Table of Contents
To plot a normal distribution in Python, first import the necessary libraries such as NumPy and Matplotlib. Then, create a sample dataset using the numpy.random.normal function. Next, use the matplotlib.pyplot.hist function to plot a histogram of the dataset. Adjust the parameters of the histogram, such as the number of bins and range, to fit the desired shape of the distribution. Finally, use the matplotlib.pyplot.plot function to overlay a line representing the normal distribution curve on top of the histogram. This will result in a visual representation of the normal distribution in Python.
Plot a Normal Distribution in Python (With Examples)
To plot a in Python, you can use the following syntax:
#x-axis ranges from -3 and 3 with .001 steps x = np.arange(-3, 3, 0.001) #plot normal distribution with mean 0 and standard deviation 1 plt.plot(x, norm.pdf(x, 0, 1))
The x array defines the range for the x-axis and the plt.plot() produces the curve for the normal distribution with the specified mean and standard deviation.
The following examples show how to use these functions in practice.
Example 1: Plot a Single Normal Distribution
The following code shows how to plot a single normal distribution curve with a mean of 0 and a standard deviation of 1:
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplotas plt from scipy.statsimport norm #x-axis ranges from -3 and 3 with .001 steps x = np.arange(-3, 3, 0.001) #plot normal distribution with mean 0 and standard deviation 1 plt.plot(x, norm.pdf(x, 0, 1))

You can also modify the color and the width of the line in the graph:
plt.plot(x, norm.pdf(x, 0, 1), color='red', linewidth=3)

Example 2: Plot Multiple Normal Distributions
The following code shows how to plot multiple normal distribution curves with different means and standard deviations:
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplotas plt from scipy.statsimport norm #x-axis ranges from -5 and 5 with .001 steps x = np.arange(-5, 5, 0.001) #define multiple normal distributions plt.plot(x, norm.pdf(x, 0, 1), label='μ: 0, σ: 1') plt.plot(x, norm.pdf(x, 0, 1.5), label='μ:0, σ: 1.5') plt.plot(x, norm.pdf(x, 0, 2), label='μ:0, σ: 2') #add legend to plot plt.legend()
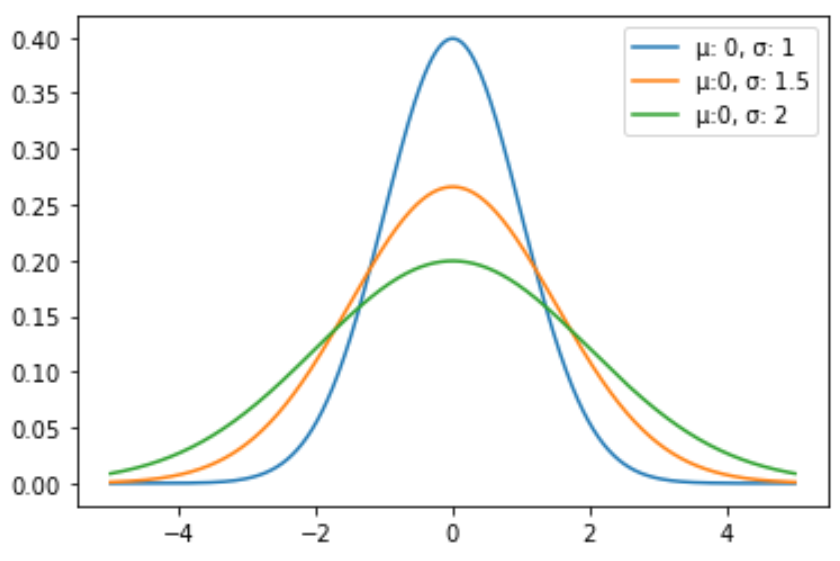
Feel free to modify the colors of the lines and add a title and axes labels to make the chart complete:
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplotas plt from scipy.statsimport norm #x-axis ranges from -5 and 5 with .001 steps x = np.arange(-5, 5, 0.001) #define multiple normal distributions plt.plot(x, norm.pdf(x, 0, 1), label='μ: 0, σ: 1', color='gold') plt.plot(x, norm.pdf(x, 0, 1.5), label='μ:0, σ: 1.5', color='red') plt.plot(x, norm.pdf(x, 0, 2), label='μ:0, σ: 2', color='pink') #add legend to plot plt.legend(title='Parameters') #add axes labels and a title plt.ylabel('Density') plt.xlabel('x') plt.title('Normal Distributions', fontsize=14)

Refer to the for an in-depth explanation of the plt.plot() function.
