Table of Contents
The scale_x_continuous function in ggplot2 allows you to adjust the displayed range of values on the x-axis of your plot. It takes three arguments: the name of the aesthetic (x for position, in this case), the limits of the values to display (a minimum and maximum), and the breaks at which the scale should display tick marks. Additionally, it is possible to specify a transformation function, such as log, to display the values in a different form. Examples of how to use this function are provided in the ggplot2 documentation.
You can use the scale_x_continuous() function in ggplot2 to customize the x-axis of a given plot.
This function uses the following basic syntax:
p +
scale_x_continuous(breaks, n.breaks, labels, limits, ...)
where:
- breaks: A numeric vector of positions for breaks on the x-axis
- n.breaks: An integer vector specifying the number of total breaks on the x-axis
- labels: A character vector of labels to use for the x-axis
- limits: A numeric vector that specifies the min and max value for the x-axis
The following examples show how to use this function in different scenarios with the following data frame in R:
#create data frame df <- data.frame(points=c(5, 7, 12, 13, 15, 19, 22, 25), assists=c(4, 3, 2, 3, 7, 8, 5, 7)) #view data frame df points assists 1 5 4 2 7 3 3 12 2 4 13 3 5 15 7 6 19 8 7 22 5 8 25 7
Example 1: Use scale_x_continuous with Custom Axis Breaks
The following code shows how to create a scatterplot in ggplot2 and use scale_x_continuous() with the breaks argument to specify custom axis breaks of 5, 15 and 25:
library(ggplot2)
#create scatterplot with custom x-axis breaks
ggplot(df, aes(x=points, y=assists)) +
geom_point(size=2) +
scale_x_continuous(breaks=c(5, 15, 25))
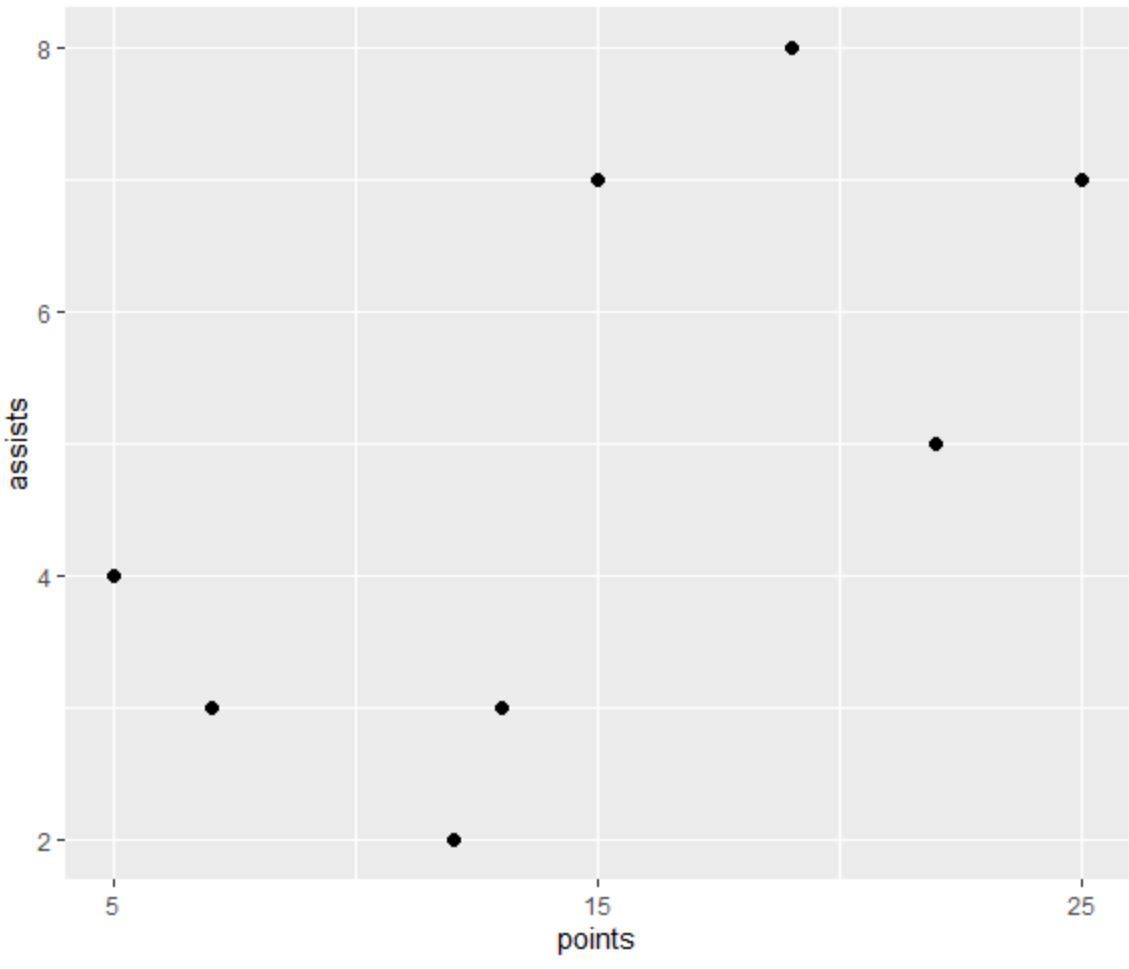
Notice that the x-axis only contains axis breaks at 5, 15 and 25, just as we specified using the breaks argument.
Example 2: Use scale_x_continuous with Custom Number of Breaks
The following code shows how to create a scatterplot in ggplot2 and use scale_x_continuous() with the n.breaks argument to place exactly 12 axis breaks on the x-axis:
library(ggplot2)
#create scatterplot with custom number of breaks on x-axis
ggplot(df, aes(x=points, y=assists)) +
geom_point(size=2) +
scale_x_continuous(n.breaks=12)
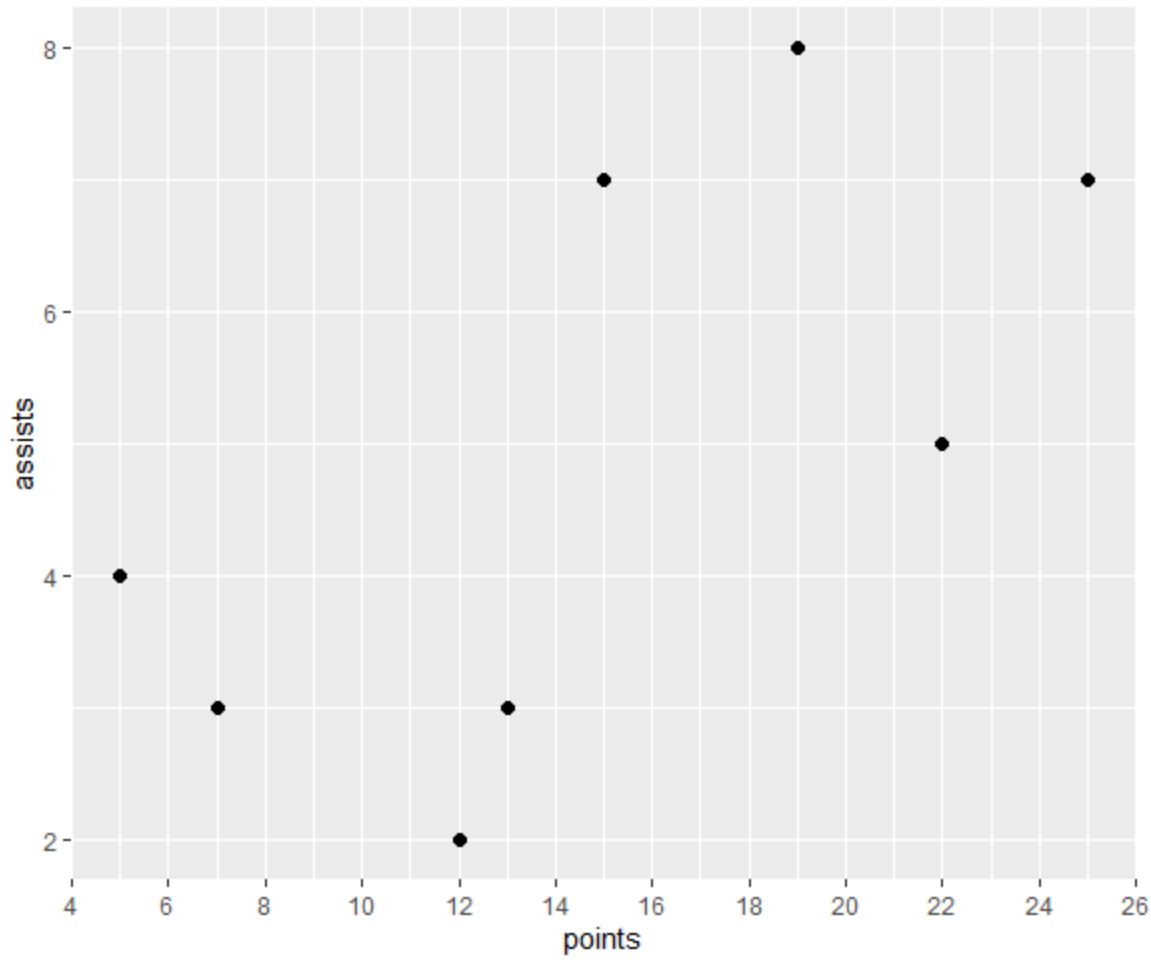
Notice that the x-axis contains exactly 12 axis breaks, just as we specified using the n.breaks argument.
Example 3: Use scale_x_continuous with Custom Labels
The following code shows how to create a scatterplot in ggplot2 and use scale_x_continuous() with the labels argument to specify the label names to place on the x-axis:
library(ggplot2)
#create scatterplot with custom labels on x-axis
ggplot(df, aes(x=points, y=assists)) +
geom_point(size=2) +
scale_x_continuous(breaks=c(5, 15, 25), labels=c('five', 'fifteen', 'twenty-five'))

Notice that the x-axis contains 3 axis breaks each with custom labels, just as we specified using the labels argument.
Example 4: Use scale_x_continuous with Custom Limits
The following code shows how to create a scatterplot in ggplot2 and use scale_x_continuous() with the limits argument to specify custom x-axis limits of 0 and 40:
library(ggplot2)
#create scatterplot with custom x-axis limits
ggplot(df, aes(x=points, y=assists)) +
geom_point(size=2) +
scale_x_continuous(limits=c(0, 40))
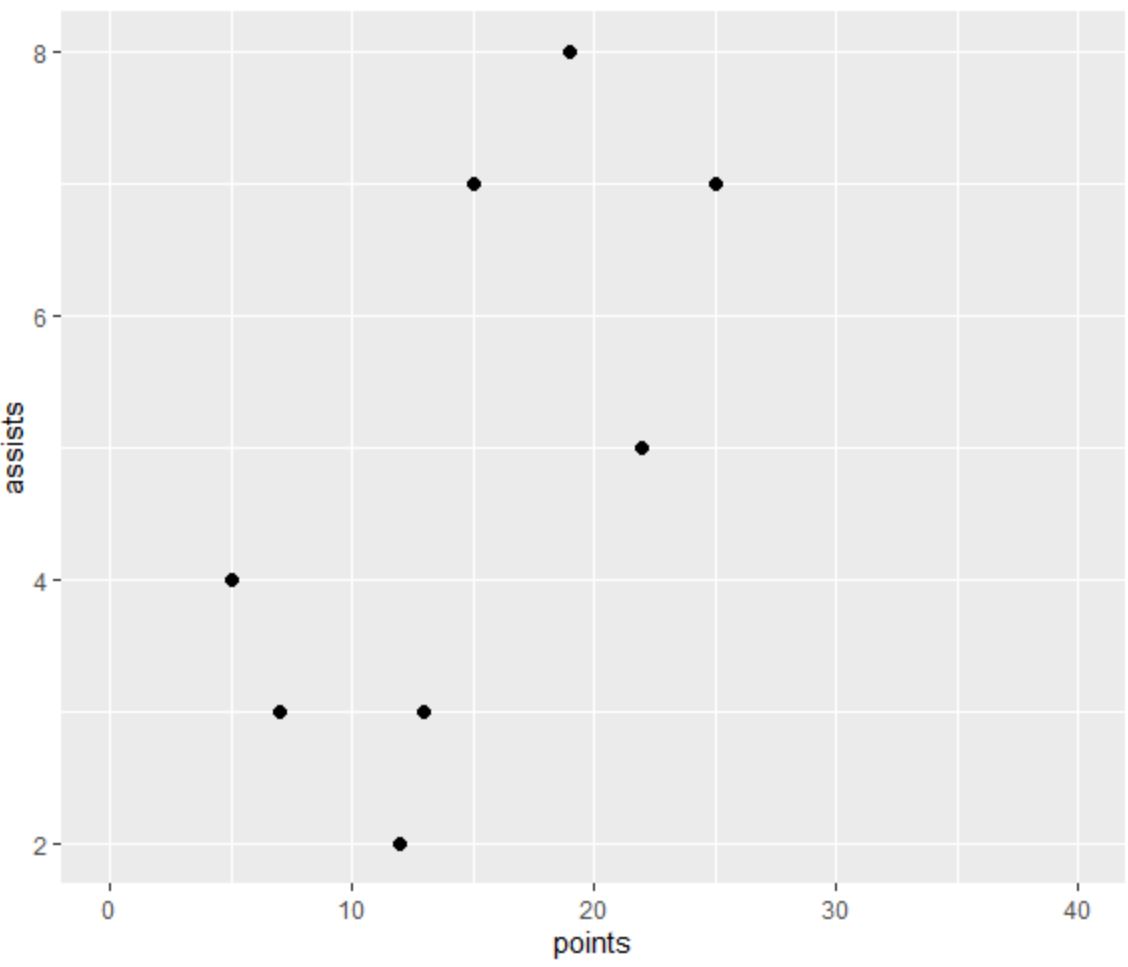
Notice that the x-axis ranges from 0 to 40, just as we specified using the limits argument.
The following tutorials explain how to perform other common tasks in ggplot2:
