Table of Contents
The rnorm() function in R generates random numbers from a normal distribution, while the runif() function generates random numbers from a uniform distribution. The normal distribution has a bell-shaped curve when plotted, while the uniform distribution has a flat line when plotted. The mean, median, and standard deviation of the normal distribution can be specified, whereas these parameters cannot be specified in the uniform distribution. The random numbers generated from both functions can be used in statistical analysis.
You can use the rnorm() and runif() functions to generate random values in R.
Here’s the difference between the two functions:
The rnorm(n, mean, sd) function is used to generate n random values from a normal distribution with a specific mean and standard deviation.
The runif(n, min, max) function is used to generate n random values from a uniform distribution with a specific minimum and maximum value.
The following examples show how to use each function in practice.
Example 1: How to Use rnorm() in R
The following code shows how to use the rnorm() function to generate 100 random values from a with a mean of 10 and a standard deviation of 2:
#make this example reproducible
set.seed(0)
#create vector of 100 random values from normal distribution
random_values <- rnorm(n=100, mean=10, sd=2)
#view first six values
head(random_values)
[1] 12.525909 9.347533 12.659599 12.544859 10.829283 6.920100
We can also use the hist() function to create a histogram to visualize the distribution of random values we just generated:
#create histogram to visualize distribution of values
hist(random_values)
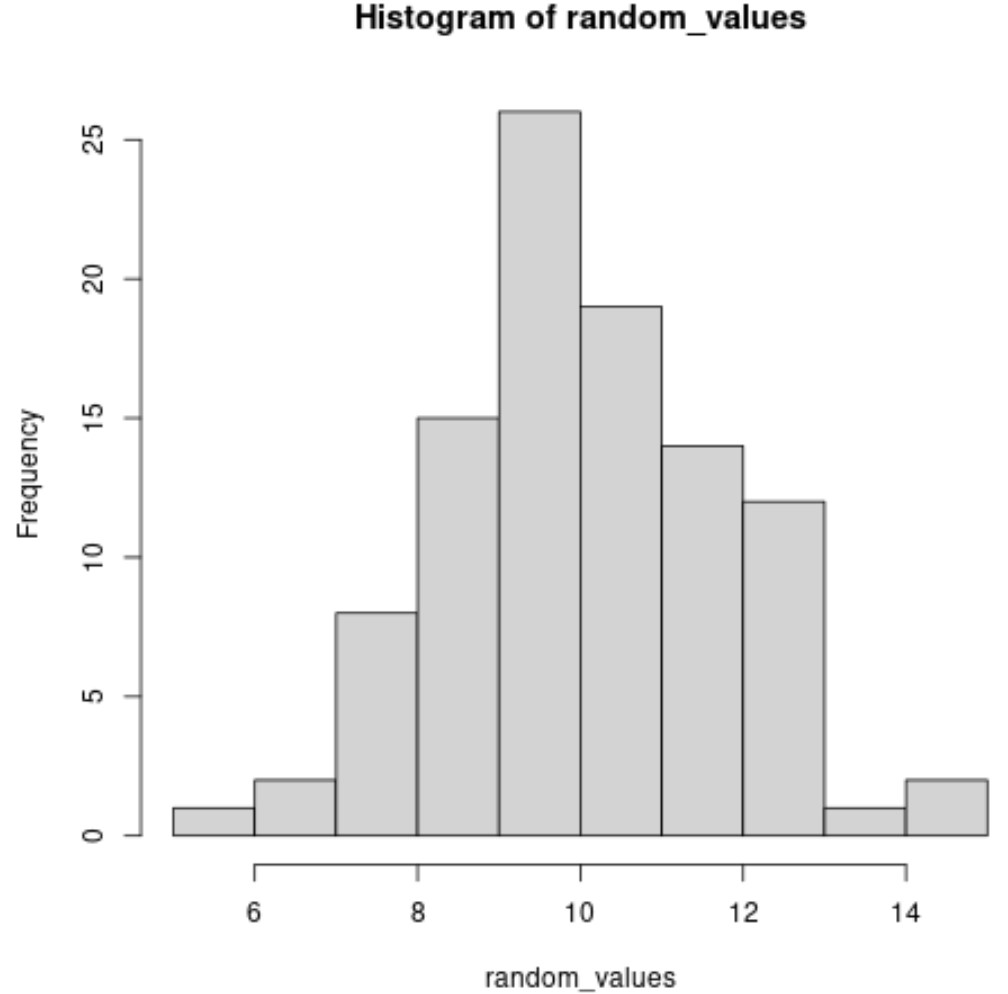
The result is a histogram that displays the distribution of the 100 values from the normal distribution.
Notice that the histogram has a bell shape and the mean is located around 10, the exact value that we specified for the mean of the distribution.
Example 2: How to Use runif() in R
The following code shows how to use the runif() function to generate 100 random values from a with a minimum value of 5 and a maximum value of 25:
#make this example reproducible
set.seed(0)
#create vector of 100 random values from uniform distribution
random_values <- runif(n=100, min=5, max=25)
#view first six values
head(random_values)
[1] 22.933944 10.310173 12.442478 16.457067 23.164156 9.033639
We can also use the hist() function to create a histogram to visualize the distribution of random values we just generated:
#create histogram to visualize distribution of values
hist(random_values)
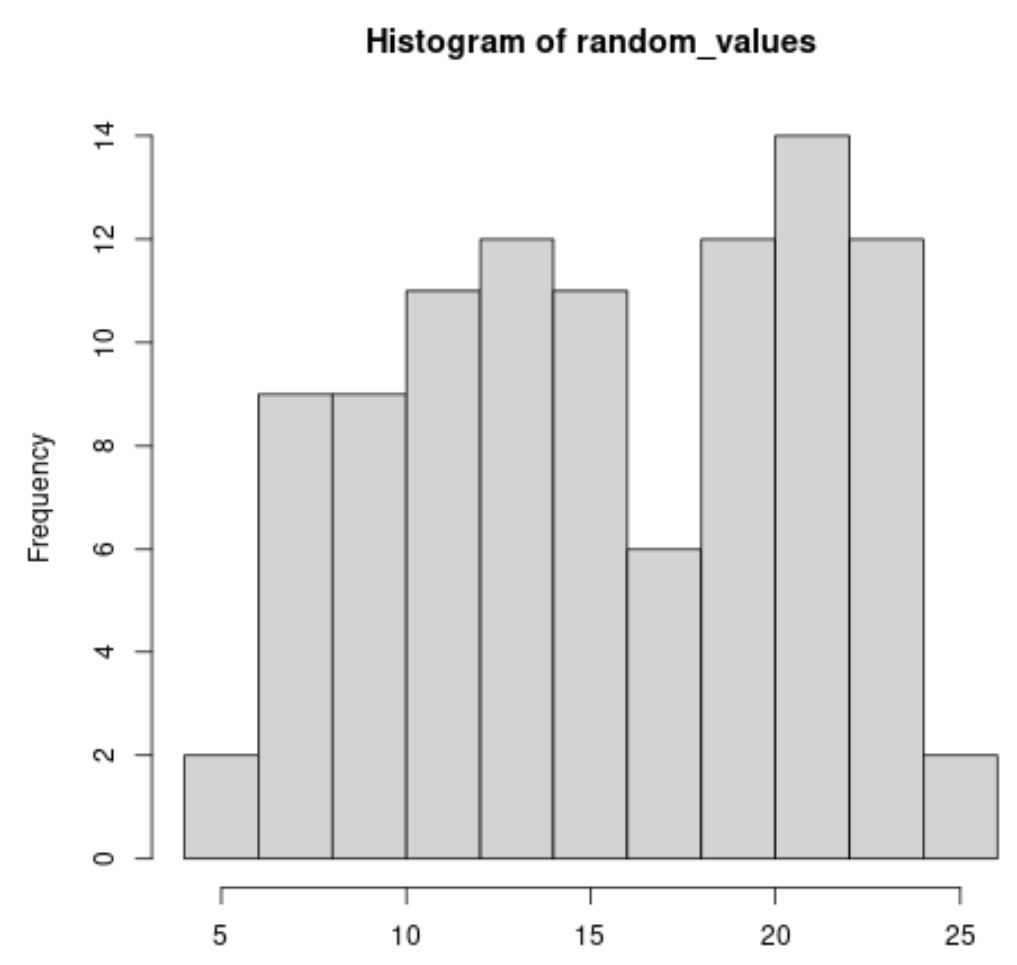
The result is a histogram that displays the distribution of the 100 values from the uniform distribution.
Notice that the histogram ranges from 5 to 25, which represent the minimum and maximum values that we specified in the runif() function.
The following tutorials explain how to perform other common tasks in R:
