Table of Contents
The probability, given a mean and standard deviation, is a measure of the likelihood that a specific event or outcome will occur within a given data set. It is determined by calculating the ratio of the number of outcomes that fall within a certain range (determined by the mean and standard deviation) to the total number of possible outcomes. This probability is useful in understanding and analyzing data, as it provides valuable insights into the distribution and variability of the data set.
Find Probability Given a Mean and Standard Deviation
We can use the following process to find the probability that a normally distributed X takes on a certain value, given a mean and standard deviation:
Step 1: Find the z-score.
A z-score tells you how many standard deviations away an individual data value falls from the mean. It is calculated as:
z-score = (x – μ) / σ
where:
- x: individual data value
- μ: population mean
- σ: population standard deviation
Step 2: Find the probability that corresponds to the z-score.
Once we’ve calculated the z-score, we can look up the probability that corresponds to it in the .
The following examples show how to use this process in different scenarios.
Example 1: Probability Less Than a Certain Value
The scores on a certain test are normally distributed with mean μ = 82 and standard deviation σ = 8. What is the probability that a given student scores less than 84 on the test?
Step 1: Find the z-score.
First, we will find the z-score associated with a score of 84:
z-score = (x – μ) / σ = (84 – 82) / 8 = 2 / 8 = 0.25
Step 2: Use the z-table to find the corresponding probability.
Next, we will look up the value 0.25 in the :

Example 2: Probability Greater Than a Certain Value
