Table of Contents
The Rayleigh distribution is a continuous probability distribution that is widely used in statistics and probability. It is used to model the magnitude of random quantities, such as the strength of a signal or the distance between two points. This distribution is characterized by a single parameter, known as the scale parameter, which determines the spread of the data. The Rayleigh distribution is significant in statistics and probability because it has a wide range of applications in various fields, including engineering, physics, and finance. It is also used in reliability analysis to model the time until failure of a system. In addition, the Rayleigh distribution is closely related to other important distributions, such as the Gaussian and the chi-square distributions, making it a useful tool for statistical modeling and inference.
An Introduction to the Rayleigh Distribution
The Rayleigh distribution is a continuous probability distribution used to model that can only take on values equal to or greater than zero.
It has the following probability density function:
f(x; σ) = (x/σ2)e-x2/(2σ2)
where σ is the scale parameter of the distribution.
Properties of the Rayleigh Distribution
The Rayleigh Distribution has the following properties:
- Mean: σ√π/2
- Variance: ((4-π)/2)σ2
- Mode: σ
Since π has a known numerical value, we can simplify the properties as follows:
- Mean: 1.253σ
- Variance: 0.429σ2
- Mode: σ
Visualizing the Rayleigh Distribution
The following chart shows the shape of the Rayleigh distribution when it takes on different values for the scale parameter:
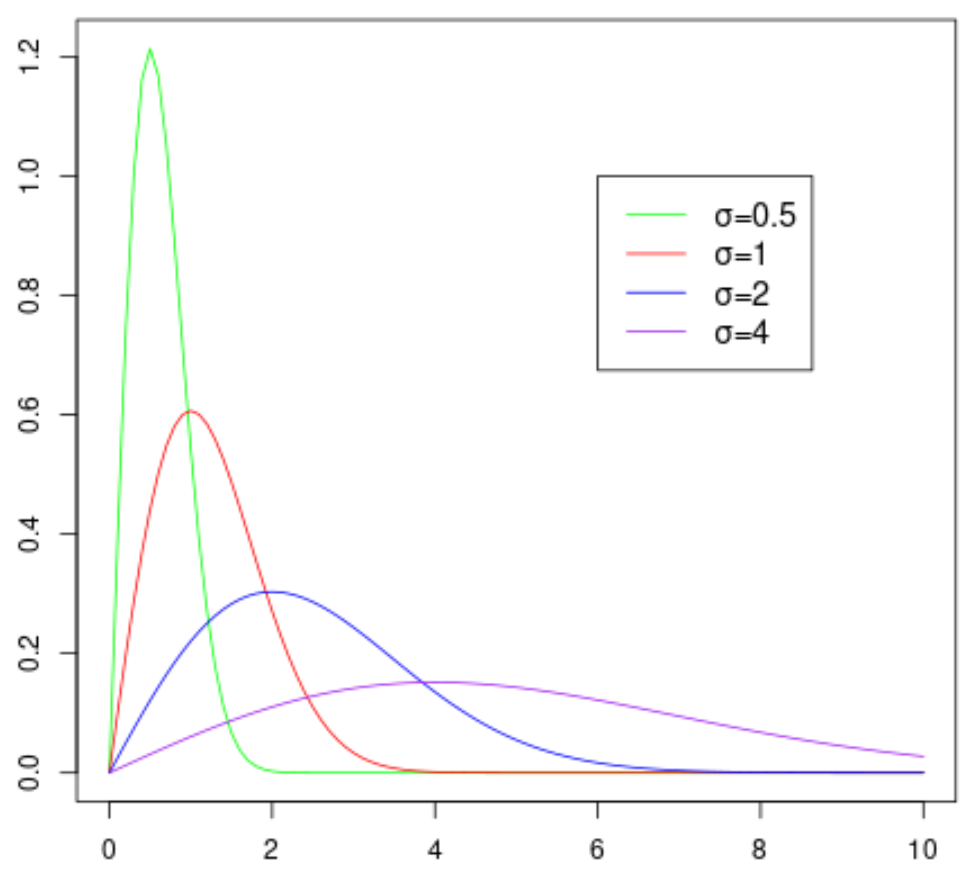
Note that the larger the value for the scale parameter σ, the wider the distribution becomes.
Bonus: For those who are curious, we used the following R code to generate the chart above:
#load VGAM package library(VGAM) #create density plots curve(drayleigh(x, scale = 0.5), from=0, to=10, col='green') curve(drayleigh(x, scale = 1), from=0, to=10, col='red', add=TRUE) curve(drayleigh(x, scale = 2), from=0, to=10, col='blue', add=TRUE) curve(drayleigh(x, scale = 4), from=0, to=10, col='purple', add=TRUE) #add legend legend(6, 1, legend=c("σ=0.5", "σ=1", "σ=2", "σ=4"), col=c("green", "red", "blue", "purple"), lty=1, cex=1.2)
Relation to Other Distributions
The Rayleigh distribution has the following relationship with other probability distributions:
2. The Rayleigh distribution is a special case of the Weibull distribution with a shape parameter of k = 2.
3. The Rayleigh distribution with scale parameter σ is equal to the Rice distribution with Rice(0, σ).
Applications
In practice, the Rayleigh distribution is used in a variety of applications including:
1. The Rayleigh distribution is used to model wave behavior in the ocean, including the time it takes waves to crest and the max height reached by waves.
2. The Rayleigh distribution is used to model the behavior of background data in magnetic resonance imaging, more commonly known as MRI.
3. The Rayleigh distribution is used in the field of nutrition to model the relationship between nutrient levels and nutrient response in both humans and animals.
Additional Resources
The following tutorials provide additional information about other distributions in statistics:
