Table of Contents
A right skewed histogram is a type of histogram in which the majority of the data values are concentrated on the left side of the graph, with a gradual decrease in frequency as you move to the right side. Examples of data sets that may result in a right skewed histogram include age, income, test scores, and body mass index. In these cases, the majority of the values will be concentrated on the lower end of the range, with fewer and fewer values as the range increases.
A histogram is a type of chart that allows us to visualize the distribution of values in a dataset.
We say that a histogram is right skewed if it has a “tail” on the right side of the distribution:
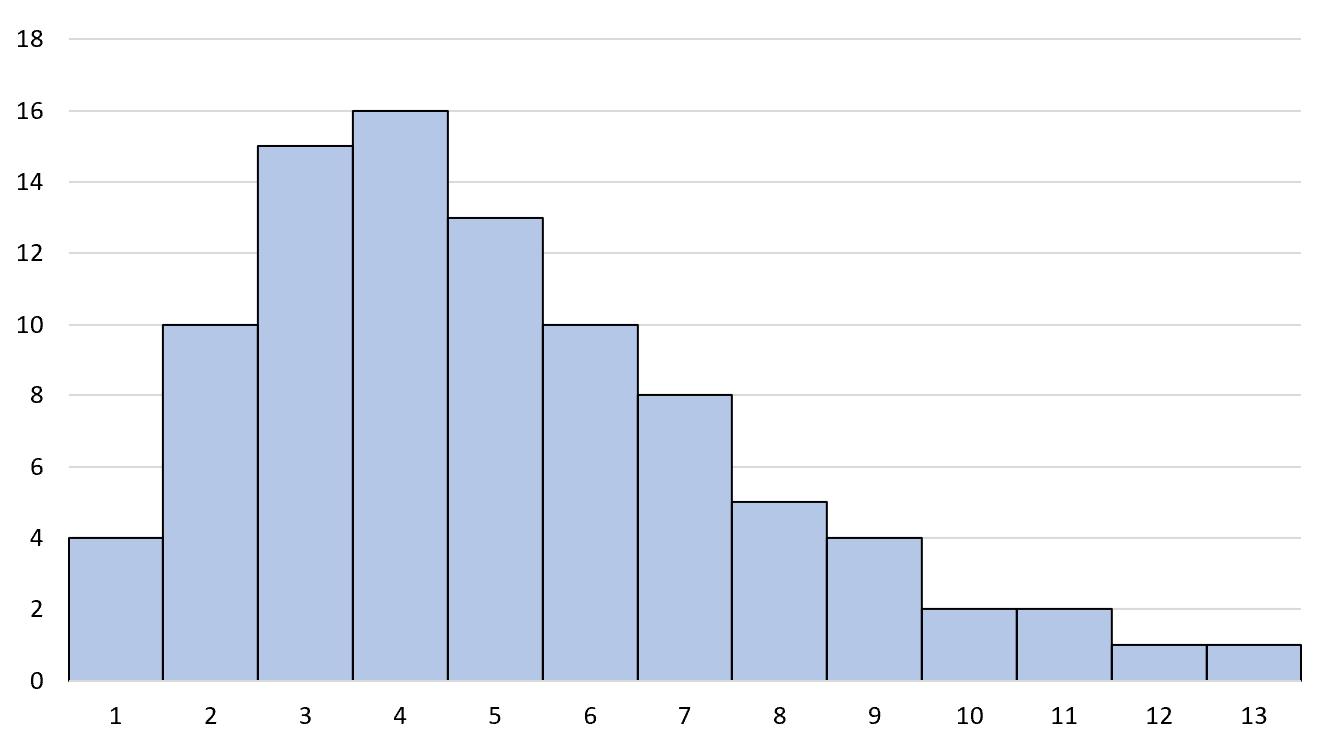
Note: Sometimes a right skewed histogram is also referred to as a positively skewed histogram.
