Table of Contents
The Central Limit Theorem is a statistical concept that states that the sample mean of a large number of independent and identically distributed variables will approximate a normal distribution, regardless of the underlying distribution of the variables. This theorem has practical applications in data analysis, as it allows for the estimation of population parameters using sample data.
One way to apply the Central Limit Theorem is through the use of Microsoft Excel. By inputting a large dataset into Excel and using the built-in functions, such as the AVERAGE function, the sample mean can be calculated. This process can be repeated multiple times, with different samples from the same population, to create a distribution of sample means.
By plotting this distribution of sample means using a histogram or a line graph, Excel can be used to demonstrate the central limit theorem in action. The resulting graph will show a bell-shaped curve, which is a characteristic of a normal distribution. This visual representation provides evidence for the applicability of the Central Limit Theorem and can be used to make inferences about the population parameters.
In conclusion, the Central Limit Theorem can be easily applied using Excel, allowing for a better understanding and analysis of data in various fields such as finance, economics, and social sciences.
Apply the Central Limit Theorem in Excel
The states that the sampling distribution of a sample mean is approximately normal if the sample size is large enough, even if the population distribution is not normal.
The central limit theorem also states that the sampling distribution will have the following properties:
1. The mean of the sampling distribution will be equal to the mean of the population distribution:
x = μ
2. The standard deviation of the sampling distribution will be equal to the standard deviation of the population divided by the sample size:
s = σ / √n
In this tutorial, we explain how to apply the central limit theorem in Excel to a given distribution.
Applying the Central Limit Theorem in Excel
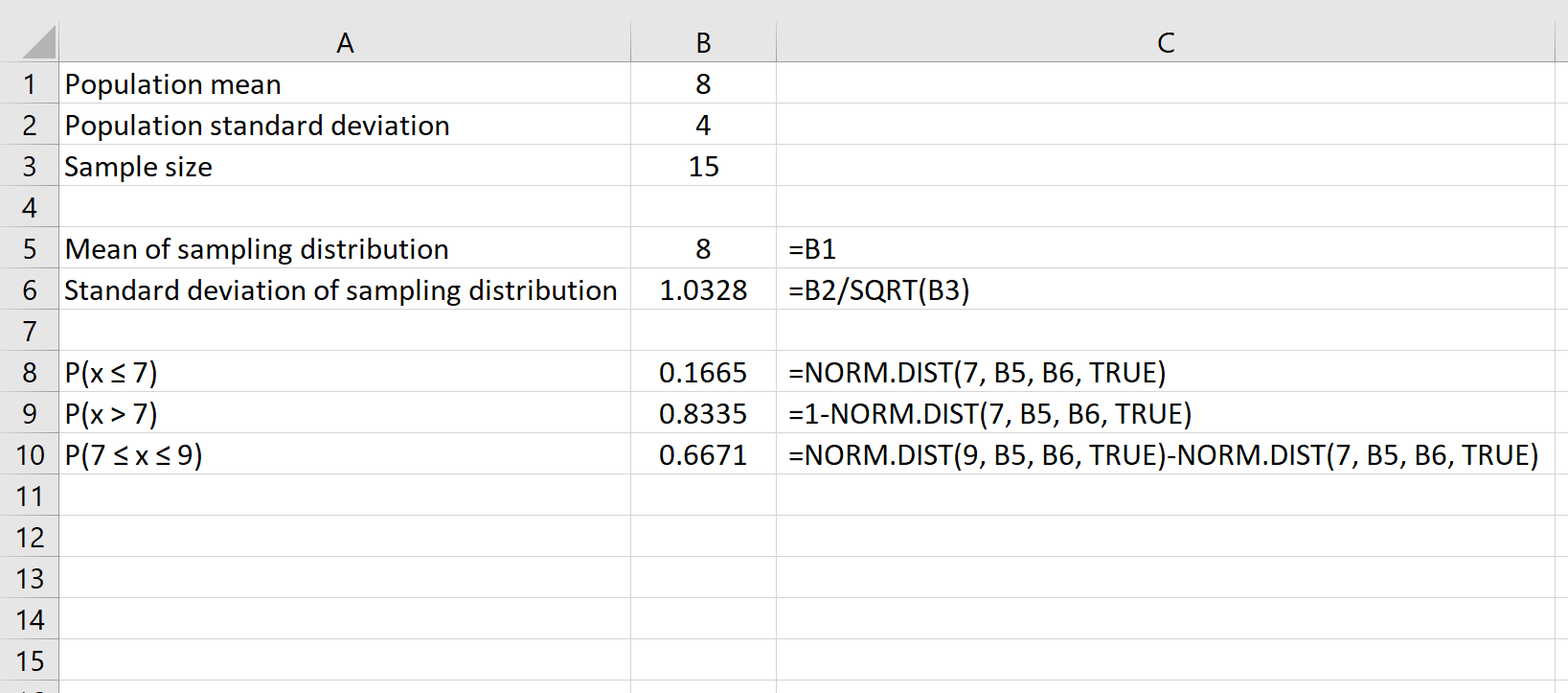
Suppose we have a distribution with a mean of 8 and a standard deviation of 4. We can use the following formulas in Excel to find both the mean and the standard deviation of the sampling distribution with a sample size of 15:
The mean of the sampling distribution is simply equal to the mean of the population distribution, which is 8.
The standard deviation of the sampling distribution is equal to the population standard deviation divided by the sample size, which is: 4 /√15 = 1.0328.
We can also use the central limit theorem to answer questions about probabilities. For example, if a given population has a mean of 8 and a standard deviation of 4, what is the probability that a given sample of size 15 has a mean less than or equal to 7?
To answer this question, we can use the NORM.DIST() function in Excel, which uses the following syntax:
NORM.DIST(x, mean, standard_dev, cumulative)
where:
- x: the sample mean you’d like to test
- mean: expected mean of sampling distribution
- standard_dev: expected standard deviation of sampling distribution
- cumulative: TRUE returns the value of the normal CDF; FALSE returns the value of the normal PDF. In our case, we will always use TRUE.
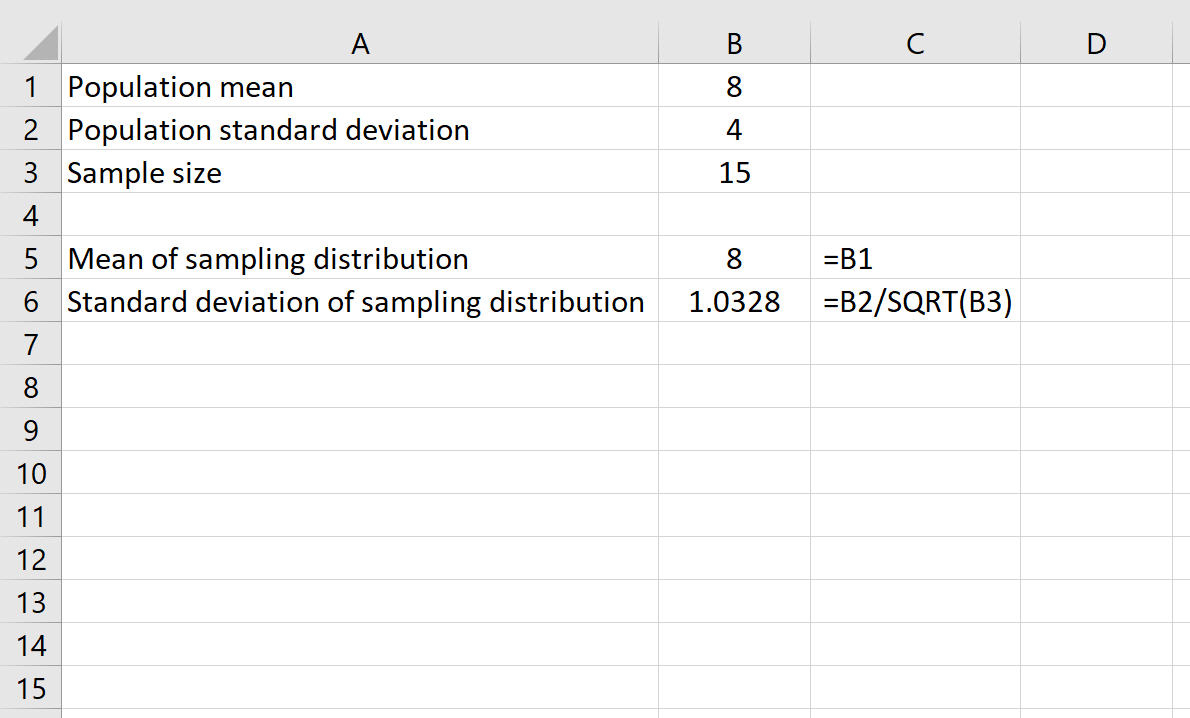
Here is the formula we would use in this example:
This tells us that for a population with a mean of 8 and a standard deviation of 4, the probability that a given sample of size 15 has a mean less than or equal to 7 is 0.1665.
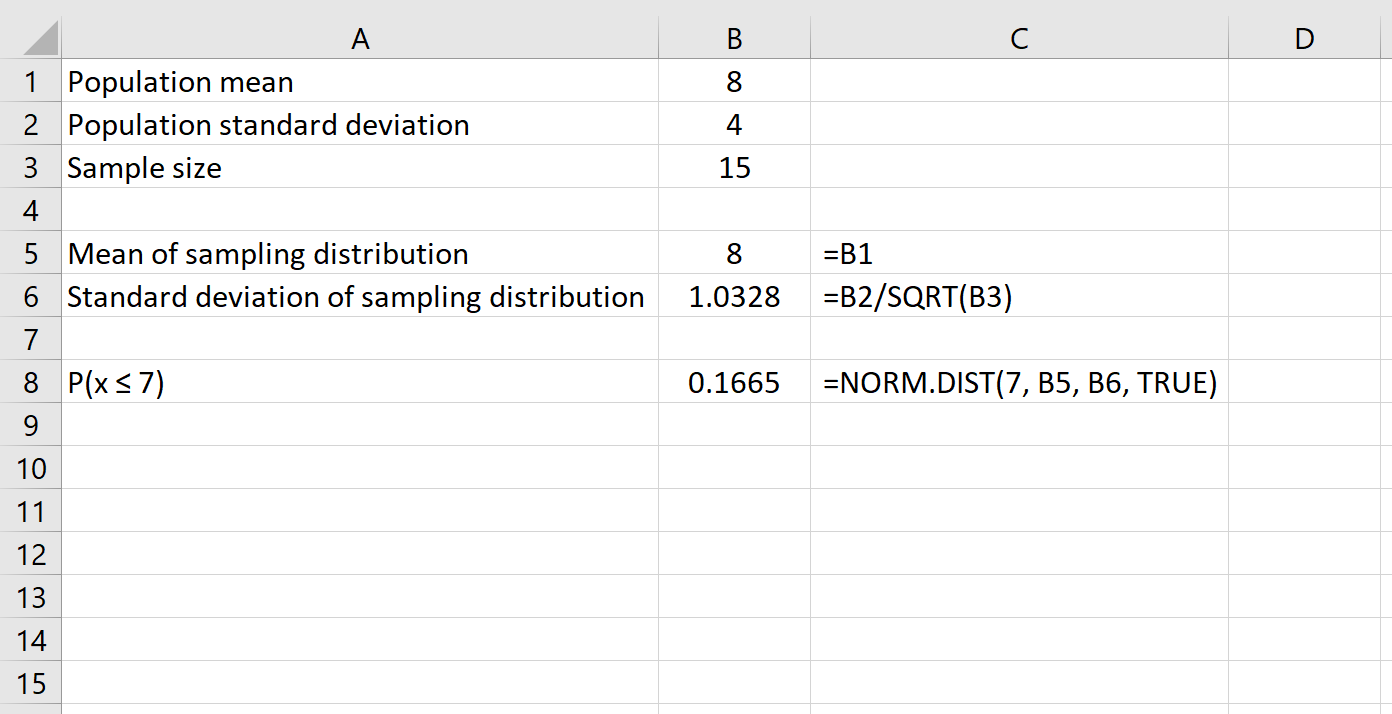
We can also find the probability that a given sample size has a mean greater than a certain number by simply using the formula 1 – NORM.DIST().
