Table of Contents
Negatively skewed distributions are those in which the majority of the data values are clustered at the higher end of the range and there is a longer tail of data values that extend to the left. Examples of negatively skewed distributions include income distribution, exam scores, housing prices, age, and height.
Skewness is a way to describe the of a distribution.
A distribution is negatively skewed if it has a “tail” on the left side of the distribution:
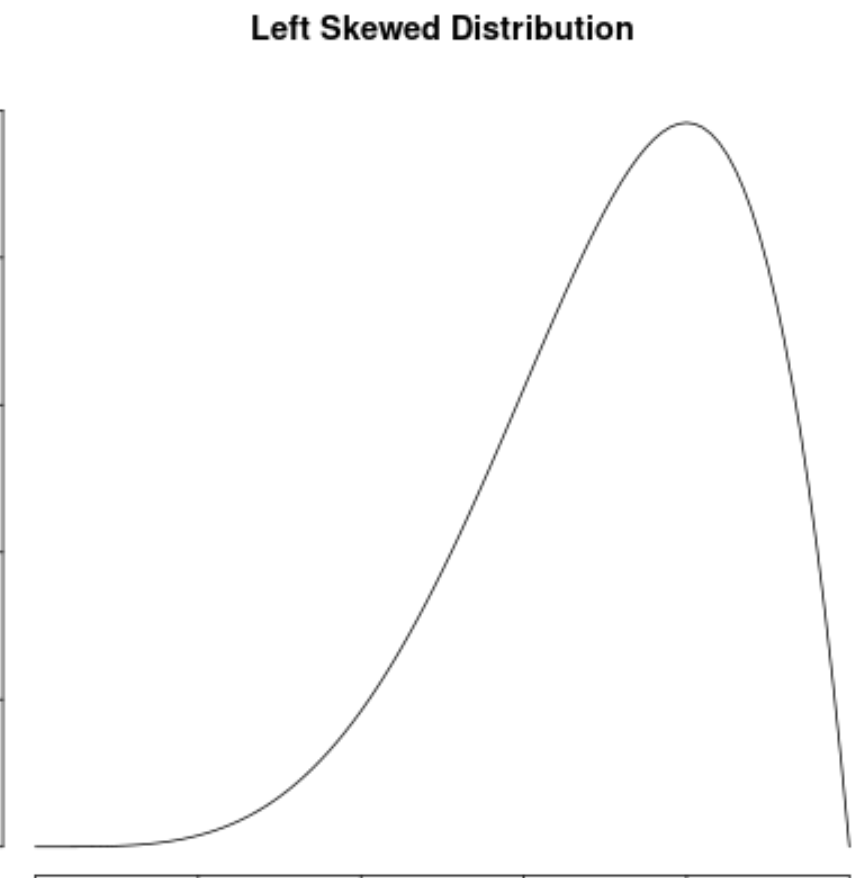
Note: Sometimes negatively skewed distributions are also called “left skewed” distributions.
In this article we share 5 examples of negatively skewed distributions in the real world.
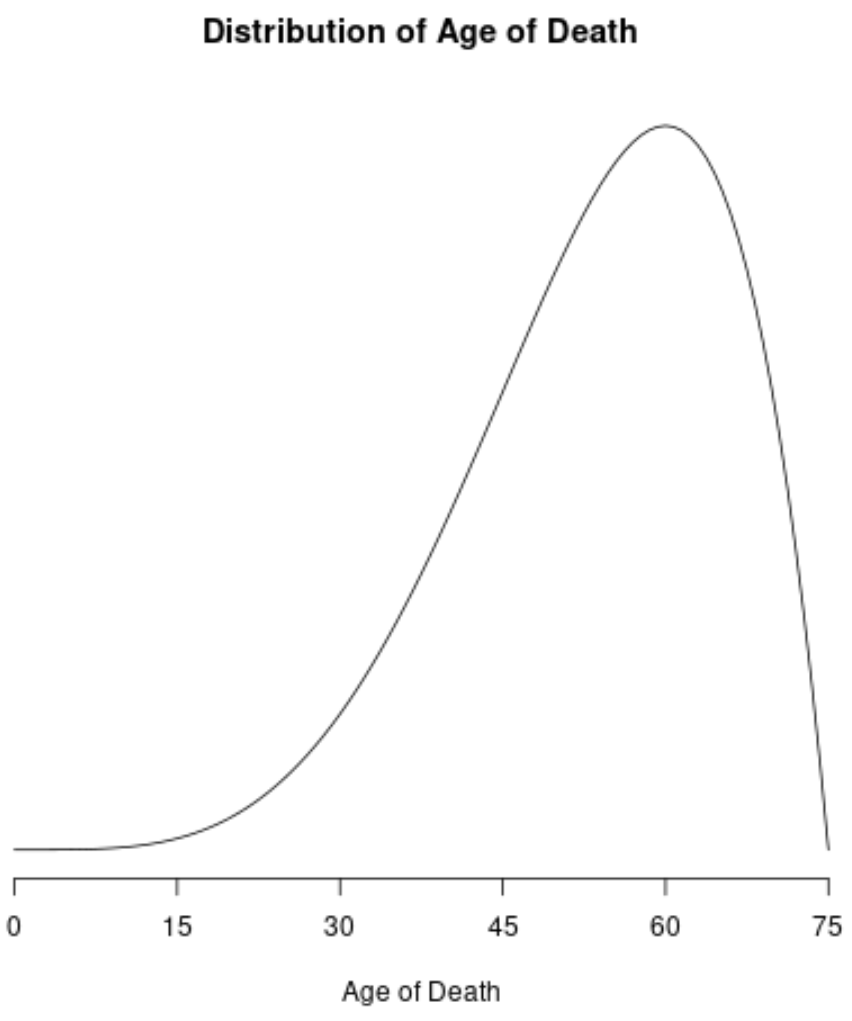
Example 1: Distribution of Age of Deaths
The distribution of the age of deaths in most populations is negatively skewed. Most people live to be between 70 and 80 years old, with fewer and fewer living less than this age.
