Table of Contents
A Normal Probability Plot is a graphical representation of data that allows one to determine if the data follows a normal distribution. To create a Normal Probability Plot in Excel, follow these steps:
1. Organize your data in a single column or row in an Excel spreadsheet.
2. Select the data and click on the “Insert” tab.
3. In the “Charts” section, click on the arrow next to “Scatter” and select “Scatter with only Markers.”
4. Right-click on the chart and click on “Select Data.”
5. In the “Select Data Source” window, click on “Add” to add a new data series.
6. In the “Edit Series” window, enter a name for the series and select the data for the Y-axis (dependent variable).
7. Click on “OK” to close the window.
8. Repeat steps 5-7 for the X-axis (independent variable) using the same data range.
9. Right-click on the chart and click on “Format Data Series.”
10. In the “Format Data Series” window, go to the “Marker Options” tab and select “None” under “Marker Type.”
11. Click on “Close” to close the window.
12. Right-click on the Y-axis and click on “Format Axis.”
13. In the “Format Axis” window, go to the “Axis Options” tab and select “Logarithmic scale.”
14. Click on “Close” to close the window.
15. Your Normal Probability Plot is now complete and can be interpreted by observing how closely the data points align with a straight line. A closer alignment indicates a normal distribution.
By following these steps, you can easily create a Normal Probability Plot in Excel to analyze the distribution of your data.
Create a Normal Probability Plot in Excel (Step-by-Step)
A normal probability plot can be used to determine if the values in a dataset are roughly .
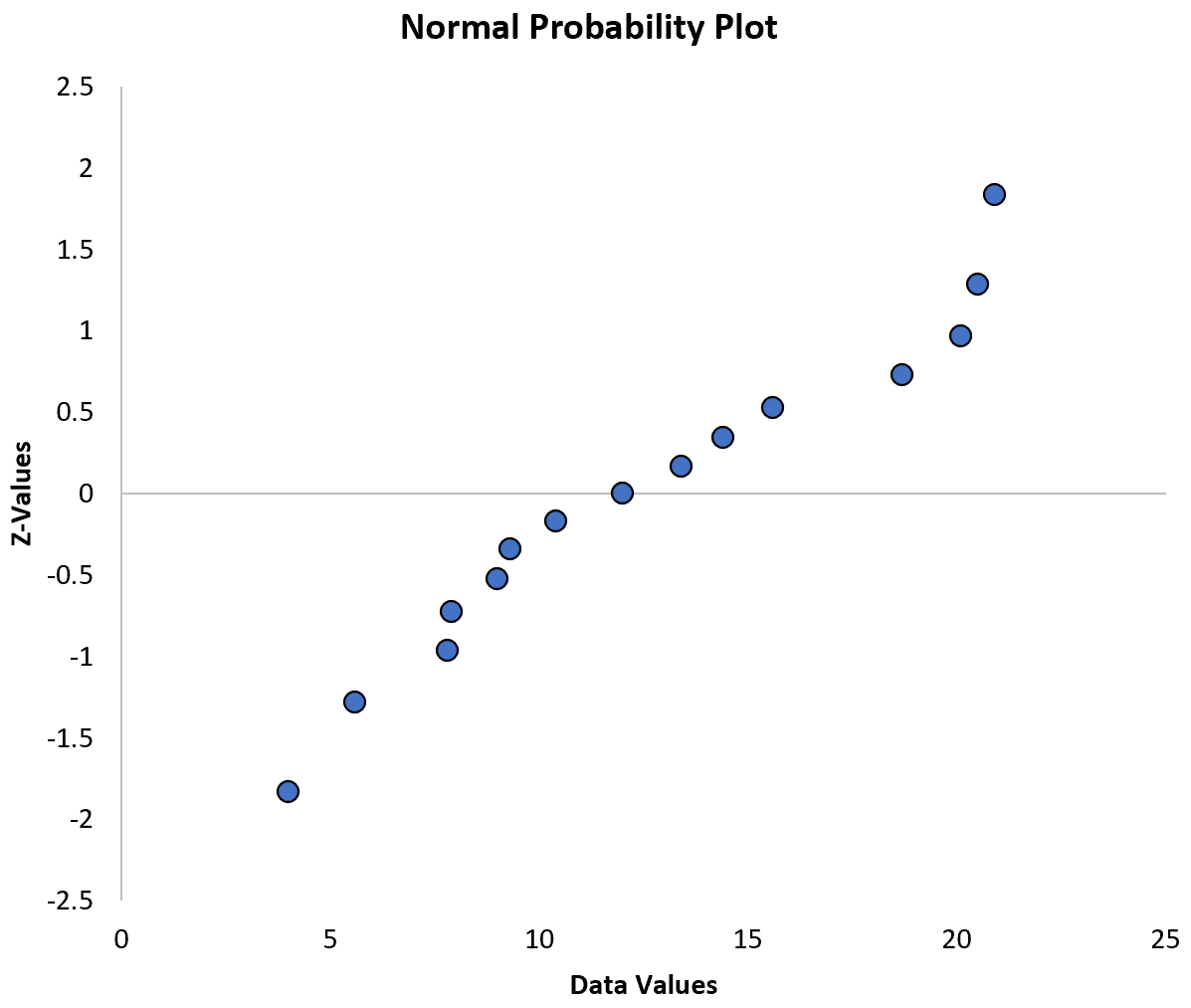
This tutorial provides a step-by-step example of how to create a normal probability plot for a given dataset in Excel
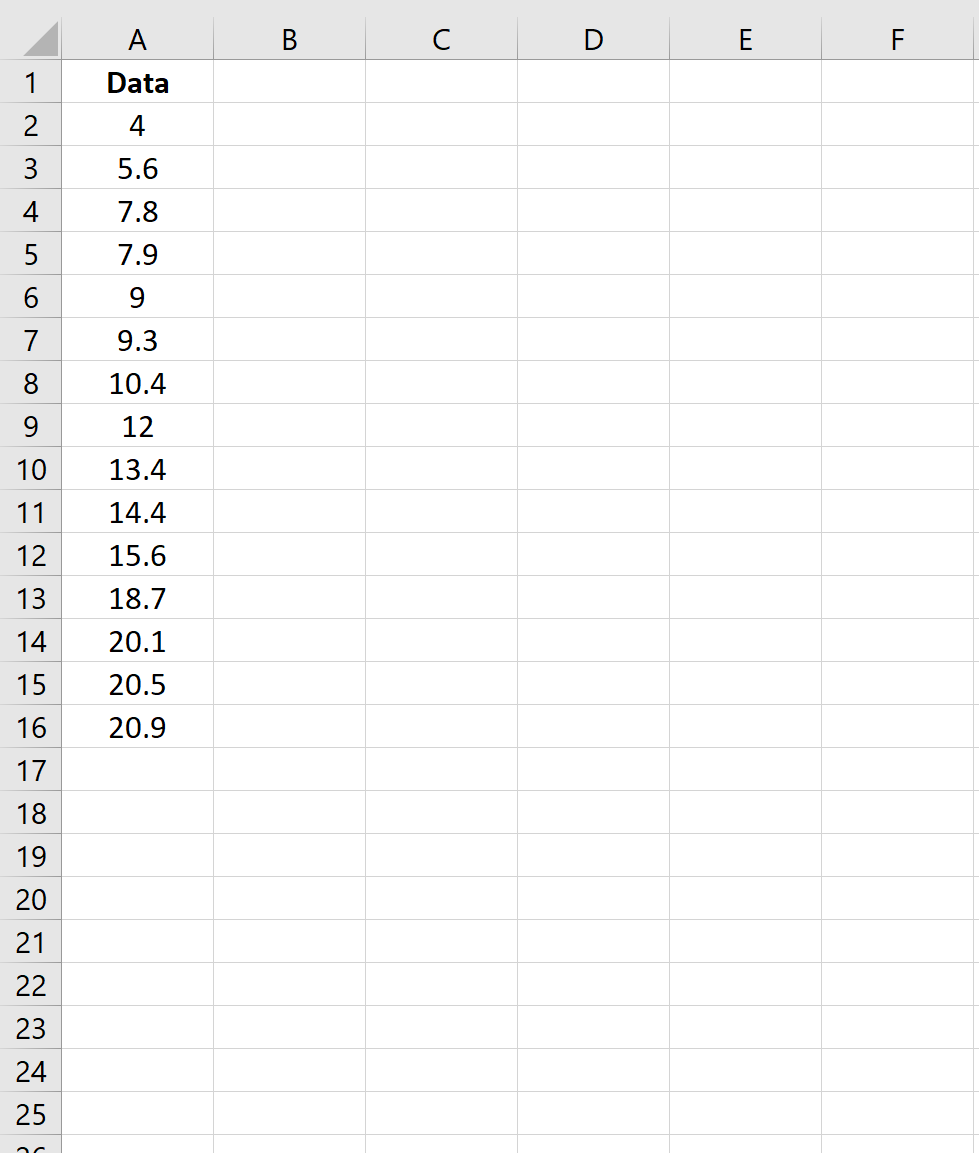
Step 1: Create the Dataset
