Table of Contents
A good Z-score is a numerical value that indicates how a person’s score compares to the scores of other people in a group. A Z-score above 1.0 is generally considered to be a good score, as it is higher than the average score for that group. Z-scores can be used to compare scores from different tests or to track a person’s performance over time.
A z-score tells us how many standard deviations away a value is from the mean. We use the following formula to calculate a z-score:
Z-Score = (x – μ) / σ
where:
- x: A raw data value
- μ: The mean of the dataset
- σ: The standard deviation of the dataset
For example:
- If a value has a z-score equal to 0, then the value is equal to the mean.
- If a value has a z-score equal to -1.3, then the value is 1.3 standard deviations below the mean.
- If a value has a z-score equal to 2.2, then the value is 2.2 standard deviations above the mean.
One question that students often have is: What is a good z-score?
The answer: A z-score simply tells us how many standard deviations a given value is from the mean, so it can’t be “good” or “bad.”
However, we can determine what percentage of values fall below a certain z-score in a distribution by using a , which gives us an idea of where a certain value lies relative to all other values in the distribution.
For example, suppose the score that Mike receives on an exam has a z-score of -1.22. We can locate the value of -1.22 in the z table:

We find that the value in the z table is 0.1112. This means that Mike only scored higher than 11.12% of all students who took the exam.
In this scenario, a z-score of -1.22 might be considered “bad” since Mike only scored higher than a small percentage of students.
Conversely, suppose the score that Tom receives has a z-score of 1.43. We can locate this value in the z table as well:
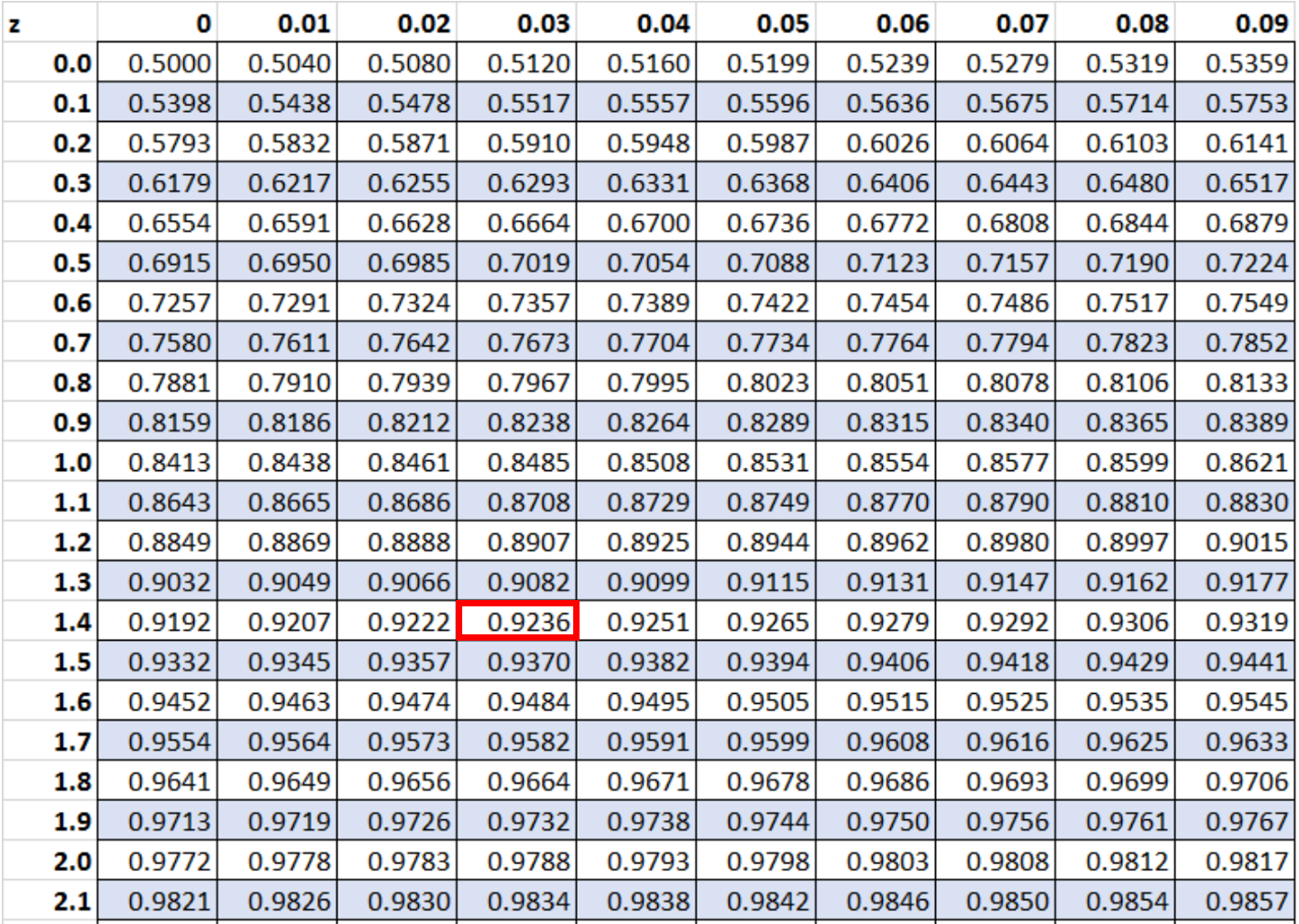
We find that the value in the z table is 0.9236. This means that Mike scored higher than 92.36% of students who took the exam.
In this scenario, a z-score of 1.43 might be considered “good” since Mike scored higher than so many other students.
How to Classify “Good” Z-Scores
To determine whether or not a certain z-score is “good” depends largely on the situation.
For example, when measuring exam scores of students, one university may consider a z-score that corresponds to the 80th percentile or higher as “good.”
According to the , the z-score that corresponds to the 80th percentile is 0.8416. Thus, any student who receives a z-score greater than or equal to 0.8416 would be considered a “good” z-score.
However, suppose another university considers a z-score that corresponds to the 90th percentile or higher as “good.”
According to the , the z-score that corresponds to the 90th percentile is 1.2816. Thus, any student who receives a z-score greater than or equal to 1.2816 would be considered a “good” z-score.
The decision of what is a “good” or “bad” z-score is subjective, but we can always make the following statements:
- A z-score equal to zero represents a value equal to the mean.
- A z-score greater than zero represents a value greater than the mean.
- A z-score less than zero represents a value less than the mean.
- It’s helpful to convert a z-score to a percentile to determine what percentage of values the value is greater than in a distribution.
It’s up to an individual company, association, school, etc. to determine whether a “good” z-score should be one that represents the 70th, 80th, 90th, 95th percentile, etc.