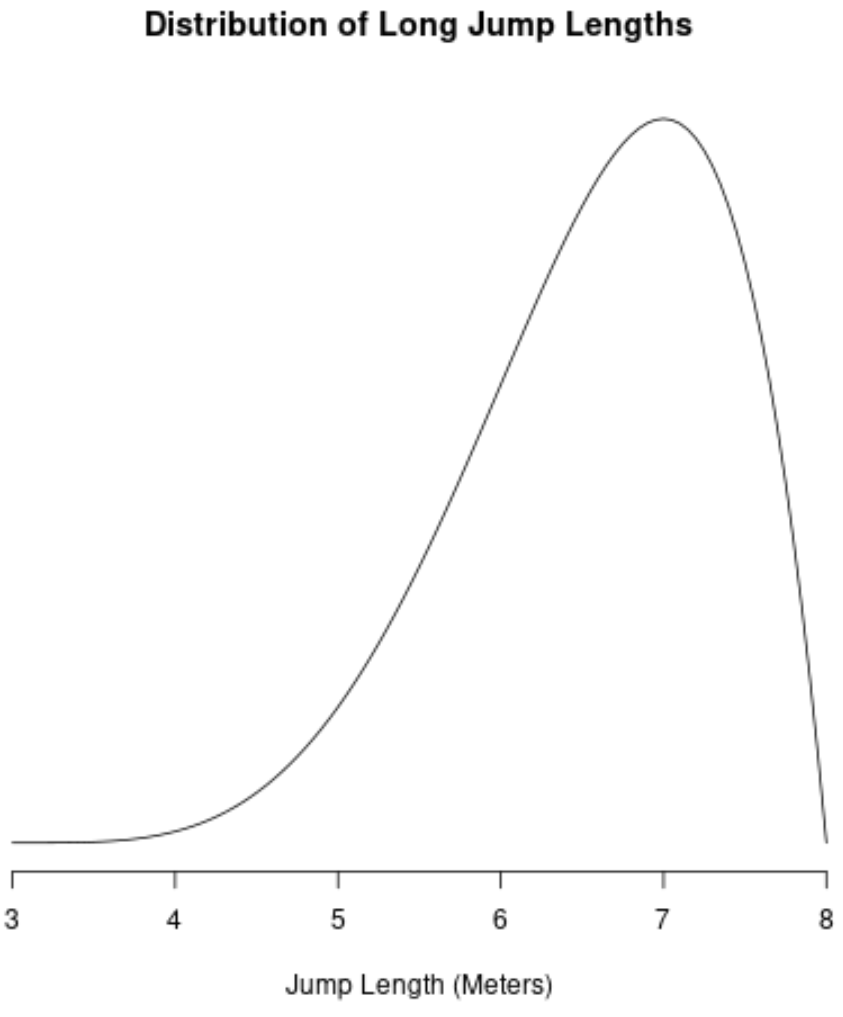
Example 2: Distribution of Olympic Long Jumps
In most years, the distribution of long jump lengths for competitors in the Olympics is negatively skewed because most competitors land a jump around 7.5-8 meters, with a few landing a jump of just 5-6 meters.
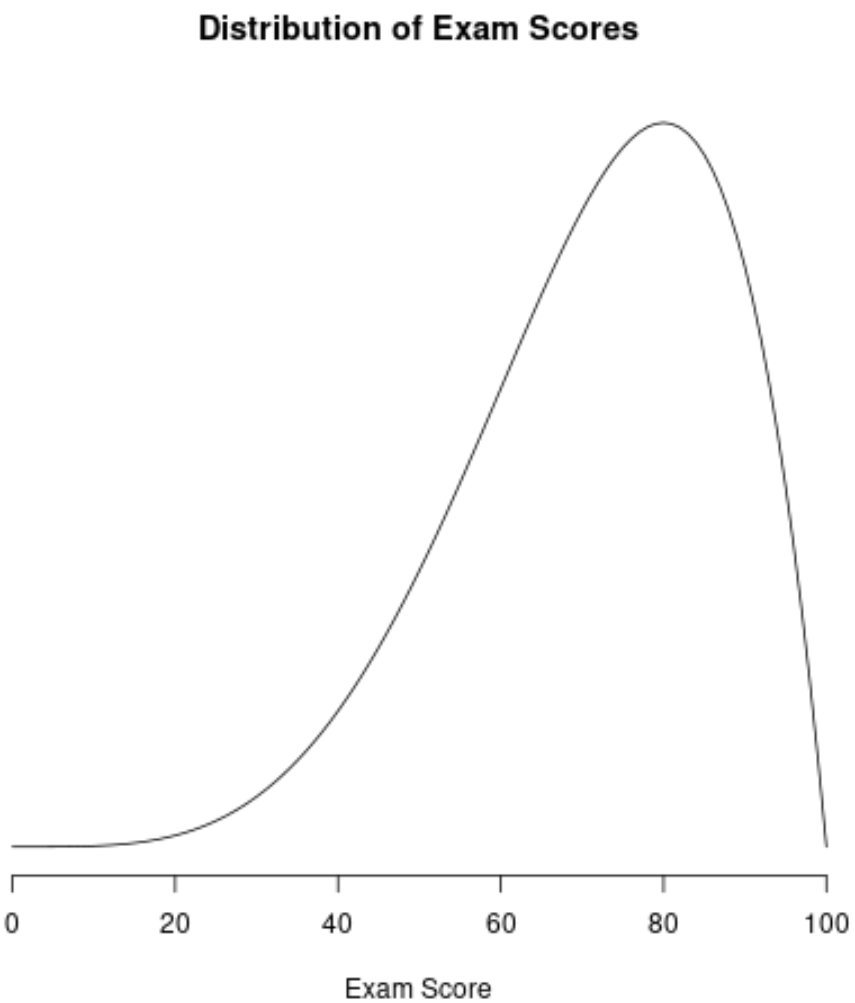
Example 3: Distribution of Scores on Easy Exams
The distribution of scores on easy exams or tests tend to be negatively skewed because most students score very high, while a few students score much lower than the average.
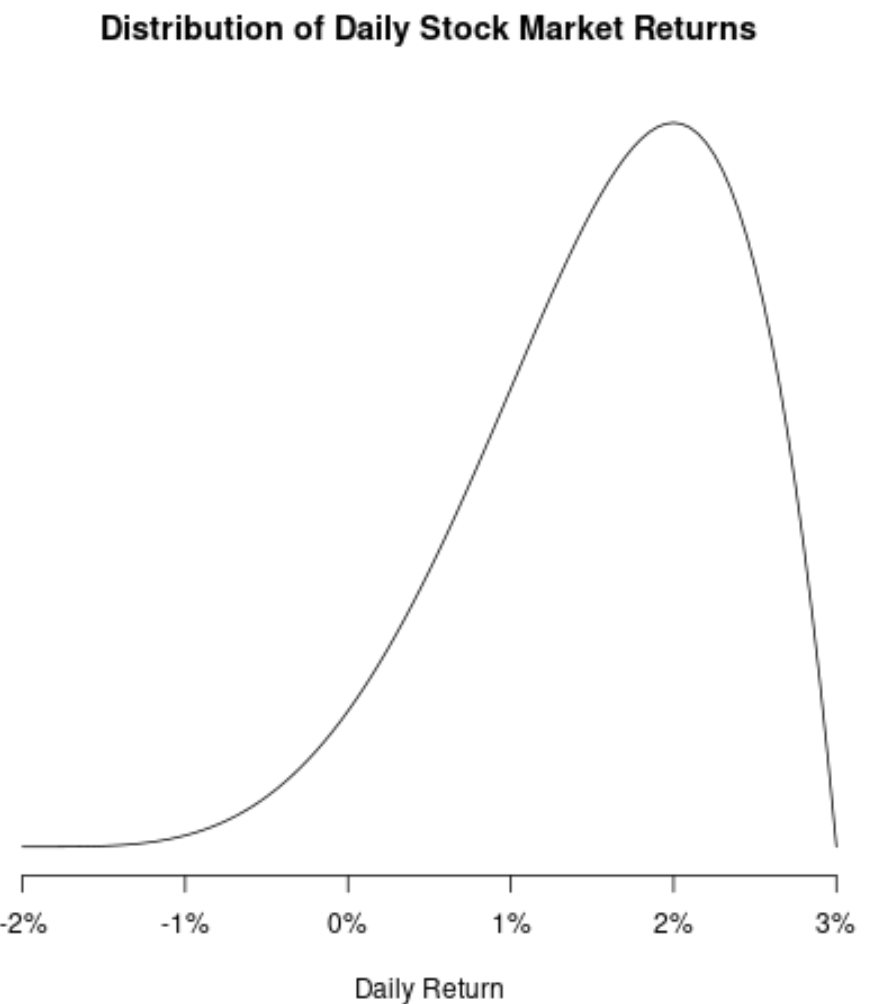
Example 4: Distribution of Daily Stock Market Returns
The distribution of daily stock market returns is negatively skewed because the stock market delivers a slightly positive return on most days, but occasionally returns huge negative returns on a few days.
Example 5: Distribution of GPA Values
The distribution of GPA among college students is negatively skewed since most students have a GPA between 2 and 4 with a few having a GPA much lower.

