Table of Contents
VBA’s VLOOKUP function allows you to search for a value in a table of data and return a value from a different column in the same row. To use VLOOKUP in VBA, you will need to have a table of data with the search key value in the leftmost column and the corresponding values in the other columns. You can then use the VLOOKUP function in a VBA subroutine to search for and return the value you need. For example, you could use the VLOOKUP function to search for a person’s name in the leftmost column of a table and return their phone number from a different column.
You can use the following basic syntax to perform a VLOOKUP using VBA:
Sub Vlookup()
Range("F2").Value = WorksheetFunction.Vlookup(Range("E2"), Range("A2:C11"),3,False)
End Sub
This particular example looks up the value in cell E2 in the range A2:C11 and finds the corresponding value in the third column of the range and then assigns the result to cell F2.
Note: The last argument of False specifies that we want an exact match.
The following example shows how to use this syntax in practice.
Example: How to Use VLOOKUP in VBA
Suppose we have the following dataset in Excel that contains information about various basketball players:
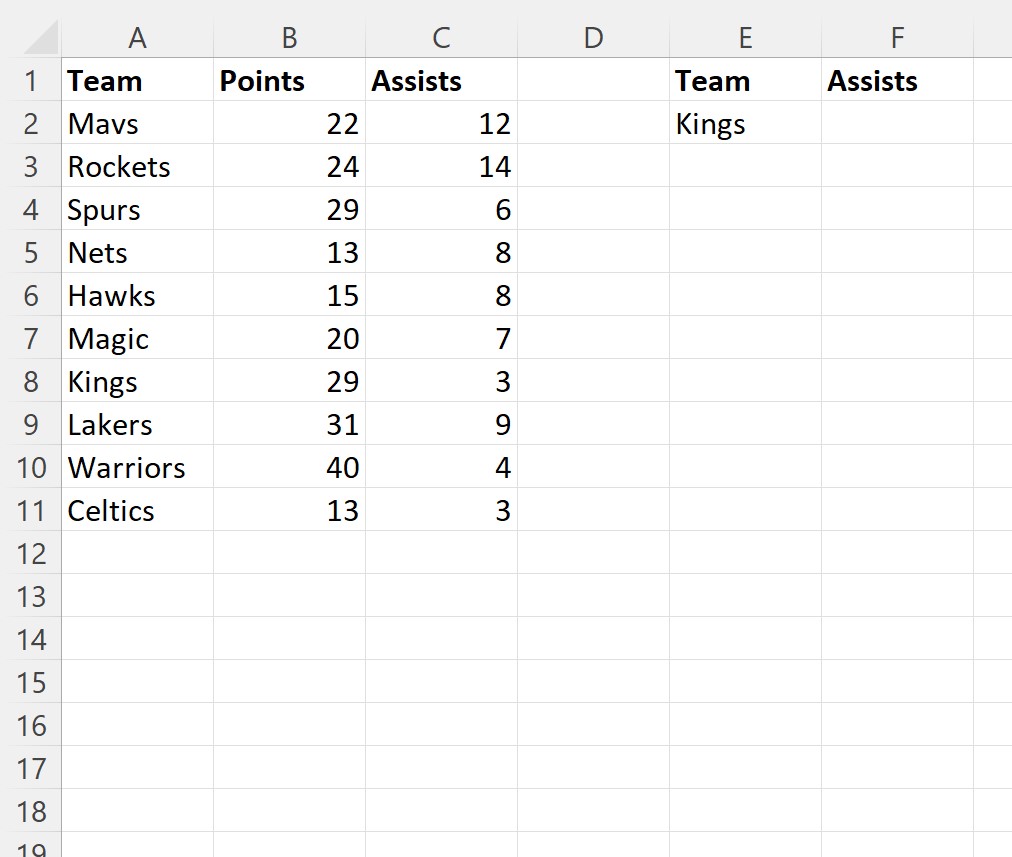
Suppose we would like to look up the team name “Kings” in the dataset and return the corresponding value in the assists column.