For example, the following formula shows how to find the probability that a given sample size of 15 has a mean greater than 7:
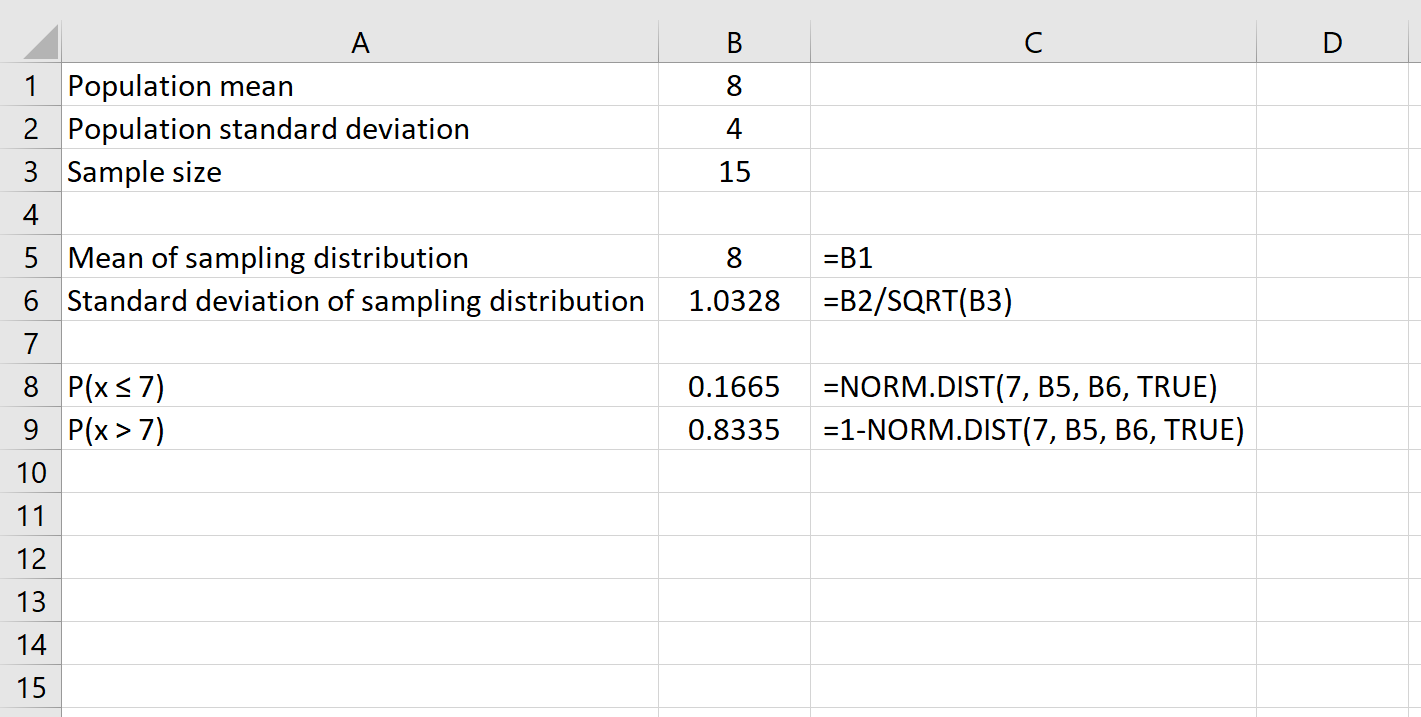
Lastly, we can find the probability that a given sample size will have a mean between two numbers by using the formula NORM.DIST(larger number) – NORM.DIST(smaller number).
For example, the following formula shows how to find the probability that a given sample size of 15 has a mean between 7 and 9: