Table of Contents
Pooled variance in Excel is a statistical measure used to combine the variances of two or more data sets into a single, representative value. This value can be used to determine the overall variability of a group of data points. To calculate pooled variance in Excel, you will need to first input your data sets into separate columns, then use the formula “=VARP(range1, range2, …)” to calculate the pooled variance. This formula takes the variances of each data set as arguments and calculates the weighted average. It is commonly used in statistical analysis and can provide valuable insights into the overall variability of a data set.
Calculate Pooled Variance in Excel (Step-by-Step)
In statistics, refers to the average of two or more group variances.
We use the word “pooled” to indicate that we’re “pooling” two or more group variances to come up with a single number for the common variance between the groups.
In practice, pooled variance is used most often in a , which is used to determine whether or not two population means are equal.
The pooled variance between two samples is typically denoted as sp2 and is calculated as:
sp2 = ( (n1-1)s12 + (n2-1)s22 ) / (n1+n2-2)
This tutorial provides a step-by-step example of how to calculate the pooled variance between two groups in Excel.
Step 1: Create the Data
First, let’s create two datasets:

Step 2: Calculate the Sample Size & Sample Variance
Next, let’s calculate the sample size and sample variance for each dataset.
Cells E17:F18 show the formulas we used:
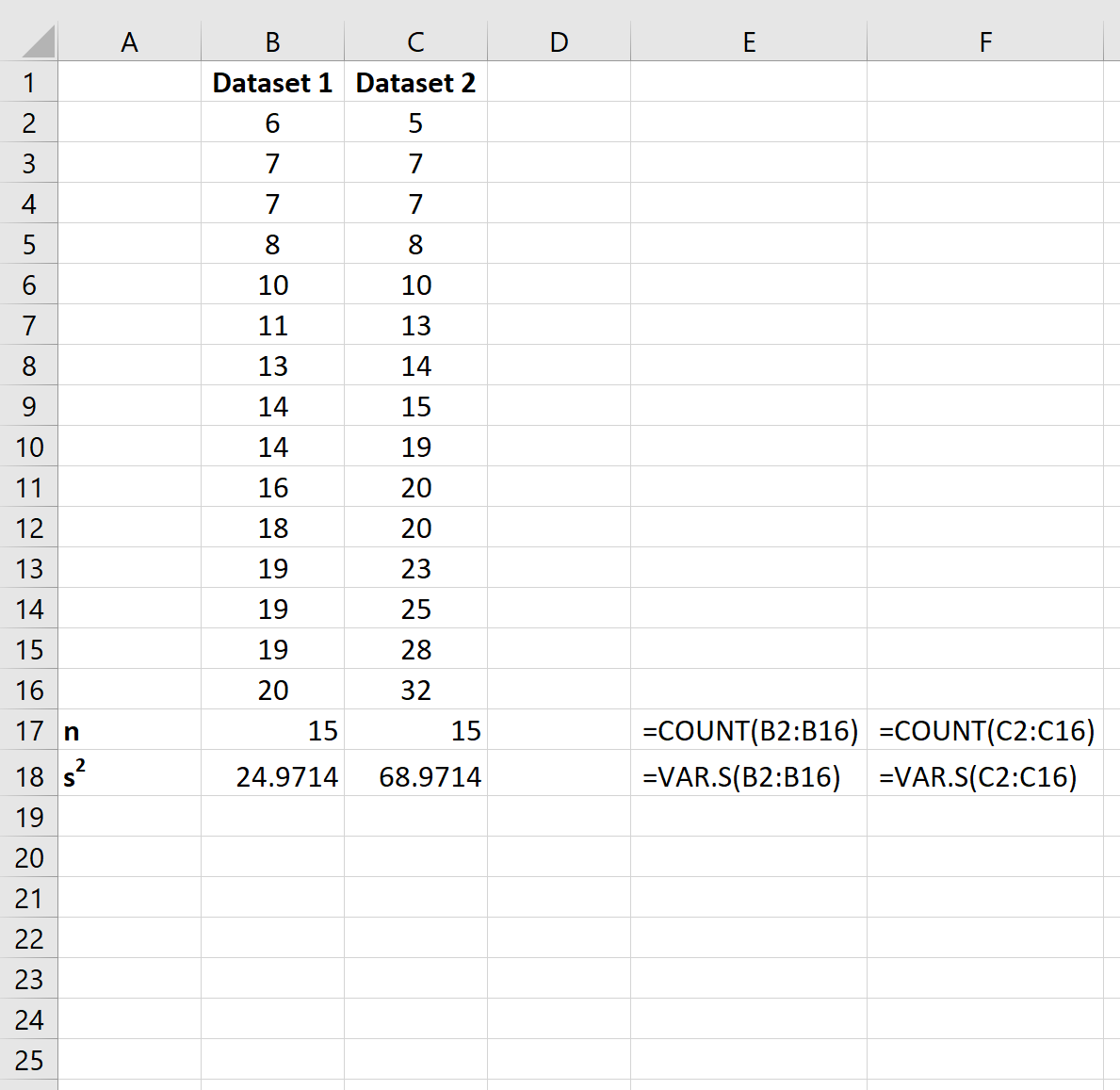
Step 3: Calculate the Pooled Variance
Lastly, we can use the following formula to calculate the pooled variance:
=((B17-1)*B18 + (C17-1)*C18) / (B17+C17-2)

Bonus: You can use this to automatically calculate the pooled variance between two groups.