First, let’s create a fake dataset with 15 values:
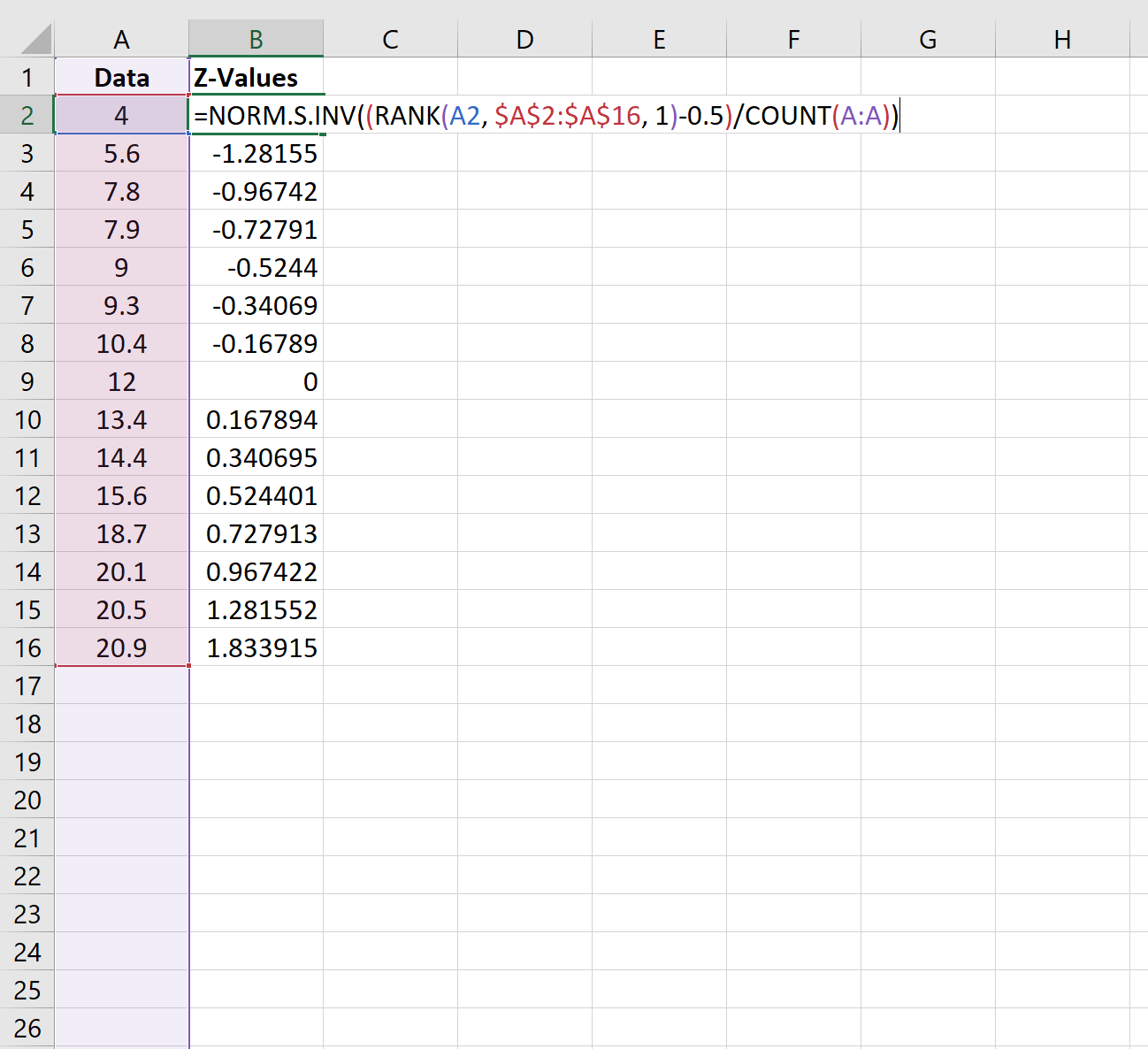
Step 2: Calculate the Z-Values
Next, we’ll use the following formula to calculate the z-value that corresponds to the first data value:
=NORM.S.INV((RANK(A2, $A$2:$A$16, 1)-0.5)/COUNT(A:A))
We’ll copy this formula down to each cell in column B:
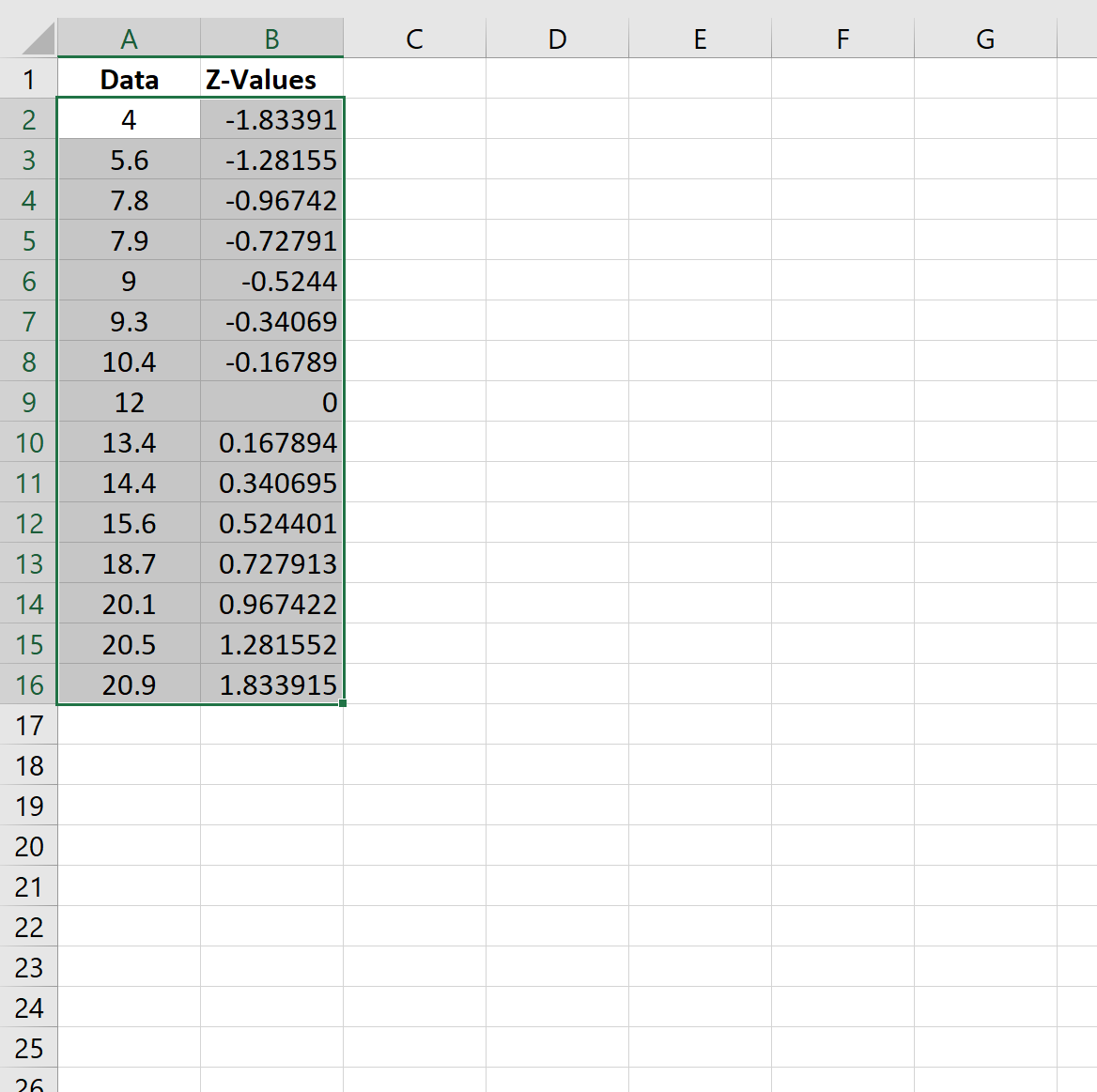
Step 3: Create the Normal Probability Plot
Next, we’ll create the normal probability plot.
First, highlight the cell range A2:B16 as follows:
Along the top ribbon, click the Insert tab. Under the Charts section, click the first option under Scatter.
