Table of Contents
An intervening variable is a factor that affects the relationship between two variables in a specific situation or context. It acts as a mediator between the independent and dependent variables, influencing the strength or direction of their association. Intervening variables can either enhance or weaken the relationship between the two variables and are often used in research to understand the underlying mechanisms or processes that drive a particular outcome. They are important to consider in order to accurately interpret the results of a study and make meaningful conclusions.
What is an Intervening Variable?
An intervening variable is a variable that affects the relationship between an and a .
Often this type of variable can appear when researchers are studying the relationship between two variables and don’t realize that another variable is actually intervening in the relationship.
Intervening variables pop up in many different research situations. Here are a few examples.
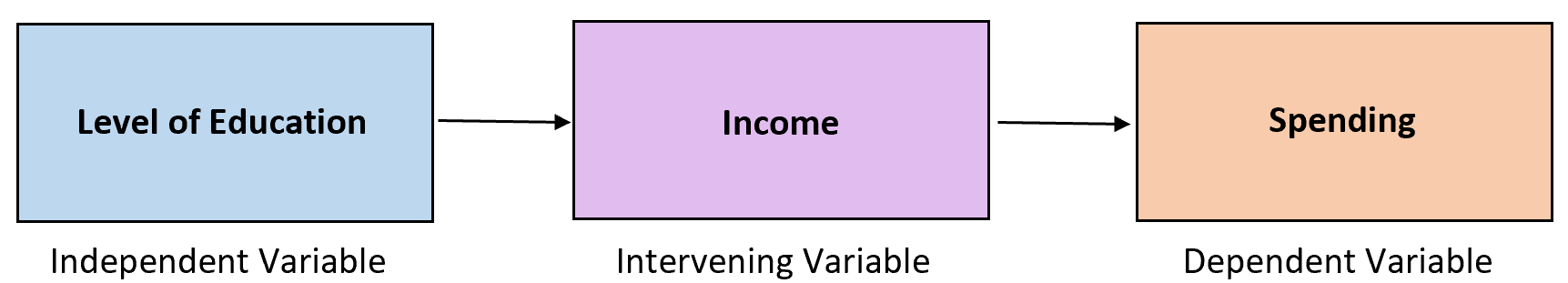
Example 1: Education & Spending
Researchers may be interested in the relationship between education (the independent variable) and yearly spending (the dependent variable).
After collecting data on education level and yearly spending for 1,000 individuals, they find that there is a strong positive correlation between the two variables. In particular, they find that individuals who have more education tend to spend more.
However, without realizing it the researchers have failed to take note of the intervening variableincome. It turns out that individuals who have higher levels of education tend to hold higher-paying jobs, which means they naturally have more money to spend.
Example 2: Poverty and Life Expectancy
Researchers may be interested in the relationship between poverty (the independent variable) and life expectancy (the dependent variable).
After collecting data on poverty and life expectancy for 10,000 individuals, they find that there is a strong correlation between the two variables. In particular, they find that more impoverished individuals tend to have lower life expectancies.
However, without realizing it the researchers have failed to take note of the intervening variablehealthcare. It turns out that individuals who are more impoverished have less reliable access to healthcare, which naturally means that they have lower life expectancies.

Example 3: Hours Spent Practicing & Points per Game
A sports researcher may be interested in the relationship between hours spent practicing by players (the independent variable) and their average points per game (the dependent variable).
After collecting data on hours spent practicing and points per game for 100 players, they find that there is a strong correlation between the two variables. In particular, they find that players who practice more tend to average more points per game.

The Importance of Identifying Intervening Variables
Understanding intervening variables can often help researchers clarify the relationship between an independent and dependent variable because the intervening variables are often the true variable that explains variations in the dependent variable.
In many cases, the independent variable causes changes in some intervening variable, which then causes changes in the dependent variable under study.
By identifying the intervening variable, it becomes easier to understand the actual relationship between the independent and dependent variable.
Technical Note: Intervening variables are sometimes also referred to as mediating variables or intermediary variables.
Additional Resources
What are Extraneous Variables?
What are Concomitant Variables?
What is Reverse Causation?
What is a Confounding Variable?

