Table of Contents
Time series refers to a set of data points collected at regular intervals over time. These data points can represent various variables such as stock prices, temperature readings, or sales data. Matplotlib is a popular Python library used for data visualization. It provides various tools to plot and analyze time series data.
To plot a time series in Matplotlib, first, the data needs to be organized in a suitable format such as a pandas DataFrame. Then, the plot function from the Matplotlib library can be used to create a line graph with time as the x-axis and the variable values as the y-axis. This can be further customized by adding labels, titles, legends, and other visual elements.
For example, to plot a time series of monthly sales data, the first step would be to import the necessary libraries and load the data into a DataFrame. Then, the plot function can be used to create a line graph. The resulting plot can be further enhanced by adding a title, axis labels, and a legend to provide a better understanding of the data.
In summary, Matplotlib provides a convenient and efficient way to plot time series data, allowing users to analyze and visualize trends and patterns over time. With the help of examples and customization options, users can effectively communicate their findings and insights to others.
Plot a Time Series in Matplotlib (With Examples)
You can use the following syntax to plot a time series in Matplotlib:
import matplotlib.pyplotas plt plt.plot(df.x, df.y)
This makes the assumption that the x variable is of the class datetime.datetime().
The following examples show how to use this syntax to plot time series data in Python.
Example 1: Plot a Basic Time Series in Matplotlib
The following code shows how to plot a time series in Matplotlib that shows the total sales made by a company during 12 consecutive days:
import matplotlib.pyplotas plt import datetime import numpy as np import pandas as pd #define data df = pd.DataFrame({'date': np.array([datetime.datetime(2020, 1, i+1) for i in range(12)]), 'sales': [3, 4, 4, 7, 8, 9, 14, 17, 12, 8, 8, 13]}) #plot time series plt.plot(df.date, df.sales, linewidth=3)

The x-axis shows the date and the y-axis shows the total sales on each date.
Example 2: Customize the Title & Axis Labels
You can use the following code to add a title and axis labels to the plot:
import matplotlib.pyplotas plt import datetime import numpy as np import pandas as pd #define data df = pd.DataFrame({'date': np.array([datetime.datetime(2020, 1, i+1) for i in range(12)]), 'sales': [3, 4, 4, 7, 8, 9, 14, 17, 12, 8, 8, 13]}) #plot time series plt.plot(df.date, df.sales, linewidth=3) #add title and axis labels plt.title('Sales by Date') plt.xlabel('Date') plt.ylabel('Sales')

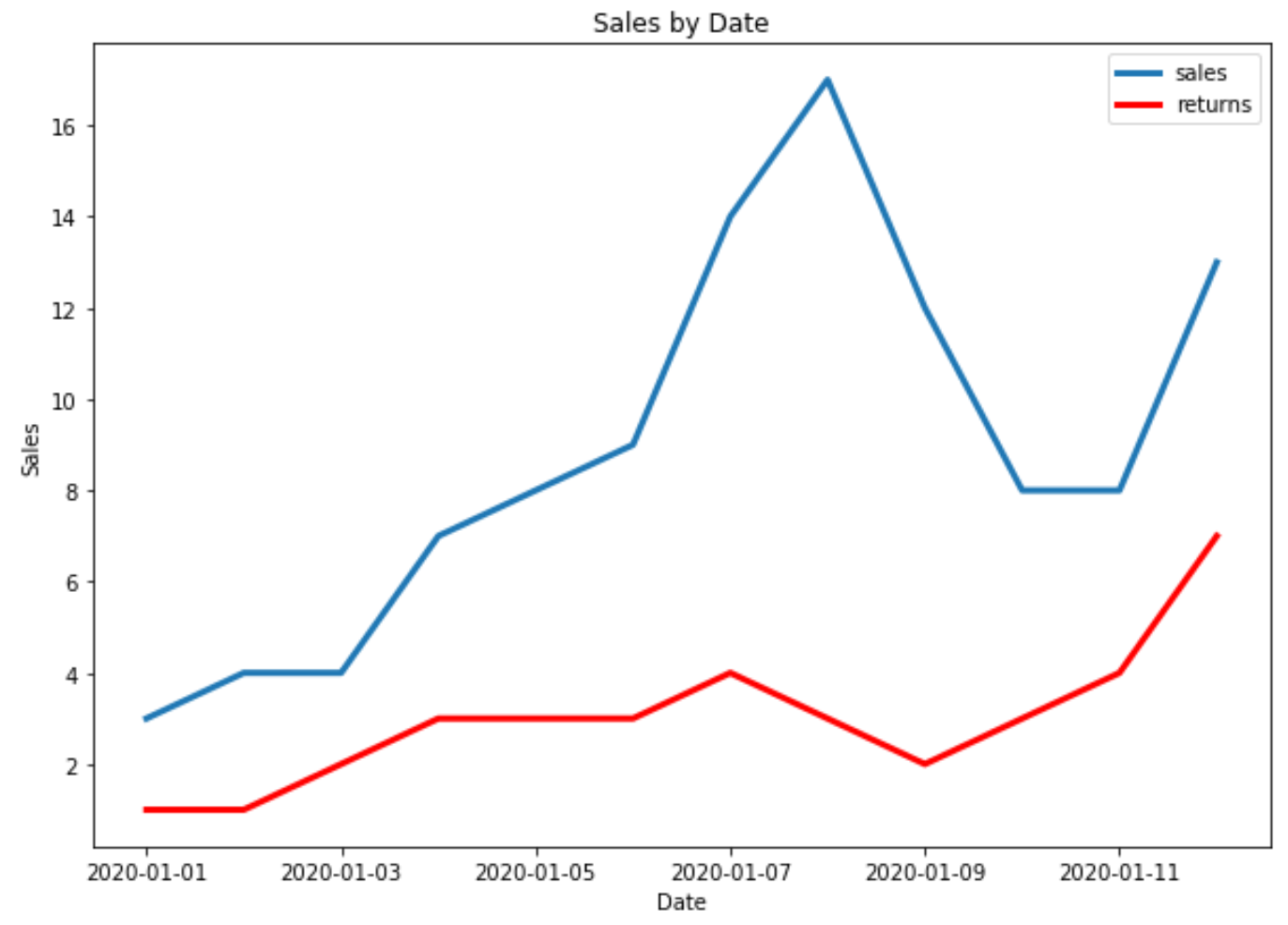
Example 3: Plot Multiple Time Series in Matplotlib
The following code shows how to plot multiple time series in one plot in Matplotlib:
import matplotlib.pyplotas plt
import datetime
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
#define data
df = pd.DataFrame({'date': np.array([datetime.datetime(2020, 1, i+1)
for i in range(12)]),
'sales': [3, 4, 4, 7, 8, 9, 14, 17, 12, 8, 8, 13]})
df2 = pd.DataFrame({'date': np.array([datetime.datetime(2020, 1, i+1)
for i in range(12)]),
'returns': [1, 1, 2, 3, 3, 3, 4, 3, 2, 3, 4, 7]})
#plot both time series
plt.plot(df.date, df.sales, label='sales', linewidth=3)
plt.plot(df2.date, df2.returns, color='red', label='returns', linewidth=3)
#add title and axis labels
plt.title('Sales by Date')
plt.xlabel('Date')
plt.ylabel('Sales')
#add legend
plt.legend()
#display plot
plt.show()