Table of Contents
A p-value is a statistical measure used to determine the significance of a result in a hypothesis test. It represents the probability of obtaining a test statistic at least as extreme as the observed value, assuming the null hypothesis is true. There are three commonly used methods to calculate a p-value from a t statistic:
1. Look up in a t-distribution table: This method involves using a pre-calculated table that provides the critical values for different degrees of freedom and levels of significance. The t statistic is compared to the critical value and the p-value is determined based on the level of significance chosen.
2. Use a statistical software or calculator: With the advancements in technology, statistical software and calculators have made it easier to calculate p-values from t statistics. These tools use complex algorithms to determine the p-value based on the provided t statistic, degrees of freedom, and the chosen level of significance.
3. Use a formula: The final method involves using a formula to calculate the p-value directly. This method requires knowledge of the t distribution and its properties. The formula involves computing the area under the t-distribution curve from the t statistic to the right or left, depending on the alternative hypothesis, and converting it to a probability.
In summary, these three methods provide different ways to determine the p-value from a t statistic, giving researchers and statisticians flexibility in choosing the most suitable approach for their analysis.
Three Ways to Find a P-Value from a t Statistic
A is a formal statistical test we use to reject or fail to reject a statistical hypothesis.
Whether we conduct a hypothesis test for a mean, a proportion, a difference in means, or a difference in proportions, we often end up with a t statistic for our test.
Once we have a t statistic, we can then find a corresponding p-value that we can use to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis of our test.
This tutorial explains three different ways to find a p-value from a t statistic.
Three Ways to Find a P-Value from a t Statistic
In each of the following examples, we’ll find the p-value for a right-tailed test with a t statistic of 1.441 and 13 degrees of freedom.
Technique 1: t Score to P Value Calculator
The first way to find a p-value from a t statistic is to use an online calculator like the . We can simply enter the value for t and the degrees of freedom, then select “one-tailed”, then click the “Calculate” button:

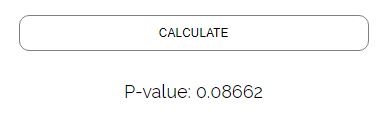
The corresponding p-value is 0.08662.
Technique 2: t Distribution Table
Another way to find the p-value for a given t statistic is to use the.
Using the table, look up the row that has degrees of freedom (DF) = 13, then find the values that 1.441 lies between. It turns out to be 1.35 and 1.771. Next, look up at the top of the table for “one-tail” and you’ll notice that these values correspond with 0.1 and 0.05. This tells us that the corresponding p-value is somewhere between 0.05 and 0.1.

Notice the drawback of using the t distribution table: it does not tell us the exact p-value; it only gives us a range of values.
Technique 3: TI-83 or TI-84 Calculator
On your calculator, click 2ND VARS (to get to DISTR), scroll down, and click the tcdf function. The syntax to use this function to find the p-value for a right-tailed test is as follows:
tcdf(smaller value, larger value, degrees of freedom)
Since we are conducting a right-tailed test, we can use 1.441 as the smaller value, 9999 as the larger value, and 13 as the degrees of freedom:
tcdf(1.441, 9999, 13)
This returns a value of 0.08662, which matches the p-value that we got from the online calculator.