A right skewed histogram has the following two properties:
1. The peak of the distribution is on the left side.
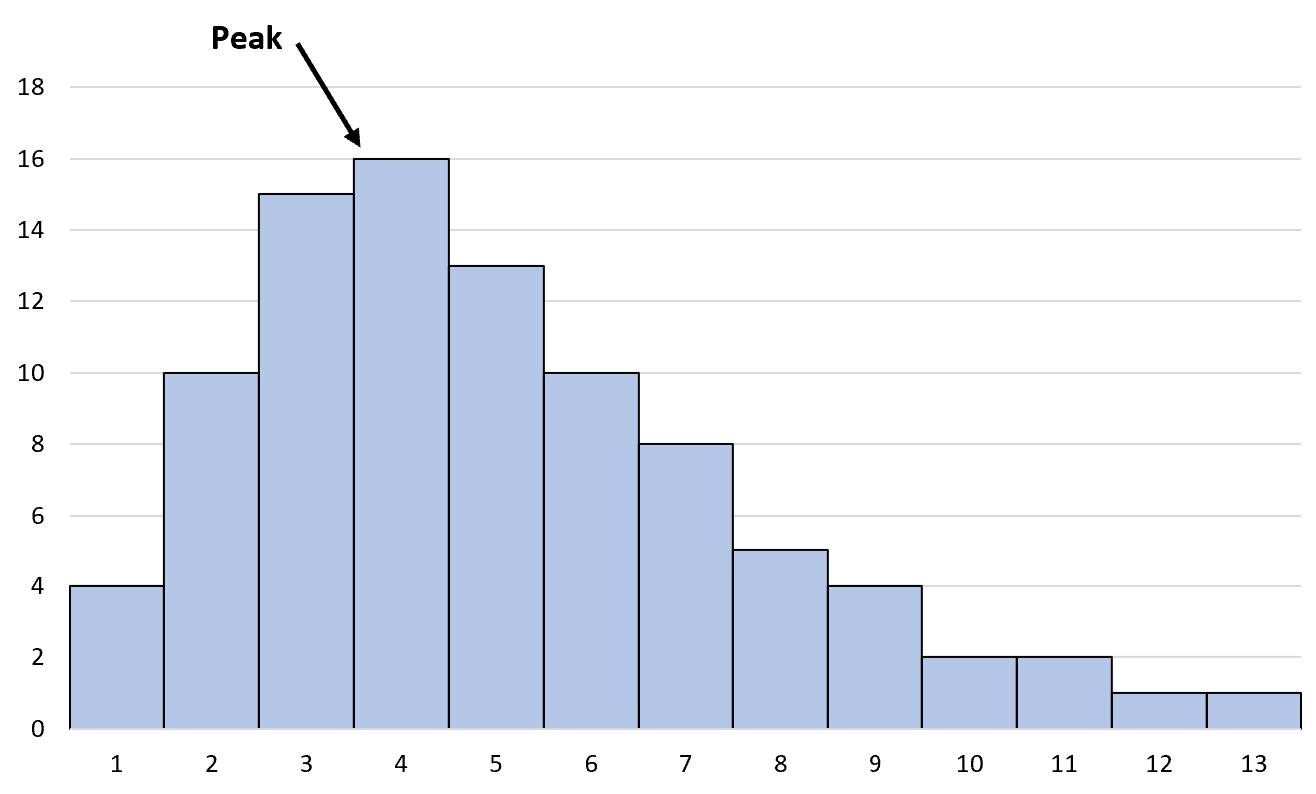
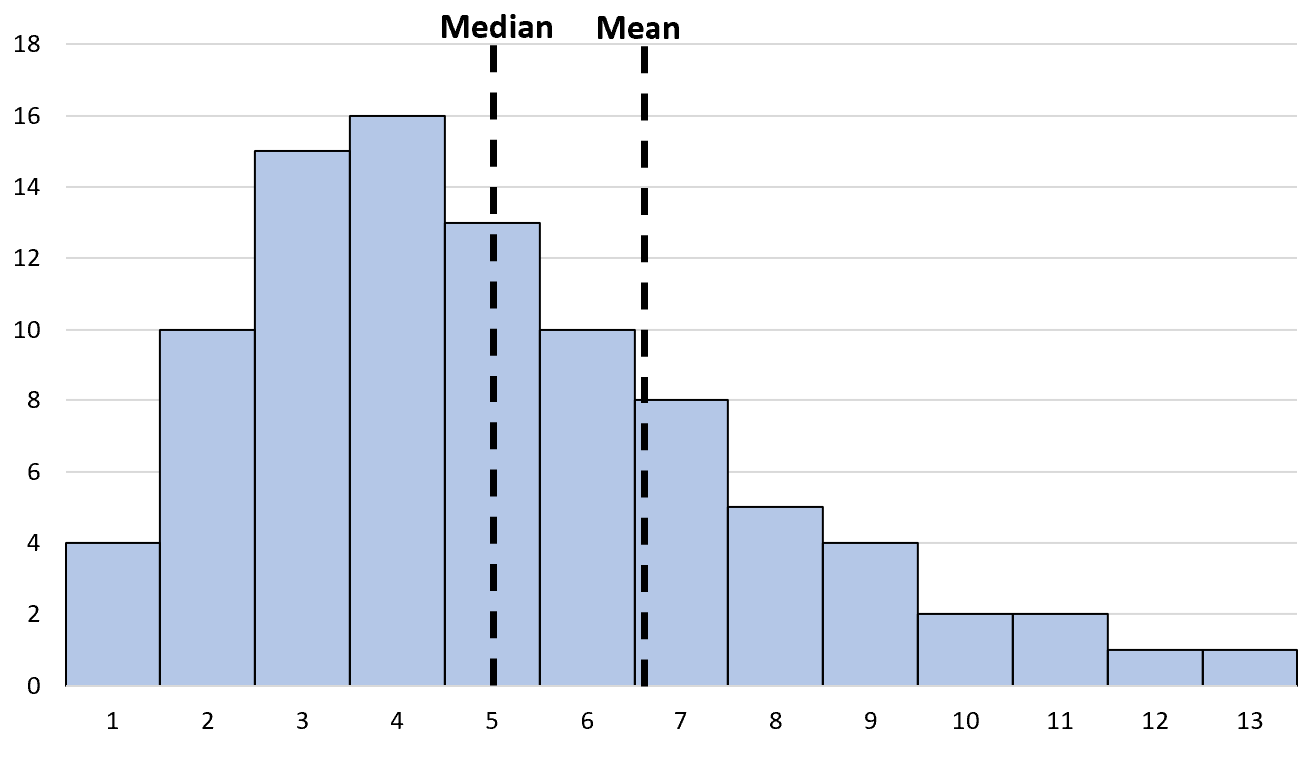
2. The mean is greater than the median.
What Causes a Histogram to Be Right Skewed?
A histogram is typically right skewed when there is a limit on the minimum possible value but no limit on the maximum possible value.
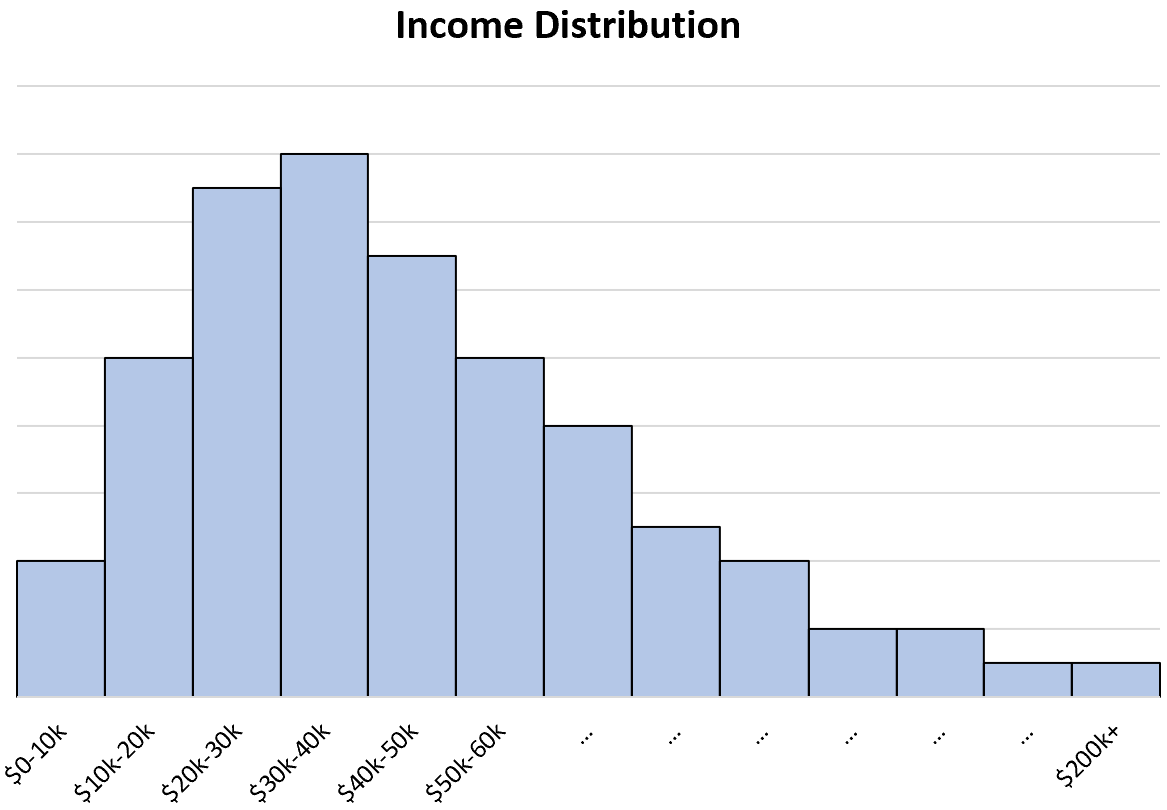
The most obvious real-life example of a right skewed histogram would be the distribution of income in a country.
The minimum income that a person could earn is zero dollars while there is no maximum income that a person could earn.
In general, most individuals might earn around $40k per year but there will be a few outliers that earn several millions of dollars per year.
When we create a histogram to visualize the distribution of income, it will naturally be right skewed:
Why is the Mean Greater than the Median in a Right Skewed Histogram?
As a simple example, suppose we have the following dataset that contains the income of 10 individuals:
Dataset 1: $30k, $35k, $35k, $40k, $50k, $55k, $55k, $70k, $90k, $110k
Here are the mean and median values of this dataset:
- Mean: $57k
- Median: $52.5k
Now suppose we have another dataset that contains the exact same incomes except the last value is now $2.5 million:
Dataset 2: $30k, $35k, $35k, $40k, $50k, $55k, $55k, $70k, $90k, $2.5 million
Here are the mean and median values of this dataset:
- Mean: $296k
- Median: $52.5k
This last outlier value causes the mean income to increase significantly.
And if we plot this distribution, it would be a right skewed histogram with the $2.5 million value located on the right “tail” of the histogram.
The Difference Between Right Skewed & Left Skewed Histograms
The opposite of a right skewed histogram is a left skewed histogram.
This is a type of histogram that has a “tail” on the left side of the distribution:

This type of histogram has the following properties:
1. The peak of the distribution is on the right side.
2. The mean is less than the median.
Notice that these are the exact opposite properties of a right skewed histogram.
Read more about left skewed histograms in .
The following tutorials provide additional information about histograms:
