Table of Contents
To calculate a p-value from a Z-score by hand, first you need to determine the area to the right of the Z-score on a standard normal distribution table, which will represent the probability of the area under the curve. Then, subtract this area from one to get the p-value. Finally, multiply the p-value by two to account for the area to the left of the Z-score, and you will have your final answer.
In most cases, when you find a z-score in statistics you can simply use a to find the corresponding p-value.
However, sometimes you may be forced to calculate a p-value from a z-score by hand. In this case, you need to use the values found in a .
The following examples show how to calculate a p-value from a z-score by hand using a z-table.
Example 1: Find P-Value for a Left-Tailed Test
Suppose we conduct a left-tailed hypothesis test and get a z-score of -1.22. What is the p-value that corresponds to this z-score?
To find the p-value, we can simply locate the value -1.22 in the :
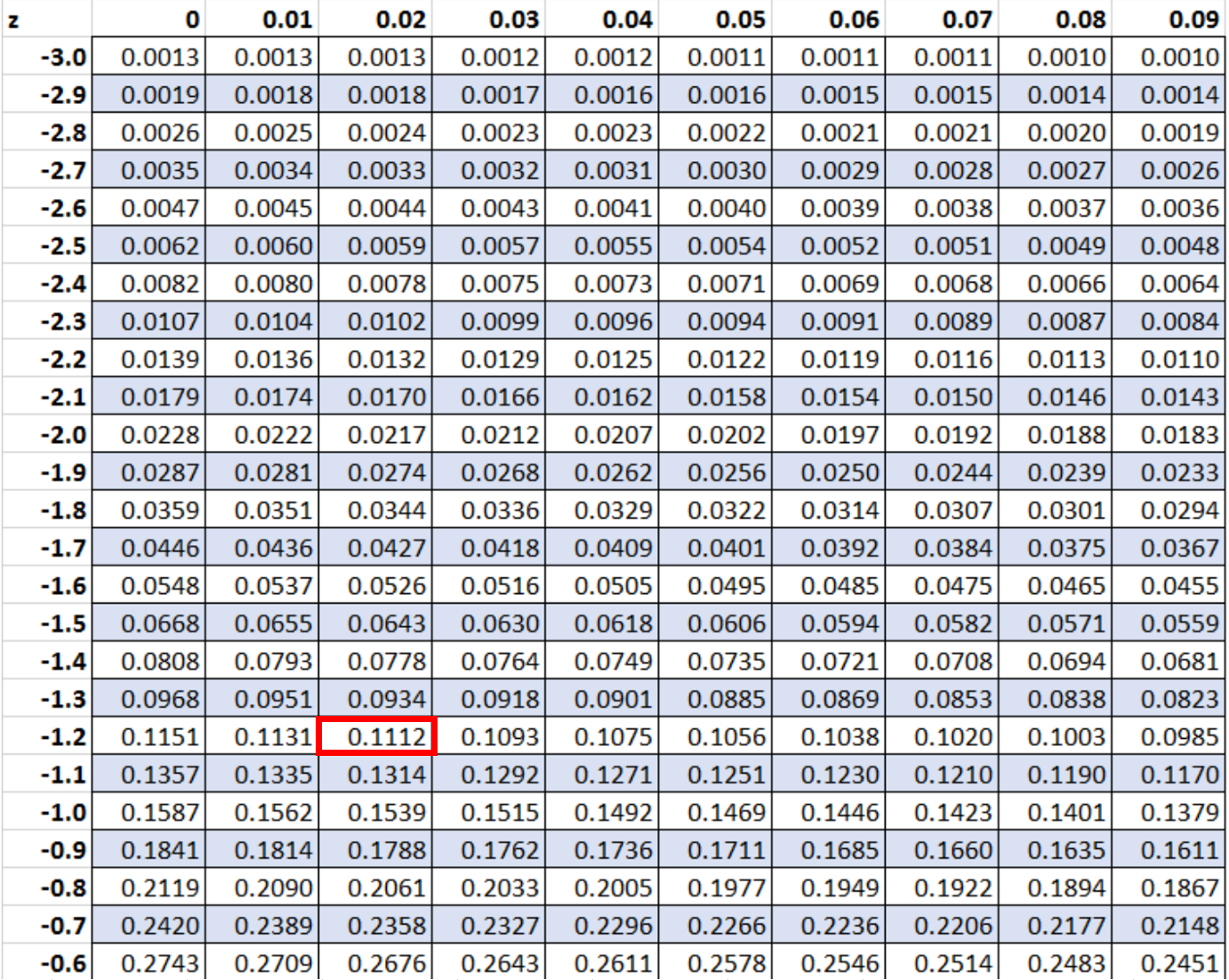
The p-value that corresponds to a z-score of -1.22 is 0.1112.
Example 2: Find P-Value for a Right-Tailed Test
Suppose we conduct a right-tailed hypothesis test and get a z-score of 1.43. What is the p-value that corresponds to this z-score?
To find the p-value, we can first locate the value 1.43 in the :
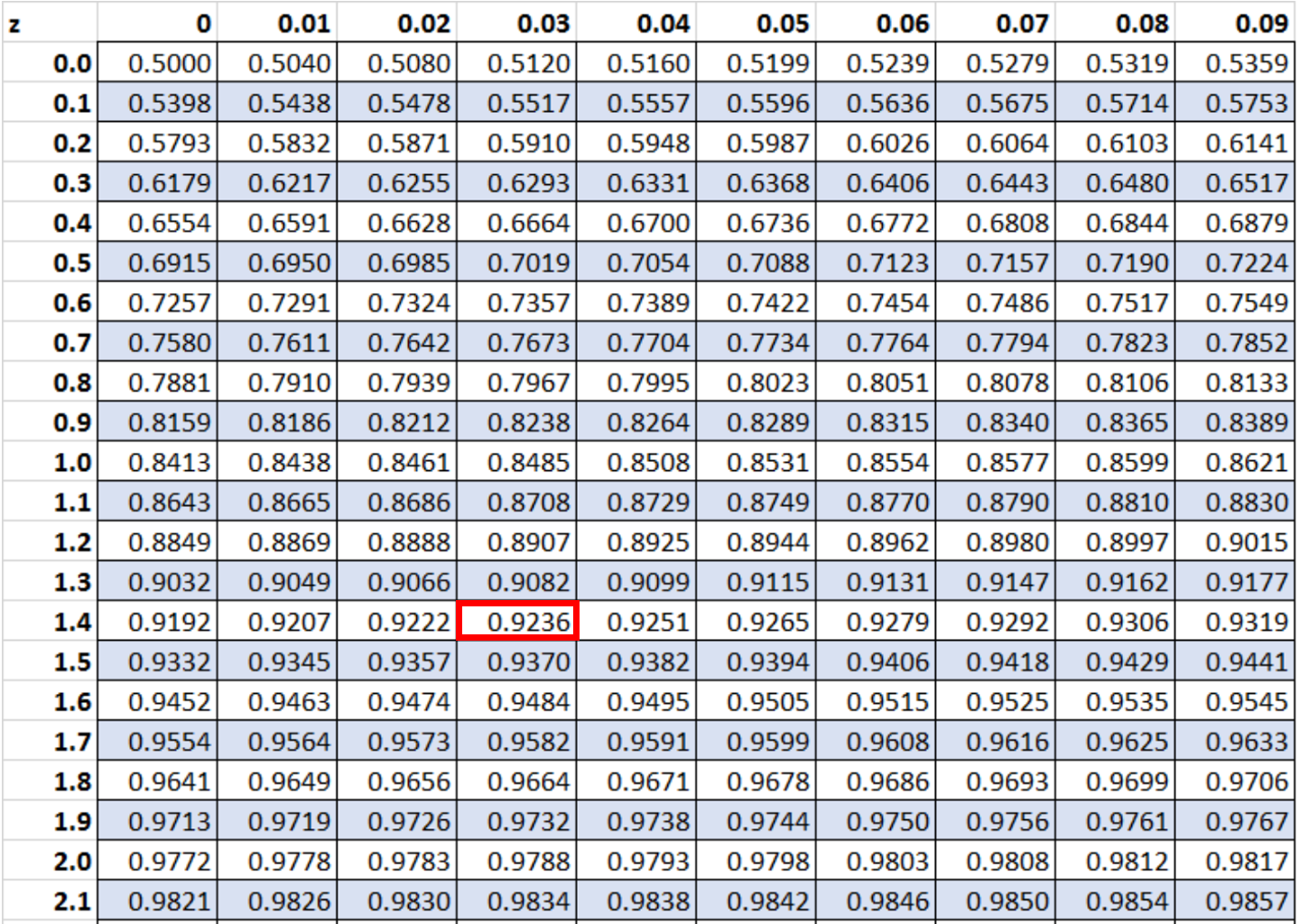
Since we’re conducting a right-tailed test, we can then subtract this value from 1.
So our final p-value is: 1 – 0.9236 = 0.0764.
Example 3: Find P-Value for a Two-Tailed Test
Suppose we conduct a two-tailed hypothesis test and get a z-score of -0.84. What is the p-value that corresponds to this z-score?
To find the p-value, we can first locate the value -0.84 in the :
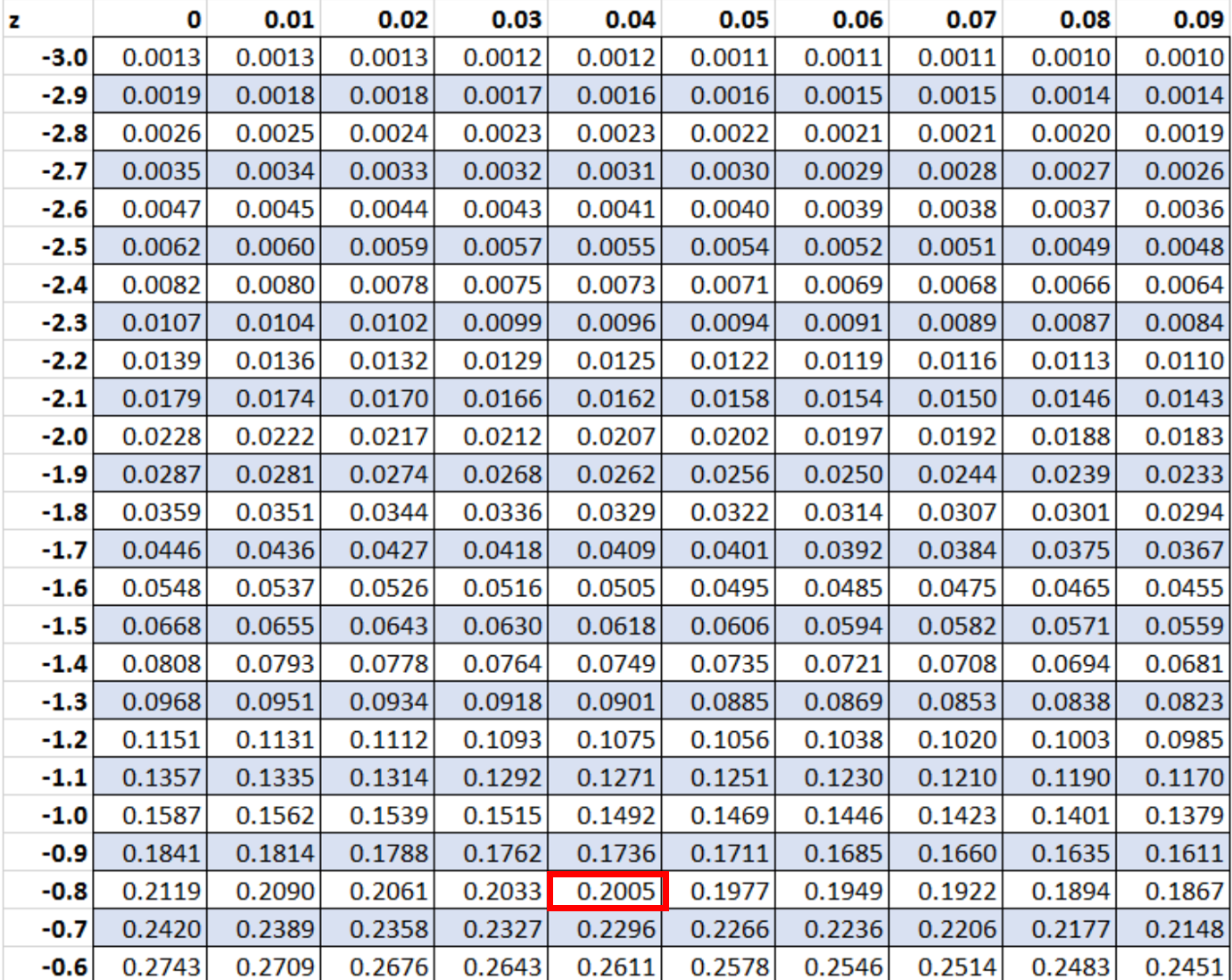
Since we’re conducting a two-tailed test, we can then multiply this value by 2.
So our final p-value is: 0.2005 * 2 = 0.401.
The following tutorials explain how to calculate p-values from z-scores using various statistical software:
