Table of Contents
Odds ratio is a measure of association between two variables and is calculated by dividing the odds of an event happening in one group by the odds of that event happening in another group. Relative risk is a measure of how much more likely an event is to occur in one group compared to another and is calculated by dividing the probability of an event happening in one group by the probability of that event happening in another group.
Two terms that students often confuse in statistics are odds ratio and relative risk.
We often use these two metrics when performing an analysis on a 2-by-2 table, which takes on the following format:
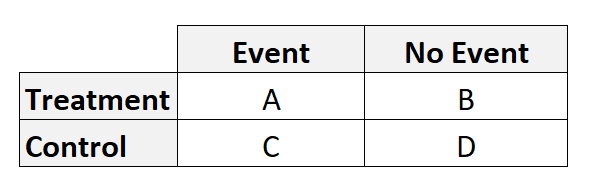
The odds ratio tells us the ratio of the odds of an event occurring in a treatment group to the odds of an event occurring in a control group. It is calculated as:
Odds ratio = (A*D) / (B*C)
The relative risk tells us the ratio of the probability of an event occurring in a treatment group to the probability of an event occurring in a control group. It is calculated as:
Relative risk = [A/(A+B)] / [C/(C+D)]
In short, here’s the difference:
- An odds ratio is a ratio of two odds.
- Relative risk is a ratio of two probabilities.
The following example shows how to calculate and interpret an odds ratio and relative risk in a real-life situation.
Example: Calculating Odds Ratio and Relative Risk
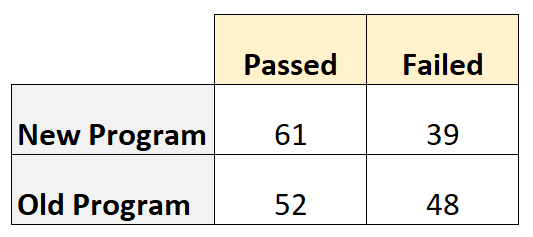
Suppose 100 basketball players use a new training program and 100 players use an old training program. At the end of the program we test each player to see if they pass a certain skills test.
The following table shows the number of players who passed and failed, based on the program they used:
The odds ratio is calculated as:
- Odds ratio = (A*D) / (B*C)
- Odds ratio = (61*48) / (39*52)
- Odds ratio = 1.44
We would interpret this to mean that the odds that a player passes the test by using the new program are 1.44 times the odds that a player passes the test by using the old program.
The relative risk is calculated as
- Relative risk = [A/(A+B)] / [C/(C+D)]
- Relative risk = [61/(61+39)] / [52/(52+48)]
- Relative risk = 1.17
We would interpret this to mean that the ratio of the probability of a player passing the test using the new program compared to the old program is 1.17.
Since this value is greater than 1, it tells us that the probability of passing is higher under the new program compared to the old program.
We can also see this by directly computing the probability that a player passes under each program:
Probability of passing under new program = 61 / 100 = 61%
Probability of passing under old program = 52 / 100 = 52%
Taking the ratio of these probabilities, we can calculate the relative risk as 61% / 52% = 1.17.
Note that the odds ratio and relative risk are both greater than 1, which tells us that the chances of experiencing some event (e.g. passing the skills test) is greater in the treatment group compared to the control group.
The odds ratio and relative risk give us similar information, but we interpret each value in slightly different ways.
In particular:
- The odds ratio tells us that the odds of passing the skills test is higher under the new program.
- The relative risk tells us that the probability of passing the skills test is higher under the new program.
Using either metric, we can easily see that the new program is better than the old program.
The following tutorials offer additional information on odds ratios and relative risk:
