Table of Contents
Lowess smoothing is a statistical technique used for smoothing out noisy data by fitting a locally weighted regression line through the data points. This can be easily performed in R by following these steps:
1. Load the necessary package: First, load the “stats” package in R, which contains the function for performing Lowess smoothing.
2. Prepare the data: Ensure that your data is in a suitable format, with the independent variable (x) and dependent variable (y) in separate columns.
3. Run the Lowess function: Use the “lowess” function in R, specifying the x and y variables, as well as the desired smoothing parameter (span) to control the amount of smoothing.
4. Visualize the results: Plot the original data points along with the smoothed line to visually assess the effectiveness of the smoothing.
5. Adjust the smoothing parameter: If necessary, try different values for the span parameter to see the effect on the smoothness of the line.
6. Save the results: Once satisfied with the smoothing, save the smoothed data as a new variable for further analysis or export the results for use in other software.
By following these steps, you can easily perform Lowess smoothing in R to effectively reduce noise in your data and identify underlying trends.
Perform Lowess Smoothing in R (Step-by-Step)
In statistics, the term lowess refers to “locally weighted scatterplot smoothing” – the process of producing a smooth curve that fits the data points in a scatterplot.
To perform lowess smoothing in R we can use the lowess() function, which uses the following syntax:
lowess(x, y, f = 2/3)
where:
- x: A numerical vector of x values.
- y: A numerical vector of y values.
- f: The value for the smoother span. This gives the proportion of points in the plot which influence the smooth at each value. Larger values result in more smoothness.
The following step-by-step example shows how to perform lowess smoothing for a given dataset in R.
Step 1: Create the Data
First, let’s create a fake dataset:
df <- data.frame(x=c(1, 1, 2, 2, 3, 4, 6, 6, 7, 8, 10, 11, 11, 12, 13, 14), y=c(4, 7, 9, 10, 14, 15, 19, 16, 17, 21, 22, 34, 44, 40, 43, 45))
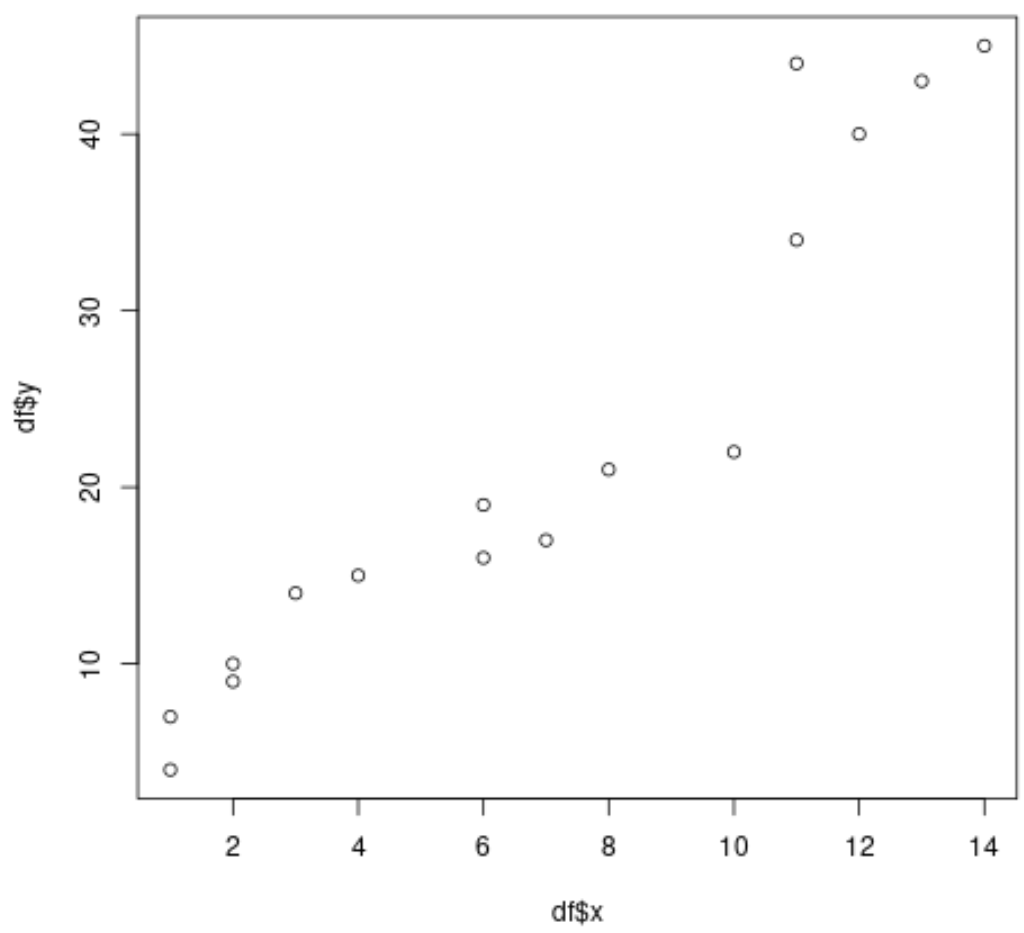
Step 2: Plot the Data
Next, let’s plot the x and y values from the dataset:
plot(df$x, df$y)
Step 3: Plot the Lowess Curve
Next, let’s plot the lowess smoothing curve over the points in the scatterplot:
#create scatterplot plot(df$x, df$y) #add lowess smoothing curve to plot lines(lowess(df$x, df$y), col='red')

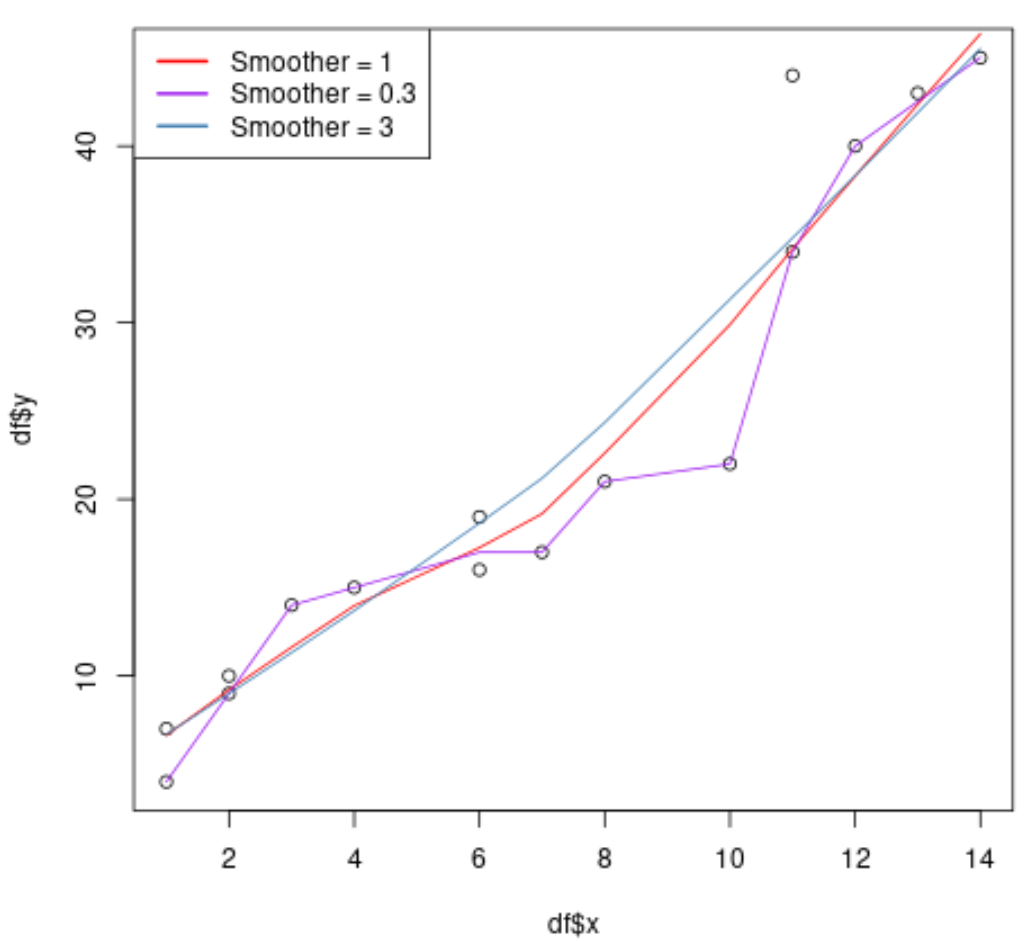
Step 4: Adjust the Smoother Span (Optional)
We can also adjust the f argument in the lowess() function to increase or decrease the value used for the smoother span.
Note that the larger the value we provide, the smoother the lowess curve will be.
#create scatterplot plot(df$x, df$y) #add lowess smoothing curves lines(lowess(df$x, df$y), col='red') lines(lowess(df$x, df$y, f=0.3), col='purple') lines(lowess(df$x, df$y, f=3), col='steelblue') #add legend to plot legend('topleft', col = c('red', 'purple', 'steelblue'), lwd = 2, c('Smoother = 1', 'Smoother = 0.3', 'Smoother = 3'))