The height of a certain species of penguin is normally distributed with a mean of μ = 30 inches and a standard deviation of σ = 4 inches. If we randomly select a penguin, what is the probability that it is greater than 28 inches tall?
Step 1: Find the z-score.
First, we will find the z-score associated with a height of 28 inches.
z-score = (x – μ) / σ = (28 – 30) / 4 = -2 / 4 = -.5
Step 2: Use the z-table to find the corresponding probability.
Next, we will look up the value -0.5 in the :

The value that corresponds to a z-score of -0.5 is .3085. This represents the probability that a penguin is less than 28 inches tall.
However, since we want to know the probability that a penguin will have a height greater than 28 inches, we need to subtract this probability from 1.
Thus, the probability that a penguin will have a height greater than 28 inches is: 1 – .3085 = 0.6915.
Example 3: Probability Between Two Values
The weight of a certain species of turtle is normally distributed with a mean of μ = 400 pounds and a standard deviation of σ = 25 pounds. If we randomly select a turtle, what is the probability that it weighs between 410 and 425 pounds?
Step 1: Find the z-scores.
First, we will find the z-scores associated with 410 pounds and 425 pounds
z-score of 410 = (x – μ) / σ = (410 – 400) / 25 = 10 / 25 = 0.4
z-score of 425 = (x – μ) / σ = (425 – 400) / 25 = 25 / 25 = 1
Step 2: Use the z-table to find the corresponding probability.
First, we will look up the value 0.4 in the :
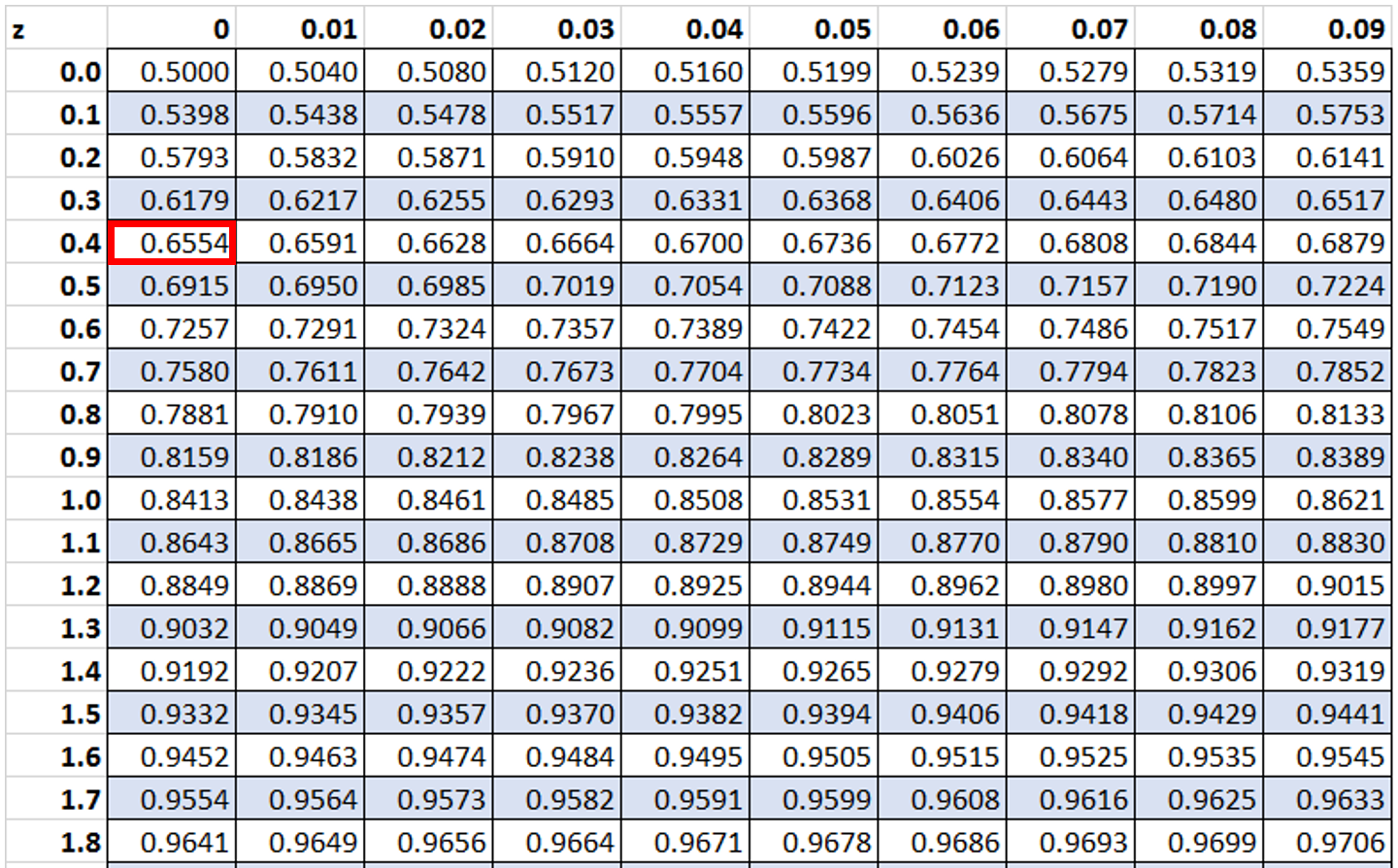
Then, we will look up the value 1 in the :
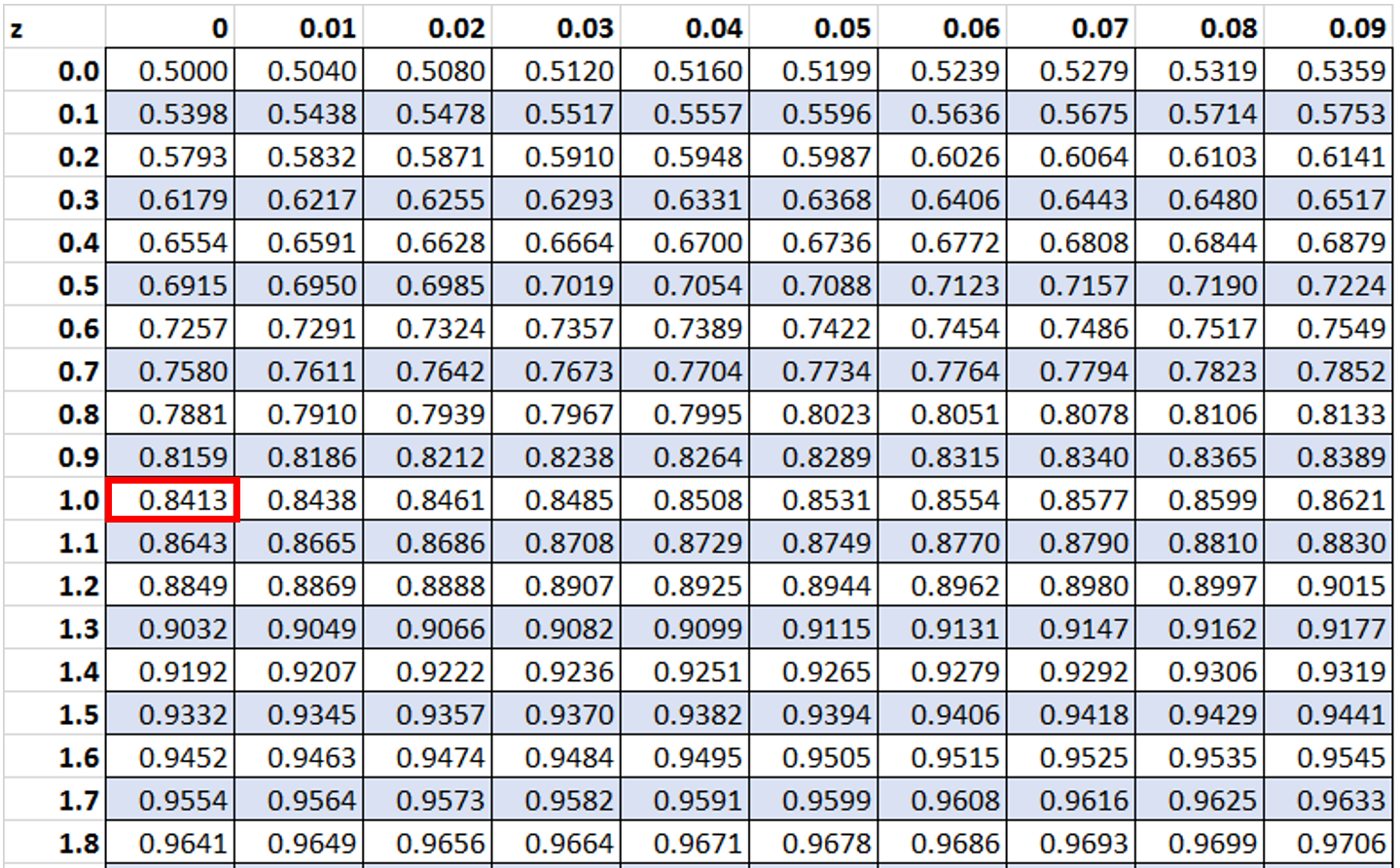
Then we will subtract the smaller value from the larger value: 0.8413 – 0.6554 = 0.1859.
Thus, the probability that a randomly selected turtle weighs between 410 pounds and 425 pounds is 18.59%.
