Table of Contents
Logarithmic regression in Python can be done by first importing the necessary libraries, such as NumPy and Scikit-learn, and then creating the independent and dependent variables. After that, the data should be scaled using the StandardScaler and then split into training and test sets. Finally, the logarithmic regression model can be fitted and then used to make predictions.
Logarithmic regression is a type of regression used to model situations where growth or decay accelerates rapidly at first and then slows over time.
For example, the following plot demonstrates an example of logarithmic decay:

For this type of situation, the relationship between a predictor variable and a could be modeled well using logarithmic regression.
The equation of a logarithmic regression model takes the following form:
y = a + b*ln(x)
where:
- y: The response variable
- x: The predictor variable
- a, b: The regression coefficients that describe the relationship between x and y
The following step-by-step example shows how to perform logarithmic regression in Python.
Step 1: Create the Data
First, let’s create some fake data for two variables: x and y:
import numpy as np x = np.arange(1, 16, 1) y = np.array([59, 50, 44, 38, 33, 28, 23, 20, 17, 15, 13, 12, 11, 10, 9.5])
Step 2: Visualize the Data
Next, let’s create a quick to visualize the relationship between x and y:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt plt.scatter(x, y) plt.show()
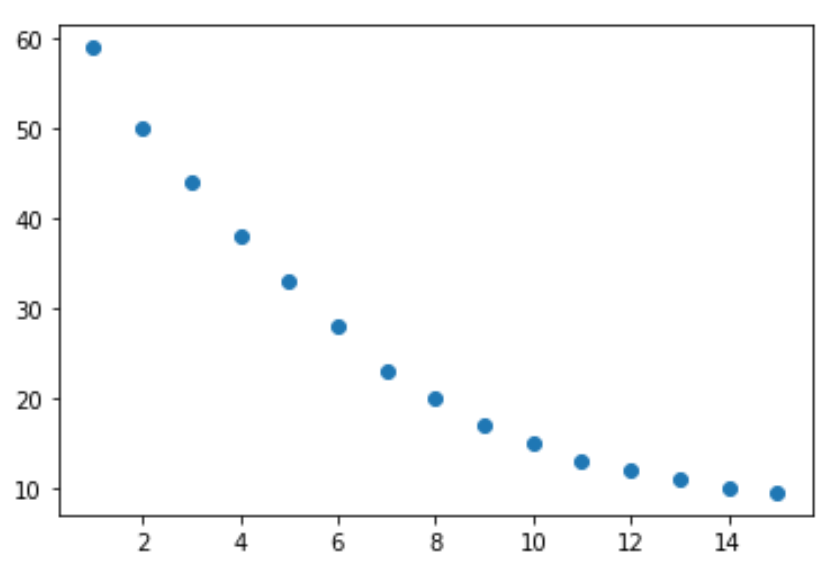
From the plot we can see that there exists a logarithmic decay pattern between the two variables. The value of the response variable, y, decreases rapidly at first and then slows over time.
Step 3: Fit the Logarithmic Regression Model
Next, we’ll use the polyfit() function to fit a logarithmic regression model, using the natural log of x as the predictor variable and y as the response variable:
#fit the model fit = np.polyfit(np.log(x), y, 1) #view the output of the model print(fit) [-20.19869943 63.06859979]
We can use the coefficients in the output to write the following fitted logarithmic regression equation:
y = 63.0686 – 20.1987 * ln(x)
We can use this equation to predict the response variable, y, based on the value of the predictor variable, x. For example, if x = 12, then we would predict that y would be 12.87:
y = 63.0686 – 20.1987 * ln(12) = 12.87
Bonus: Feel free to use this online to automatically compute the logarithmic regression equation for a given predictor and response variable.
