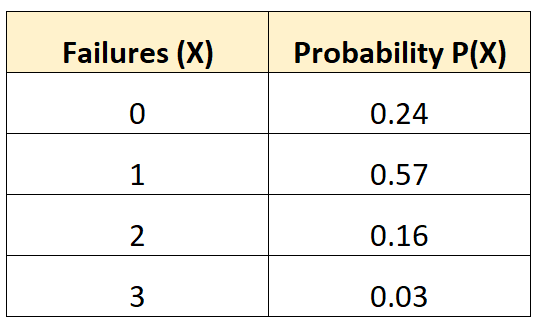
Question: What is the standard deviation of the number of failures for this vehicle?
Solution: The mean number of expected failures is calculated as:
μ = 0*0.24 + 1*0.57 + 2*0.16 + 3*0.03 = 0.98 failures.
We could then calculate the standard deviation as:
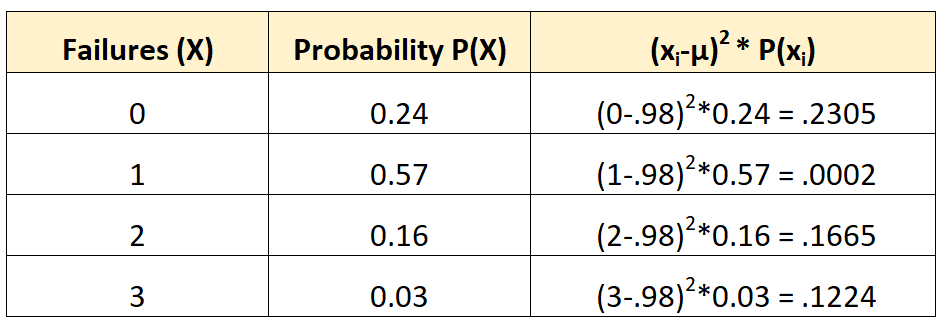
The standard deviation is the square root of the sum of the values in the third column. Thus, we would calculate it as:
Standard deviation = √(.2305 + .0002 + .1665 + .1224) = 0.7208
Example 2: Standard Deviation of Sales
The following probability distribution tells us the probability that a given salesman will make a certain number of sales in the upcoming month:
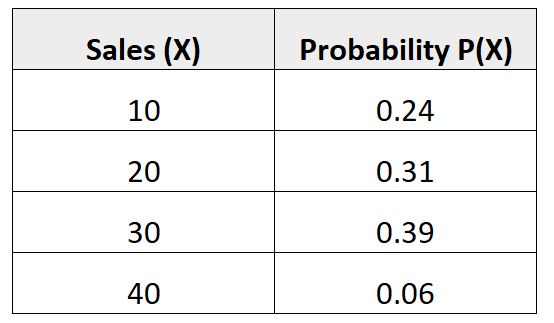
Question: What is the standard deviation of the number of sales for this salesman in the upcoming month?
Solution: The mean number of expected sales is calculated as:
μ = 10*.24 + 20*.31 + 30*0.39 + 40*0.06 = 22.7 sales.
We could then calculate the standard deviation as:

The standard deviation is the square root of the sum of the values in the third column. Thus, we would calculate it as:
Standard deviation = √(38.7096 + 2.2599 + 20.7831 + 17.9574) = 8.928