We can create the following macro to do so:
Sub Vlookup()
Range("F2").Value = WorksheetFunction.Vlookup(Range("E2"), Range("A2:C11"),3,False)
End Sub
When we run this macro, we receive the following output:
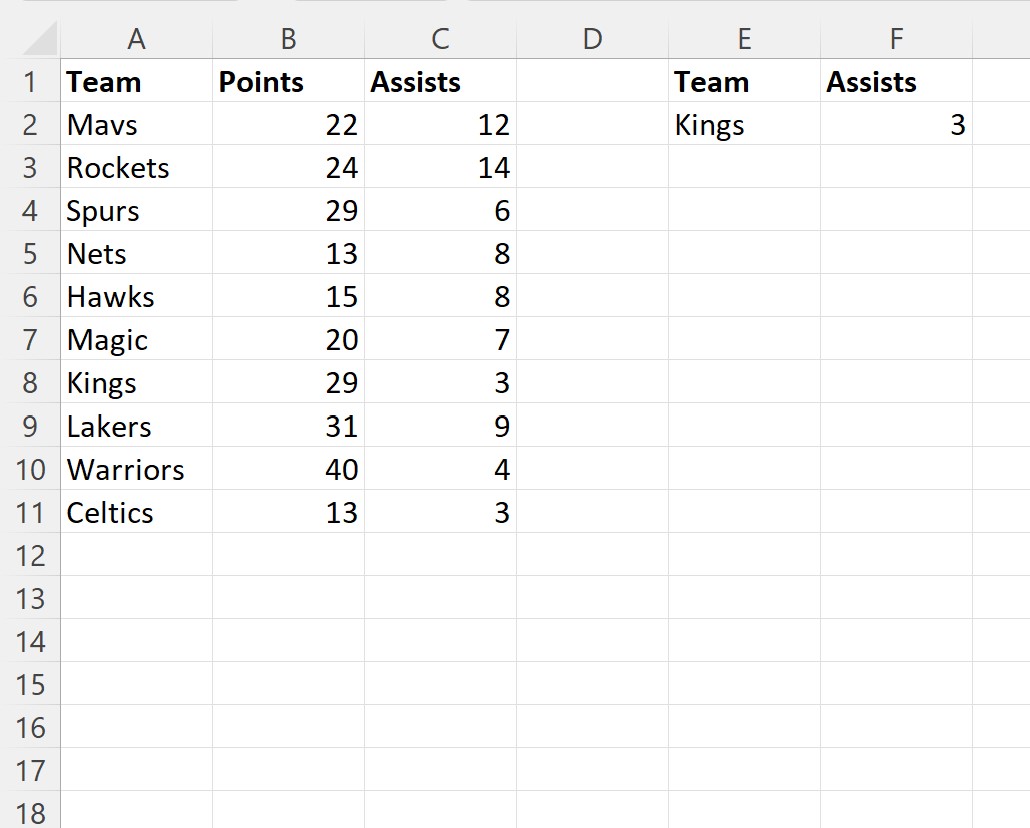
The macro correctly returns a value of 3 assists for the Kings.
If we change the name of the team in cell E2 and then run the macro again, it will correctly find the assists value for the new team name.
For example, suppose we change the team name to “Warriors” and run the macro again:
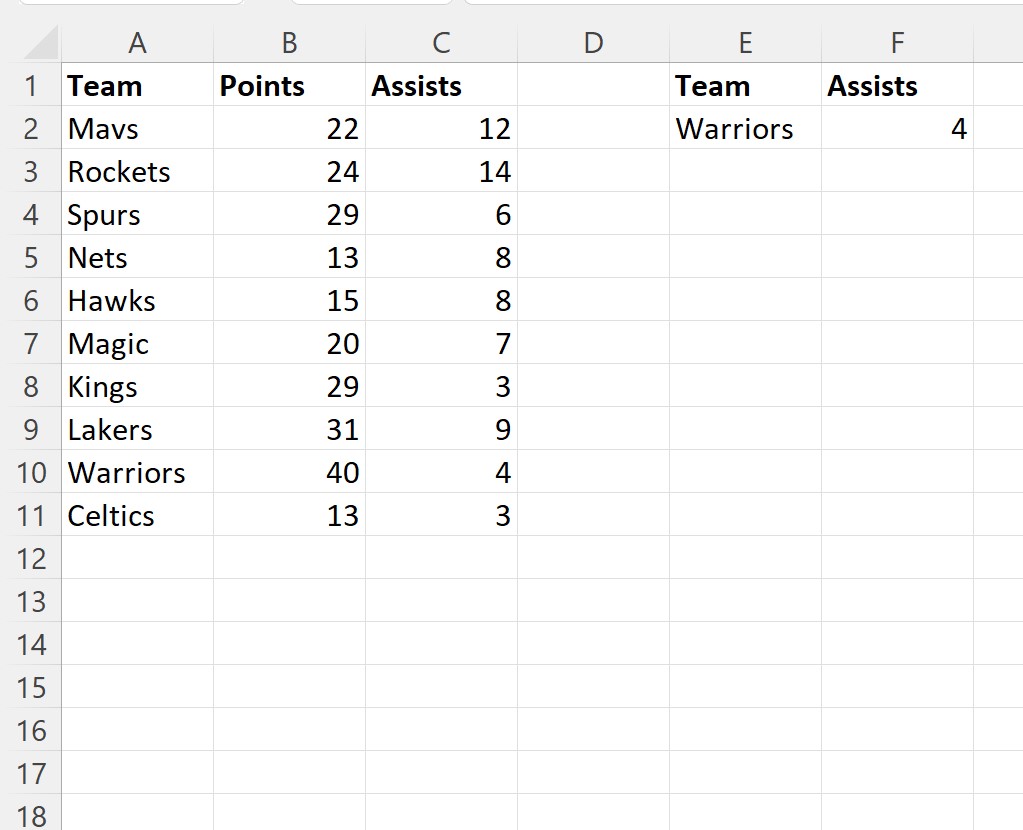
Note: You can find the complete documentation for the VBA VLookup method .
