The maximum likelihood estimator (MLE) for a Poisson distribution is the parameter λ which is the mean of the distribution. The MLE for λ is equal to the sample mean, which is calculated by summing all of the data points and dividing by the number of data points. This is the most likely, or maximum, value for the parameter λ given the data.
Maximum likelihood estimation (MLE) is a method that can be used to estimate the parameters of a given distribution.
This tutorial explains how to calculate the MLE for the parameter λ of a Poisson distribution.
Step 1: Write the PDF.
First, write the probability density function of the Poisson distribution:
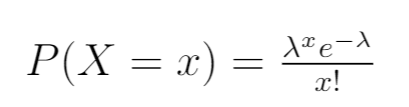
Step 2: Write the likelihood function.
Next, write the likelihood function. This is simply the product of the PDF for the observed values x1, …, xn.
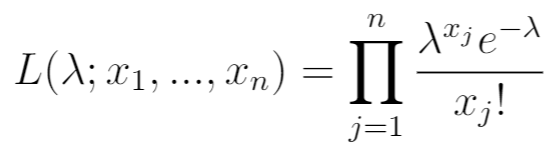
Step 3: Write the natural log likelihood function.
To simplify the calculations, we can write the natural log likelihood function:
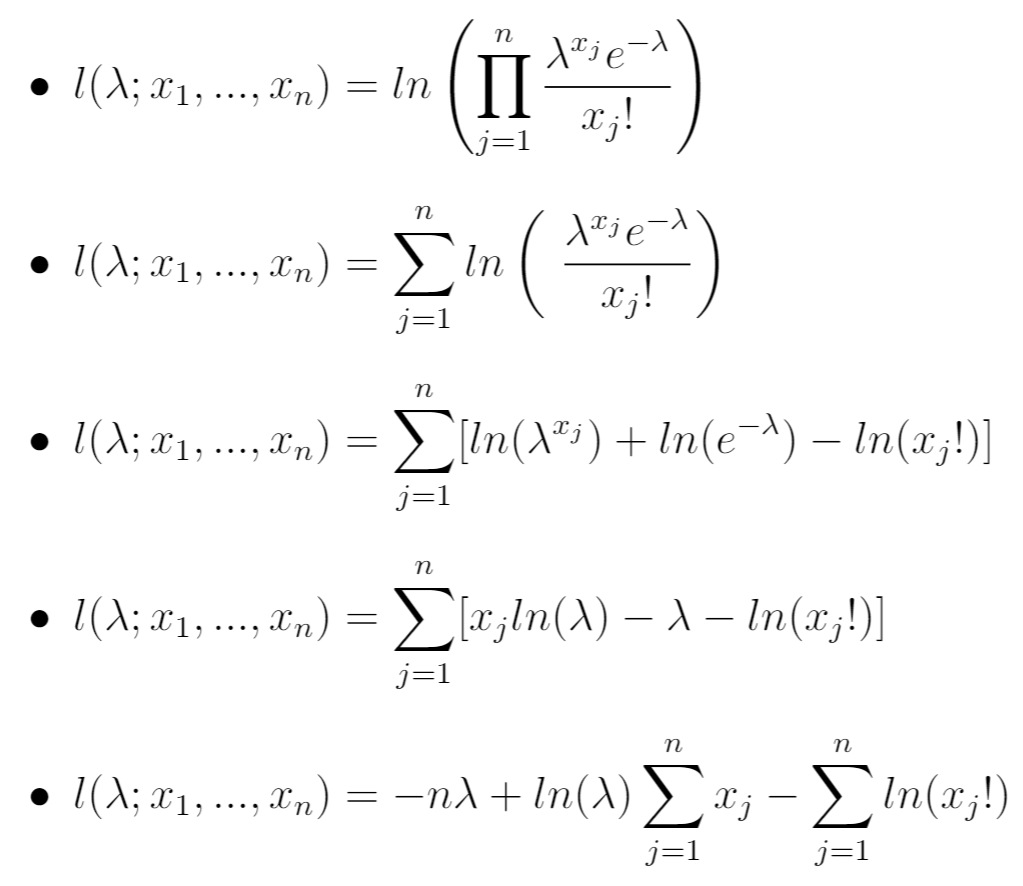
Step 4: Calculate the derivative of the natural log likelihood function with respect to λ.
Next, we can calculate the derivative of the natural log likelihood function with respect to the parameter λ:
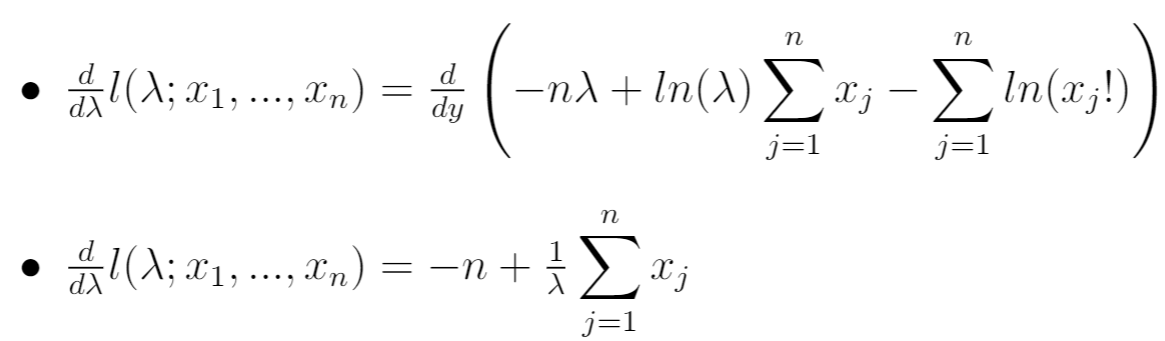
Step 5: Set the derivative equal to zero and solve for λ.
Lastly, we set the derivative in the previous step equal to zero and simply solve for λ:
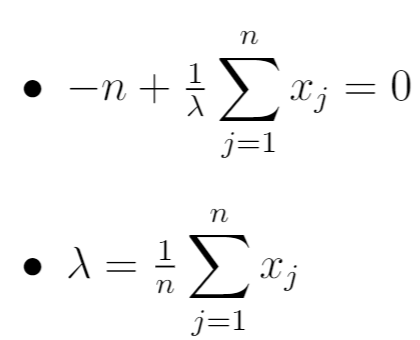
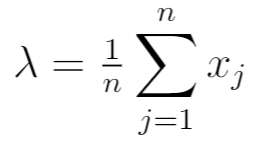
This is equivalent to the sample mean of the n observations in the sample.
An Introduction to the Poisson Distribution
Poisson Distribution Calculator
How to Use the Poisson Distribution in Excel
