Table of Contents
The Exponential Moving Average (EMA) is a popular statistical tool used to analyze time series data in R. It calculates the average value of a variable over a specified period, giving more weight to recent data points. This allows for a smoother representation of the data and helps to identify trends and patterns. To calculate the EMA in R, you first need to choose a time period and a smoothing factor. Then, using the EMA formula, the current EMA value is calculated by combining the previous EMA value and the current data point. This process is repeated for each data point, resulting in a series of EMA values. R has built-in functions, such as “EMA” and “SMA”, that can be used to calculate the EMA. This powerful tool can aid in making informed decisions in various fields, including finance, economics, and engineering.
Calculate an Exponential Moving Average in R
In time series analysis, a moving average is simply the average value of a certain number of previous periods.
An exponential moving average is a type of moving average that gives more weight to recent observations, which means it’s able to capture recent trends more quickly.
This tutorial explains how to calculate an exponential moving average in R.
Example: Exponential Moving Average in R
Suppose we have the following data frame in R:
#create data frame df <- data.frame(period=1:10, sales=c(25, 20, 14, 16, 27, 20, 12, 15, 14, 19)) #view data frame df period sales 1 1 25 2 2 20 3 3 14 4 4 16 5 5 27 6 6 20 7 7 12 8 8 15 9 9 14 10 10 19
We can use the movavg() function from the pracma package to calculate the exponentially weighted moving average for a certain number of previous periods.
This function uses the following syntax:
movavg(x, n, type=c(“s”, “t”, “w”, “m”, “e”, “r”))
where:
- x: Time series as numeric vector
- n: Number of previous periods to use for average
- type: Type of moving average to calculate. We will use “e” for exponential weighted moving average.
For example, here’s how to calculate the exponentially weighted moving average using the four previous periods:
library(pracma) #create new column to hold 4-day exponentially weighted moving average df$EWM_4day <- movavg(df$sales, n=4, type='e') #view DataFrame df period sales 4dayEWM 0 1 25 25.000000 1 2 20 23.000000 2 3 14 19.400000 3 4 16 18.040000 4 5 27 21.624000 5 6 20 20.974400 6 7 12 17.384640 7 8 15 16.430784 8 9 14 15.458470 9 10 19 16.875082
We can also use the ggplot2 visualization library to visualize the sales compared to the 4-day exponentially weighted moving average:
library(ggplot2)
library(reshape2)
#melt data into format for easy plotting
df <- melt(df , id.vars = 'period', variable.name = 'series')
#plot sales vs. 4-day exponentially weighted moving average
ggplot(df, aes(period, value)) +
geom_line(aes(colour = series))
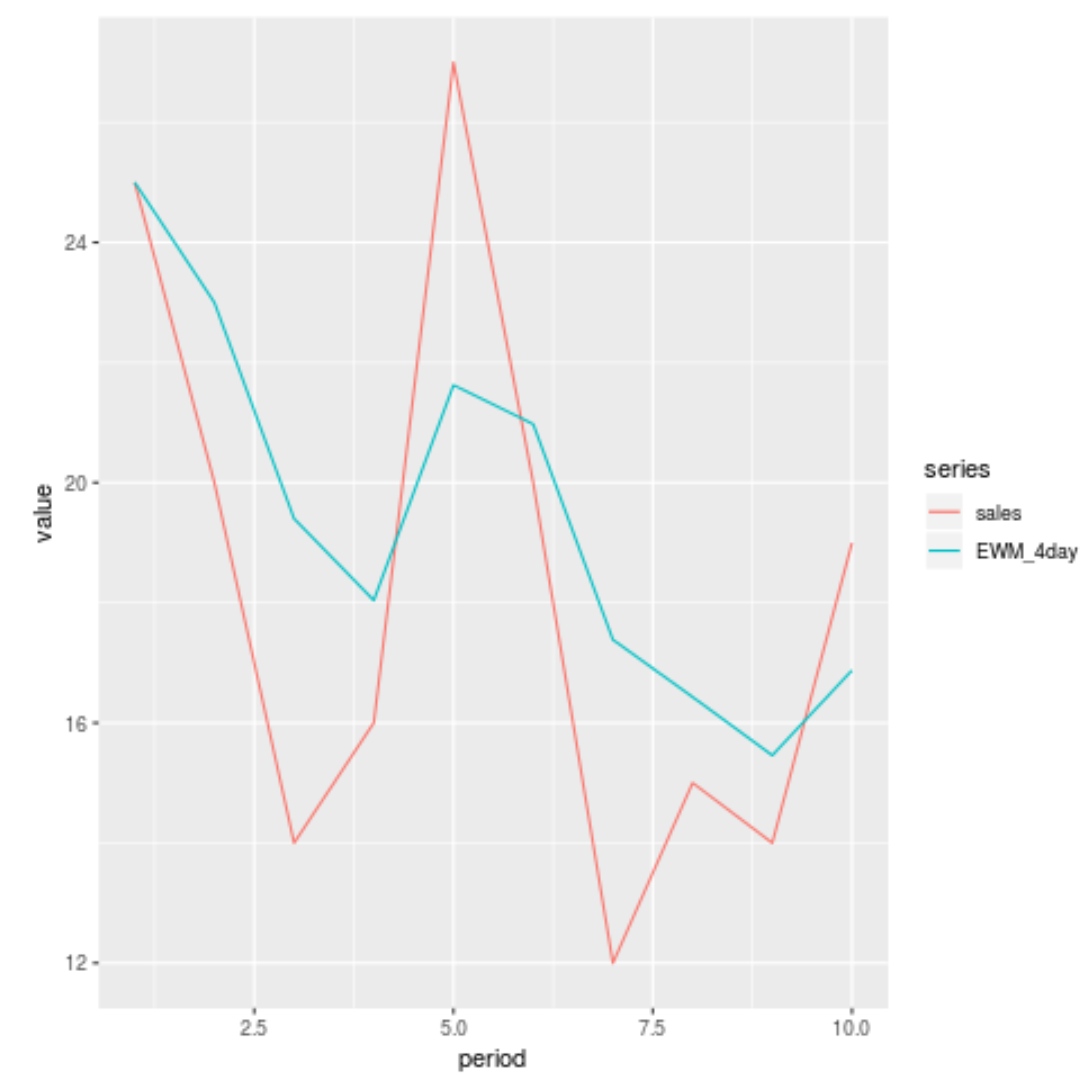
The red line displays the sales during each period and the blue line displays the exponentially weighted moving average.
Additional Resources
How to Plot Multiple Columns in R
How to Average Across Columns in R
How to Calculate the Mean by Group in R