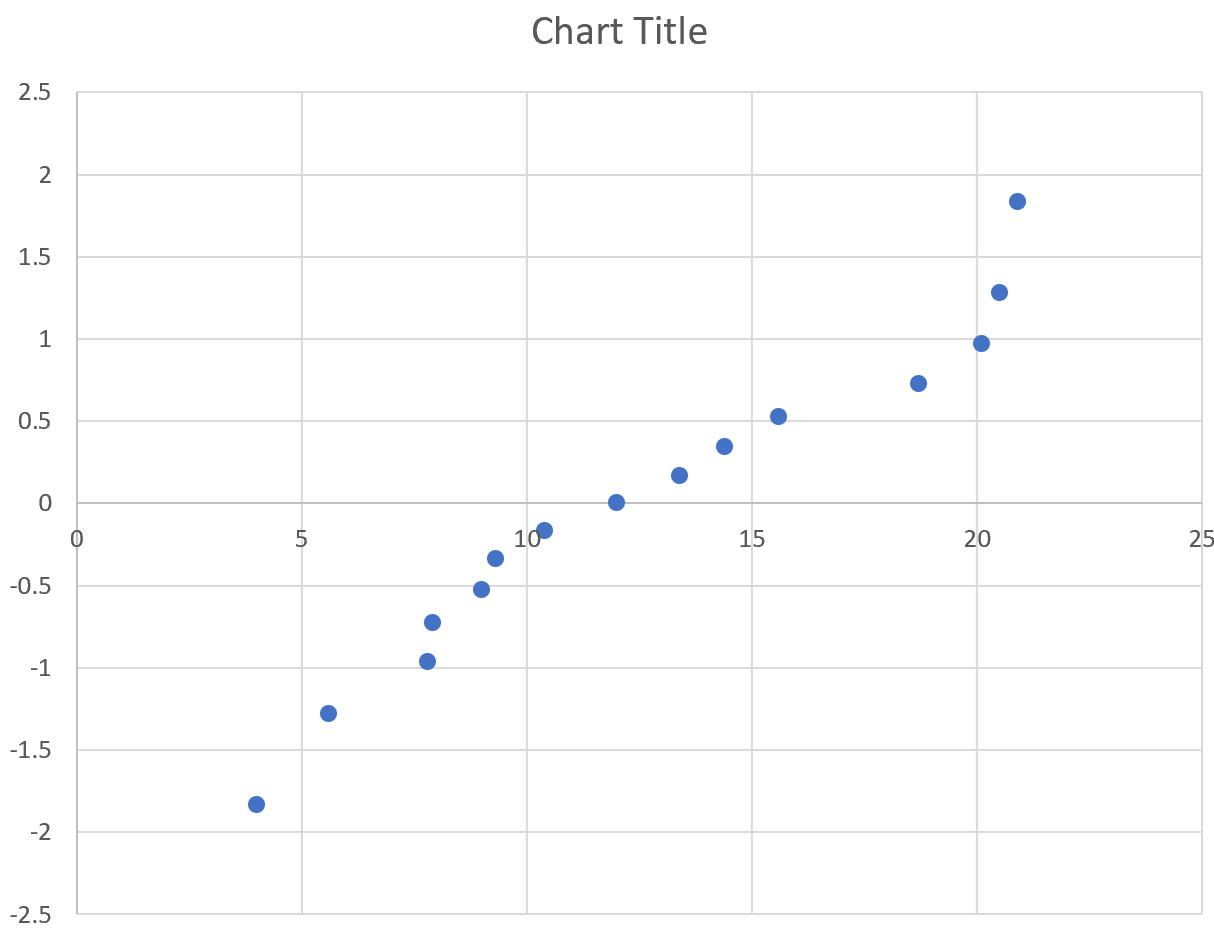
The x-axis displays the ordered data values and the y-value displays their corresponding z-values.
Feel free to modify the title, axes, and labels to make the plot more aesthetically pleasing:

How to Interpret a Normal Probability Plot
The way to interpret a normal probability plot is simple: if the data values fall along a roughly straight line at a 45-degree angle, then the data is normally distributed.
In our plot above we can see that the values tend to deviate from a straight line at a 45-degree angle, especially on the tail ends. This likely indicates that the data is not normally distributed.
Although a normal probability plot isn’t a formal statistical test, it offers an easy way to visually check whether or not a data set is normally distributed.
If you’re looking for a formal normality test, read on how to perform a normality test in Excel.
