Table of Contents
Chebyshev’s Theorem is a statistical concept that can be applied in Excel to analyze data sets with large variances. In Excel, this theorem can be utilized by using the functions and tools available in the program to calculate the range of values within a given standard deviation. By inputting the mean, standard deviation, and desired confidence level, Excel can provide the range of values within which a certain percentage of the data falls. This allows for a more accurate understanding of the data and can be used to identify outliers or unusual data points. Overall, the application of Chebyshev’s Theorem in Excel can aid in making data-driven decisions and improving data analysis processes.
Apply Chebyshev’s Theorem in Excel
Chebyshev’s Theorem states that for any number k greater than 1, at least 1 – 1/k2 of the data values in any shaped distribution lie within k standard deviations of the mean.
For example, for any shaped distribution at least 1 – 1/32 = 88.89% of the values in the distribution will lie within 3 standard deviations of the mean.
This tutorial illustrates several examples of how to apply Chebyshev’s Theorem in Excel.
Example 1: Use Chebyshev’s Theorem to find what percentage of values will fall between 30 and 70 for a dataset with a mean of 50 and standard deviation of 10.
First, determine the value for k. We can do this by finding out how many standard deviations away 30 and 70 are from the mean:
(30 – mean) / standard deviation = (30 – 50) / 10 = -20 / 10 = -2
(70 – mean) / standard deviation = (70 – 50) / 10 = 20 / 10 = 2
The values 30 and 70 are 2 standard deviations below and above the mean, respectively. Thus, k = 2.
We can then use the following formula in Excel to find the minimum percentage of values that fall within 2 standard deviations of the mean for this dataset:
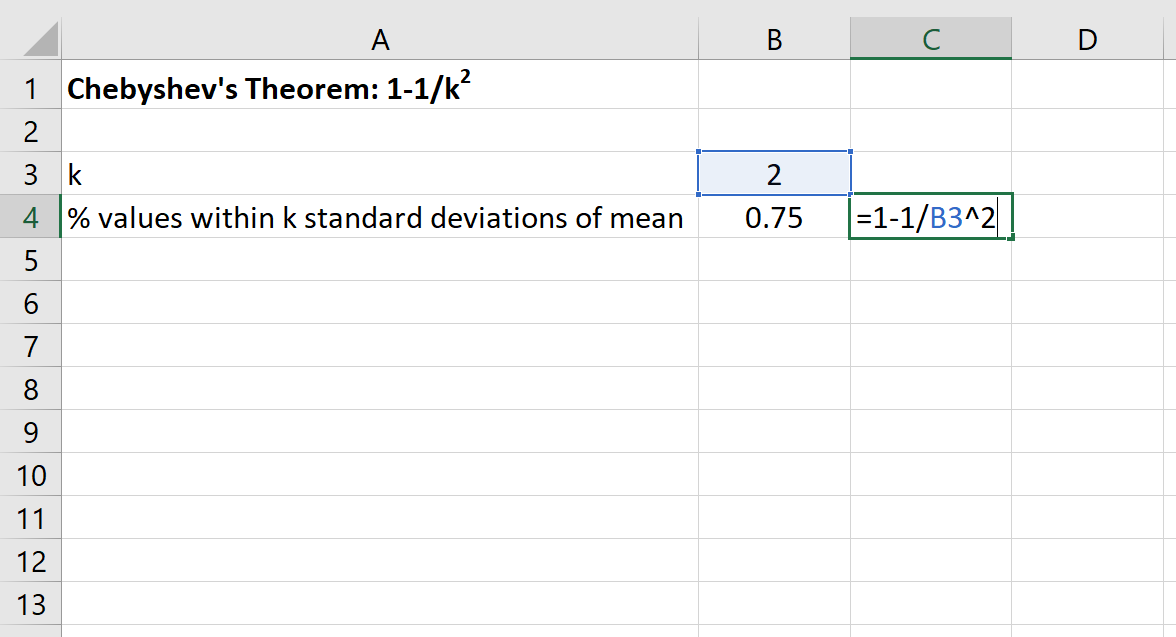
The percentage of values that fall within 30 and 70 for this dataset will be at least 75%.
Example 2: Use Chebyshev’s Theorem to find what percentage of values will fall between 20 and 50 for a dataset with a mean of 35 and standard deviation of 5.
First, determine the value for k. We can do this by finding out how many standard deviations away 20 and 50 are from the mean:
(20 – mean) / standard deviation = (20 – 35) / 5 = -15 / 5 = -3
(50 – mean) / standard deviation = (50 – 35) / 5 = 15 / 5 = 3
The values 20 and 50 are 3 standard deviations below and above the mean, respectively. Thus, k = 3.
We can then use the following formula in Excel to find the minimum percentage of values that fall within 3 standard deviations of the mean for this dataset:
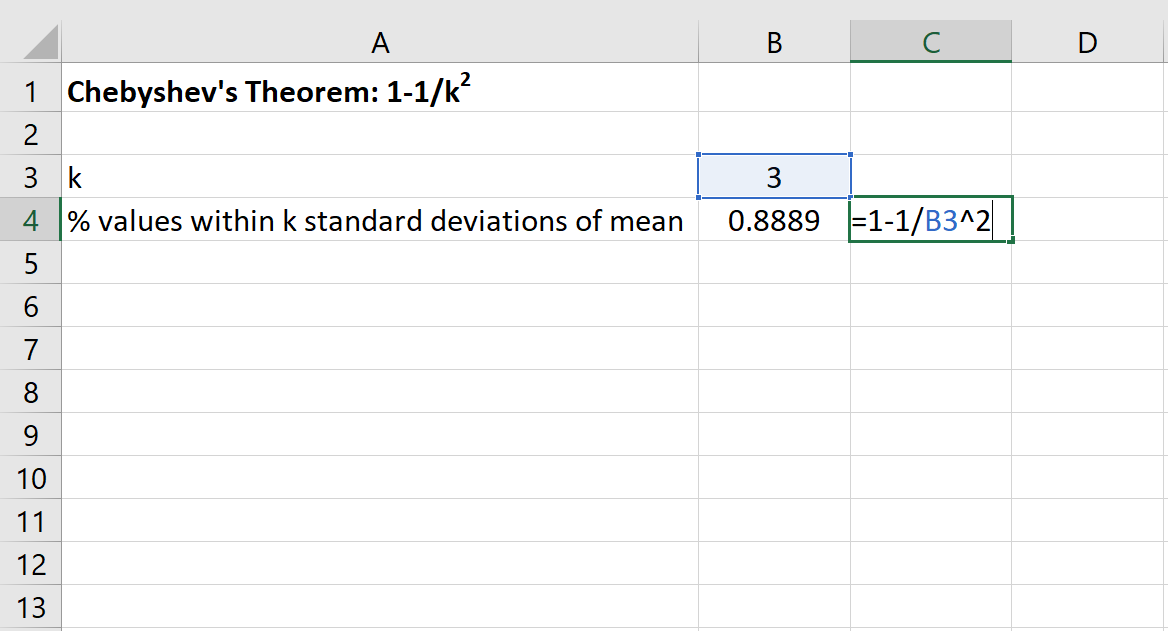
The percentage of values that fall within 20 and 50 for this dataset will be at least 88.89%.
Example 3: Use Chebyshev’s Theorem to find what percentage of values will fall between 80 and 120 for a dataset with a mean of 100 and standard deviation of 5.
First, determine the value for k. We can do this by finding out how many standard deviations away 80 and 120 are from the mean:
(80 – mean) / standard deviation = (80 – 100) / 5 = -20 / 5 = -4
(120 – mean) / standard deviation = (120 – 100) / 5 = 20 / 5 = 4
The values 80 and 120 are 4 standard deviations below and above the mean, respectively. Thus, k = 4.
We can then use the following formula in Excel to find the minimum percentage of values that fall within 4 standard deviations of the mean for this dataset:

The percentage of values that fall within 80 and 120 for this dataset will be at least 93.75%.
