Table of Contents
A break-even analysis is a financial tool used to determine the point at which a company’s total revenue equals its total expenses, resulting in a net profit of zero. Performing this analysis in Google Sheets is a simple and effective way to evaluate the financial viability of a business venture. To do so, one can input the relevant data into a spreadsheet, including fixed and variable costs, expected sales volume and price, and the desired profit margin. Google Sheets can then be used to calculate the break-even point, as well as provide a visual representation of the data through graphs and charts. This allows for a comprehensive and organized analysis of the financial situation, aiding in decision-making and predicting future profitability. By utilizing the features of Google Sheets, performing a break-even analysis becomes a straightforward and efficient process.
Perform Break-Even Analysis in Google Sheets
Break-even analysis is a calculation that tells you the number of units a business must sell of some product in order to break even, i.e. make a profit of exactly zero dollars.
After this point, additional units sold will result in a positive profit.
To perform break-even analysis, you can use the following simple formula:
Break-Even Point = Fixed Cost / (Selling Price Per Unit – Cost Per Unit)
The following example shows how to use this formula to perform break-even analysis in Google Sheets.
Example: Break-Even Analysis in Google Sheets
Suppose Doug plans on opening a bagel shop.
His fixed costs will include the equipment he needs to buy along with the ingredients for the bagels, which comes to a total of $1,000.
Each bagel will cost $1 to make and he plans to sell them for $5 each.
Suppose we would like to perform break-even analysis to determine how many bagels he must sell to break even.
To do so, we can enter his fixed costs, selling price per unit, and cost per unit in Google Sheets.
We can then type the following formula into cell B5 to calculate the number of units he must sell to break even:
=B1/(B2-B3)
The following screenshot shows how to use this formula in practice:
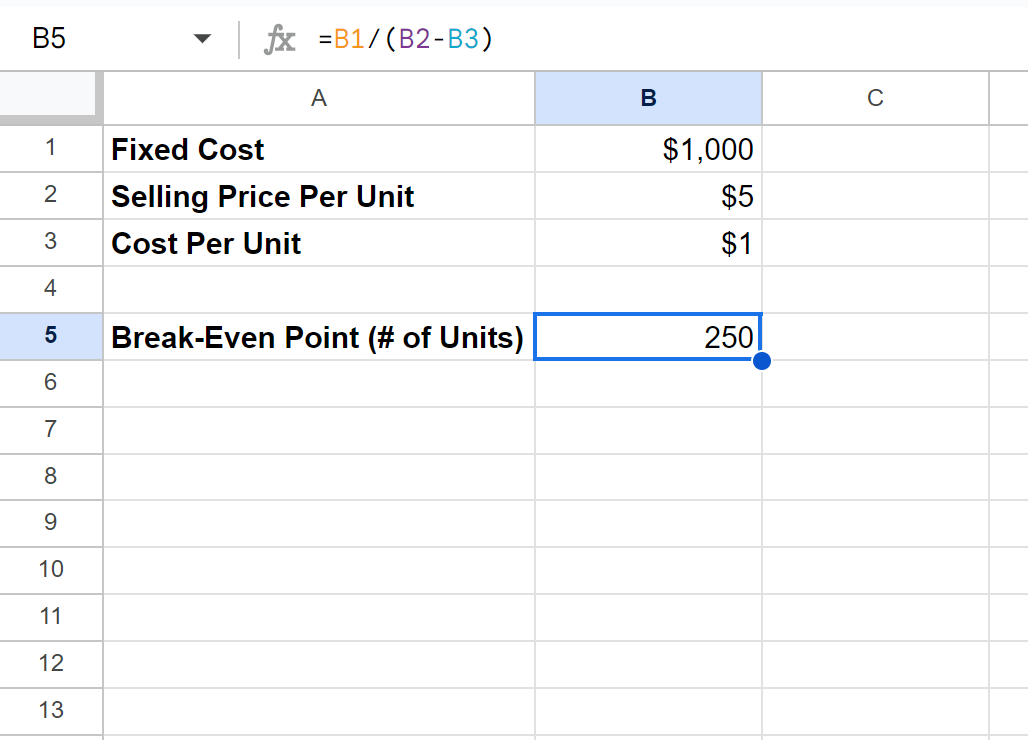
In order to break even, i.e. achieve a profit of exactly zero dollars, he must sell 250 units.
If we’d like, we can also type the following formulas into the following cells to calculate the total revenue, total cost, and total profit Doug will earn by selling this many units:
- B6: =B5*B2
- B7: =B1+(B5*B3)
- B8: =B6-B7
The following screenshot shows how to use these formulas in practice:
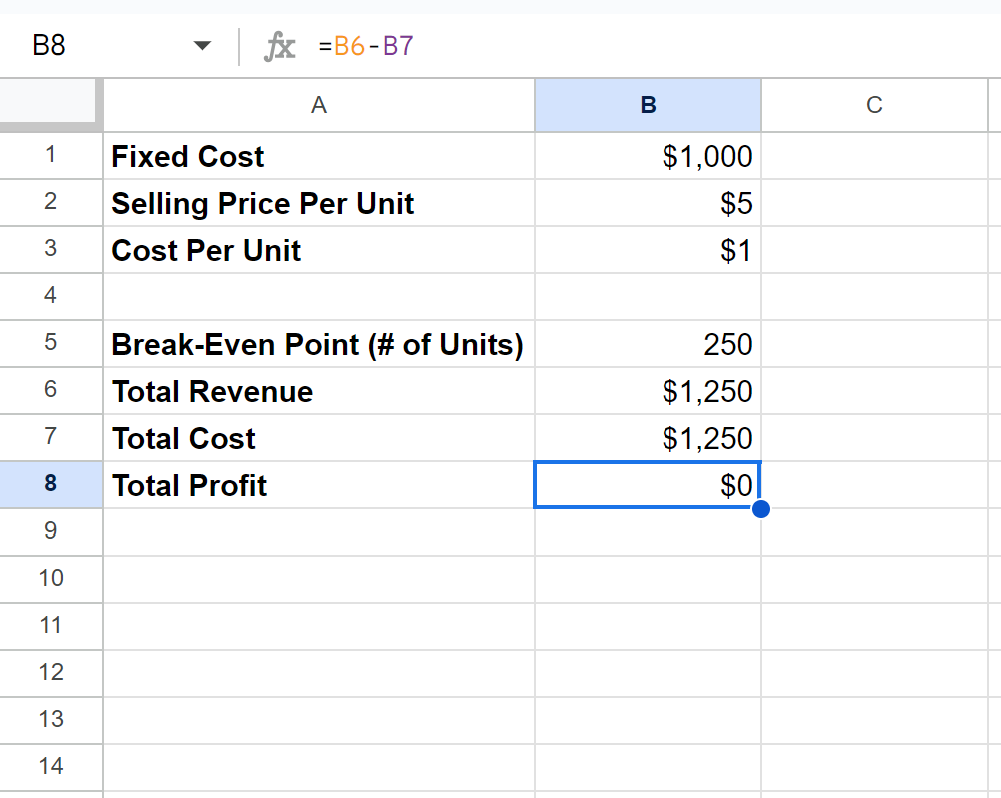
We can see that his total revenue will be $1,250, total cost will be $1,250 and total profit will be $0.
Once we have all these formulas in place, we could also change the selling price per unit in cell B2 to see how various prices affect the number of units he must sell to break even.
For example, suppose we change the selling price per unit to $6:
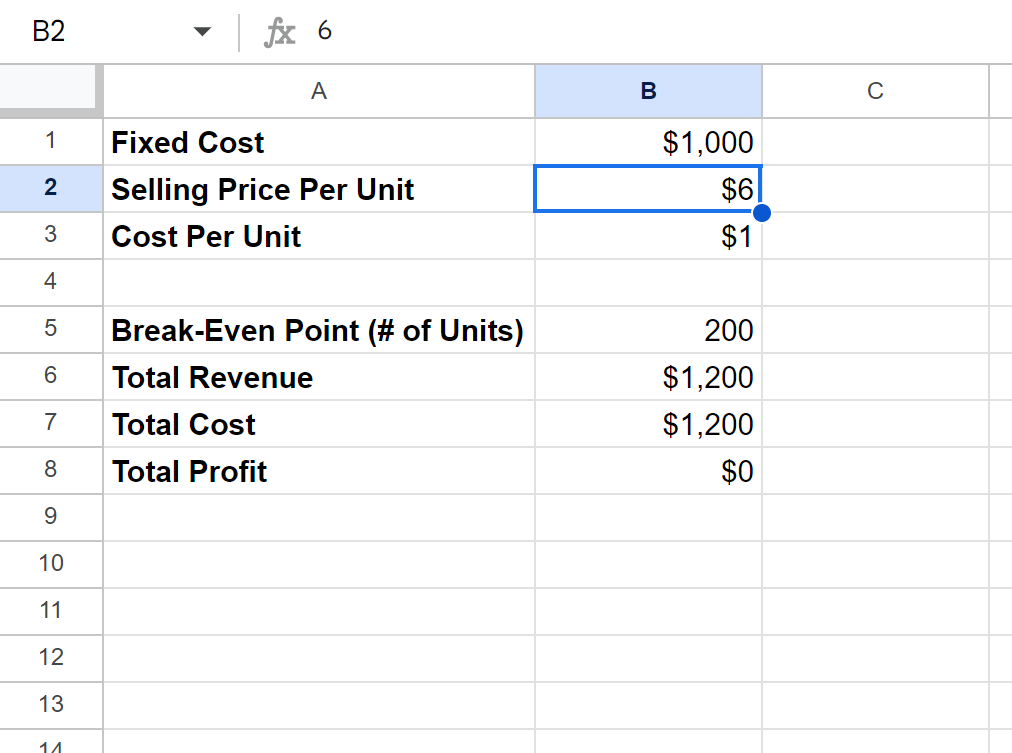
We can see that the number of units he must sell in order to break even drops to 200.
This should make sense. The higher the selling price per unit, the greater the profit per bagel and the fewer number of bagels he must sell in order to break even.
Feel free to play around with the values in cells B1, B2 and B3 to see how changing different price changes the value for the break even point.
Additional Resources
The following tutorials explain how to perform other common tasks in Google Sheets:
