Table of Contents
When interpreting data, it is possible for the mean to be less than the median. This occurs when the data is skewed, meaning it is not evenly distributed around the center. In such cases, the mean is pulled in the direction of the skewed values, resulting in a lower value than the median which represents the exact middle point of the data. This phenomenon is commonly observed in data sets with outliers or extreme values, which can significantly impact the mean but have less effect on the median. Therefore, it is important to consider both the mean and median when interpreting data to get a more accurate understanding of the central tendency of the data.
Interpret Data where Mean is Less than Median
When the mean is less than the median in a dataset, we say that the distribution of the data is left skewed.
This means there is a “tail” on the left side of the distribution:
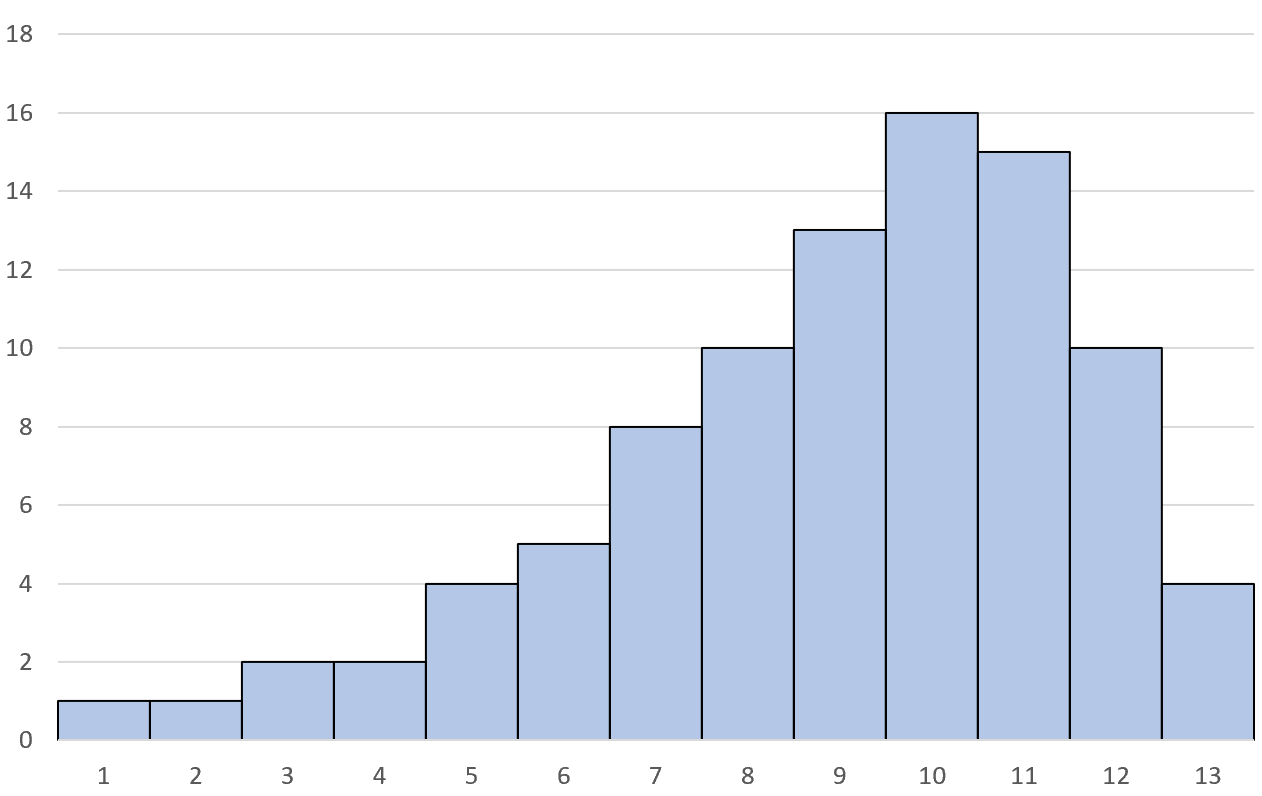
Note: Sometimes a left skewed distribution is also referred to as a negatively skewed distribution.
In a left skewed distribution, the mean is less than the median:
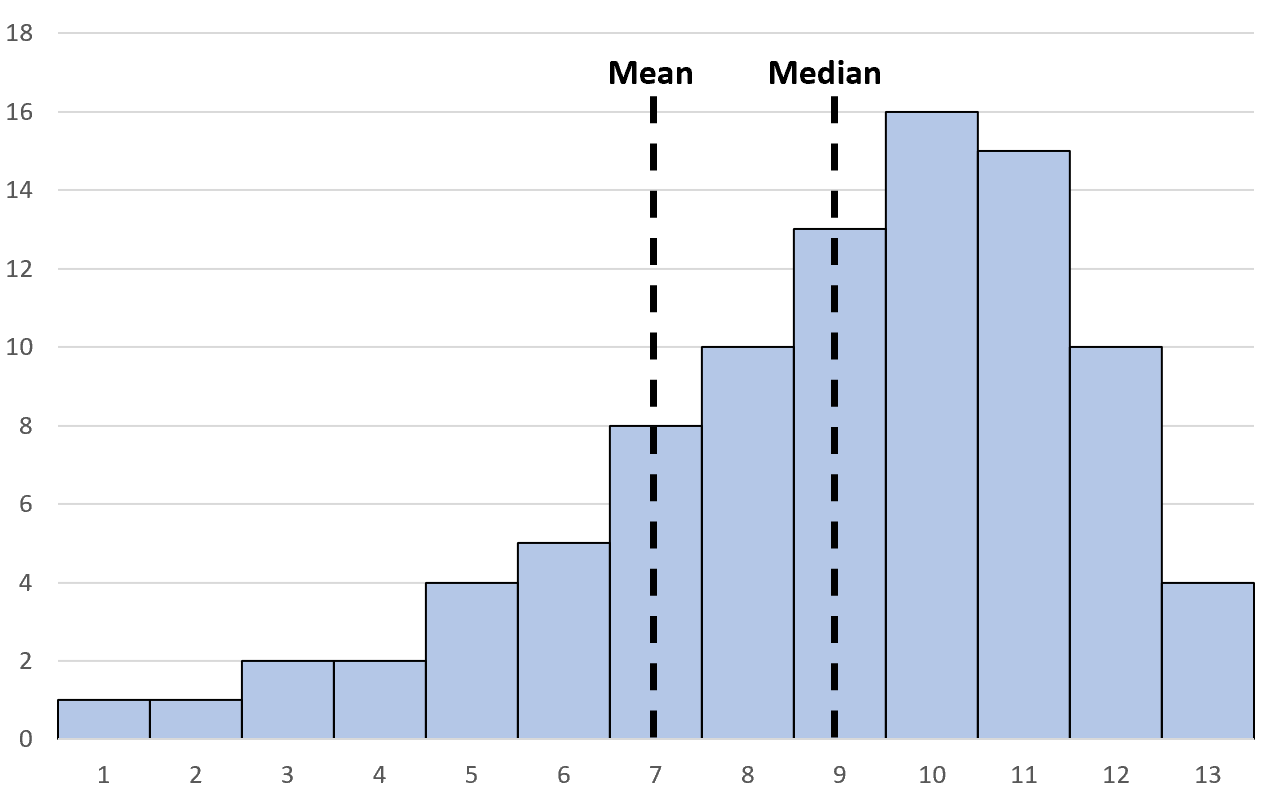
What Causes the Mean to be Less than the Median?
A distribution is typically left skewed when it is uncommon for a variable to take on a small value and much more common for a variable to take on values concentrated around a larger value.
One real-life example of a left skewed distribution would be exam scores among students.
Most students might score between 70 and 90 on a particular exam and it’s extremely uncommon for many students to score near a zero.
When we create a histogram to visualize the distribution of exam scores for some class, it will naturally be left skewed:
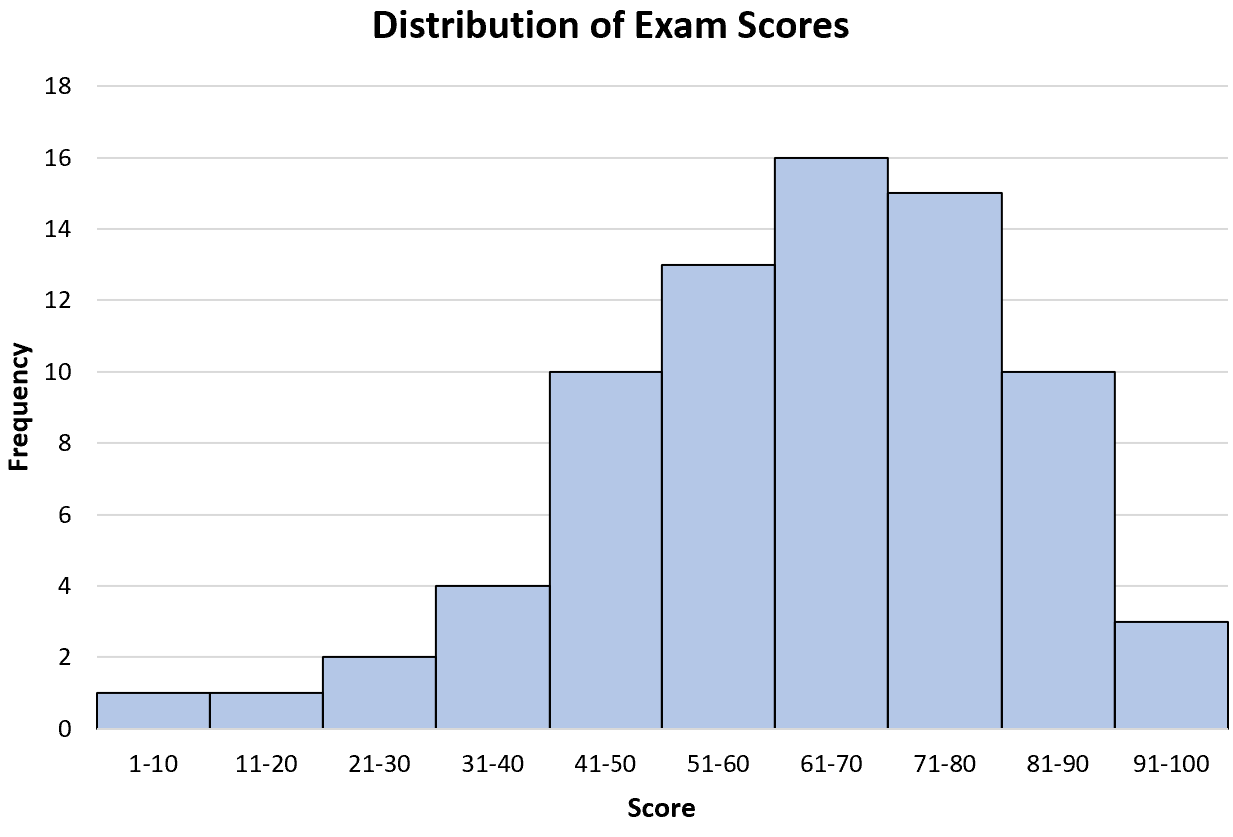
The mean is naturally less than the median because the high frequency of values on the right side of the distribution causes the median value to be larger.
As a simple example, suppose we have the following dataset that contains the exam scores of 20 students in a class:
Dataset: 24, 45, 56, 71, 78, 80, 81, 81, 82, 83, 84, 85, 85, 89, 91, 91, 92, 93, 96, 97
Here are the mean and median values of this dataset:
- Mean: 79.2
- Median: 83.5
If we plot this distribution, it would be a left skewed histogram with most of the values concentrated on the right side of the histogram.
Additional Resources
The following tutorials provide additional information about skewed distributions:
