Table of Contents
Plotting a normal distribution in Python is a relatively straightforward task using the Matplotlib library. The Matplotlib library has a method called norm that creates a probability density function (PDF) from the given mean and standard deviation. This PDF can then be used to plot the normal distribution curve. To plot a normal distribution in Python, we can first generate a range of values for the x-axis, then calculate the corresponding y-axis values for those x-axis values, and finally plot the results using Matplotlib. All of this can be accomplished using basic Python code. Examples of plotting a normal distribution in Python are provided.
To plot a in Python, you can use the following syntax:
#x-axis ranges from -3 and 3 with .001 steps x = np.arange(-3, 3, 0.001) #plot normal distribution with mean 0 and standard deviation 1 plt.plot(x, norm.pdf(x, 0, 1))
The x array defines the range for the x-axis and the plt.plot() produces the curve for the normal distribution with the specified mean and standard deviation.
The following examples show how to use these functions in practice.
Example 1: Plot a Single Normal Distribution
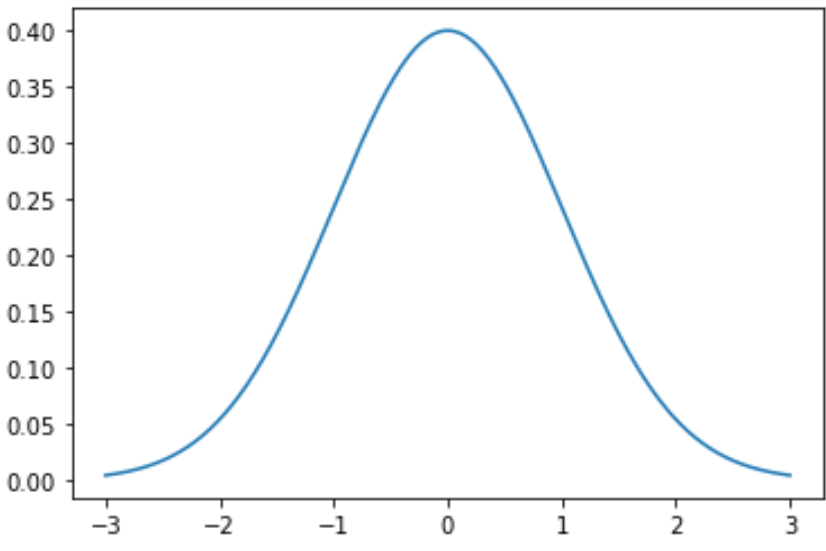
The following code shows how to plot a single normal distribution curve with a mean of 0 and a standard deviation of 1:
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from scipy.stats import norm #x-axis ranges from -3 and 3 with .001 steps x = np.arange(-3, 3, 0.001) #plot normal distribution with mean 0 and standard deviation 1 plt.plot(x, norm.pdf(x, 0, 1))
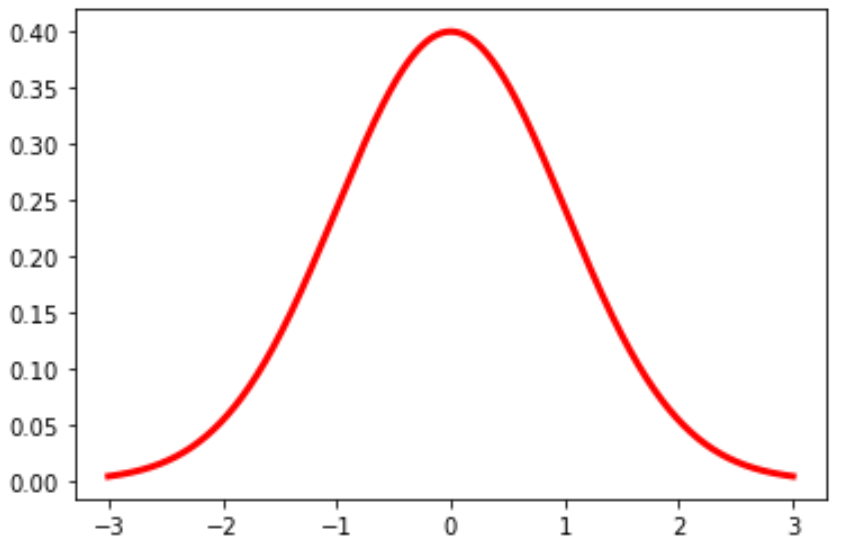
You can also modify the color and the width of the line in the graph:
plt.plot(x, norm.pdf(x, 0, 1), color='red', linewidth=3)
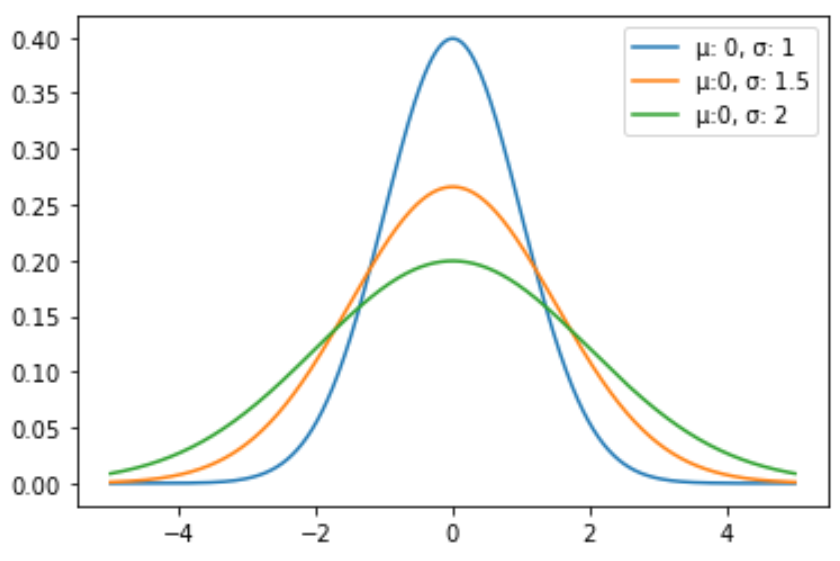
Example 2: Plot Multiple Normal Distributions
The following code shows how to plot multiple normal distribution curves with different means and standard deviations:
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from scipy.stats import norm #x-axis ranges from -5 and 5 with .001 steps x = np.arange(-5, 5, 0.001) #define multiple normal distributions plt.plot(x, norm.pdf(x, 0, 1), label='μ: 0, σ: 1') plt.plot(x, norm.pdf(x, 0, 1.5), label='μ:0, σ: 1.5') plt.plot(x, norm.pdf(x, 0, 2), label='μ:0, σ: 2') #add legend to plot plt.legend()
Feel free to modify the colors of the lines and add a title and axes labels to make the chart complete:
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from scipy.stats import norm #x-axis ranges from -5 and 5 with .001 steps x = np.arange(-5, 5, 0.001) #define multiple normal distributions plt.plot(x, norm.pdf(x, 0, 1), label='μ: 0, σ: 1', color='gold') plt.plot(x, norm.pdf(x, 0, 1.5), label='μ:0, σ: 1.5', color='red') plt.plot(x, norm.pdf(x, 0, 2), label='μ:0, σ: 2', color='pink') #add legend to plot plt.legend(title='Parameters') #add axes labels and a title plt.ylabel('Density') plt.xlabel('x') plt.title('Normal Distributions', fontsize=14)

Refer to the for an in-depth explanation of the plt.plot() function.
