Table of Contents
Seaborn is a powerful Python library used for creating visually appealing and informative data visualizations. One of its notable features is the ability to generate heatmaps, which are graphical representations of data where the values are represented by different colors.
To create a heatmap with Seaborn, first import the library and load the desired dataset. Then, use the “heatmap” function to plot a matrix of data, with the values being mapped to different colors according to a specified color palette. This can be further customized by adjusting parameters such as the size, annotations, and axes labels.
Some examples of using Seaborn to create heatmaps include visualizing correlation matrices, analyzing sales data by region, and monitoring changes in temperature over time. Heatmaps can also be used for tasks such as identifying patterns and trends, detecting outliers, and comparing data across different categories. Overall, Seaborn provides a user-friendly and versatile tool for generating heatmaps, making it a valuable resource for data analysis and visualization.
Make Heatmaps with Seaborn (With Examples)
A heatmap is a type of chart that uses different shades of colors to represent data values.
This tutorial explains how to create heatmaps using the Python visualization library with the following dataset:
#import seabornimport seaborn as sns #load "flights" dataset data = sns.load_dataset("flights") data = data.pivot("month", "year", "passengers") #view first five rows of dataset data.head()

Create a Basic Heatmap
We can use the following syntax to create a basic heatmap for this dataset:
sns.heatmap(data)
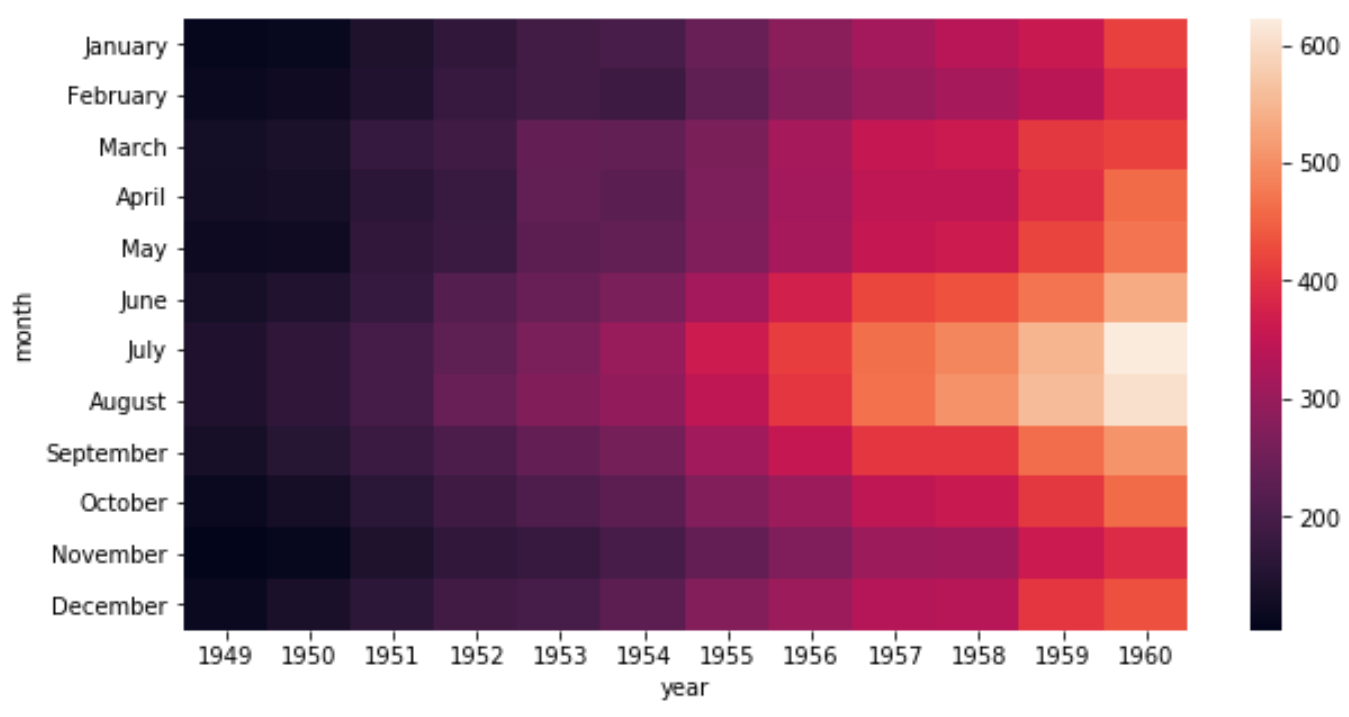
The x-axis displays the year, the y-axis displays the month, and the color of the squares within the heatmap represent the number of flights in those particular year-month combinations.
Adjust the Size of the Heatmap
We can use the figsize argument to adjust the overall size of the heatmap:
#set heatmap size import matplotlib.pyplotas pltplt.figure(figsize = (12,8))#create heatmap sns.heatmap(data)

Change the Colors of the Heatmap
We can use the cmap argument to change the colors used in the heatmap. For example, we could choose the “Spectral” color map:
sns.heatmap(data, cmap="Spectral")
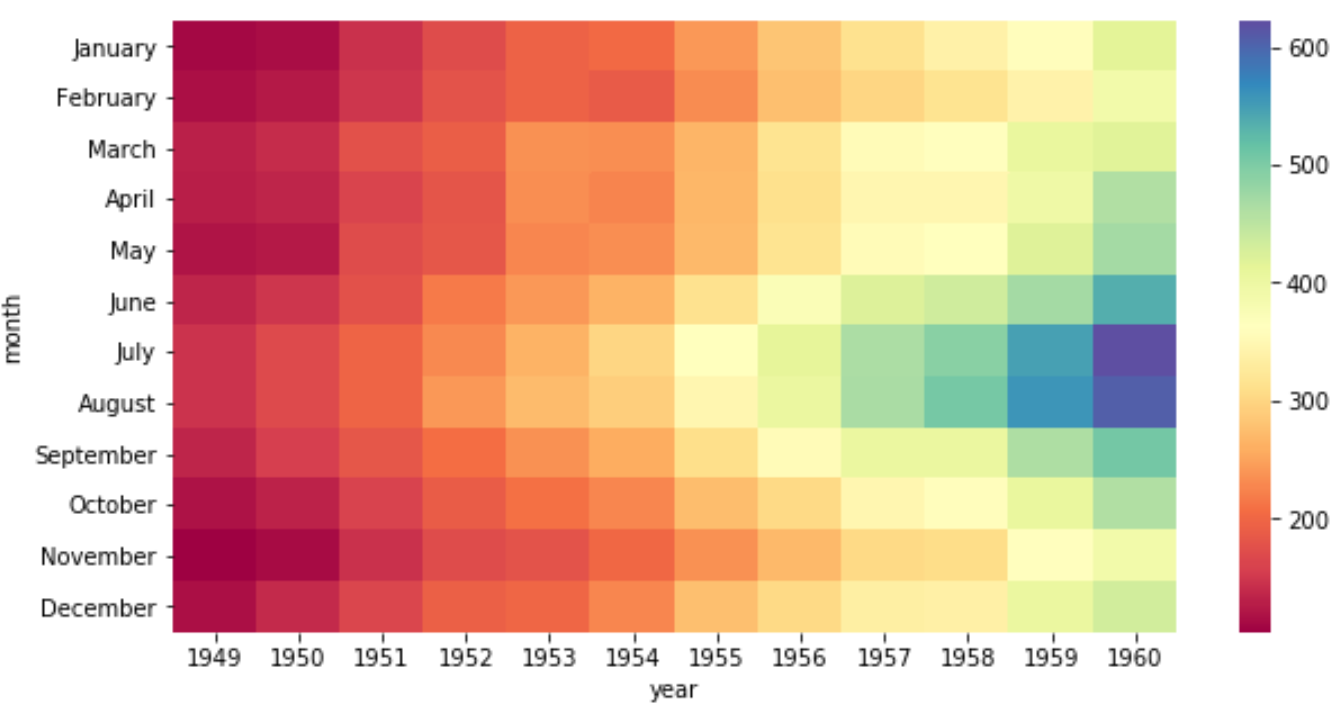
sns.heatmap(data, cmap="coolwarm")

Find a complete list of cmap options available .
Annotate the Heatmap
We can use the following syntax to annotate each cell in the heatmap with integer formatting and specify the font size:
sns.heatmap(data, annot=True, fmt="d", annot_kws={"size":13})

Modify the Colorbar of the Heatmap
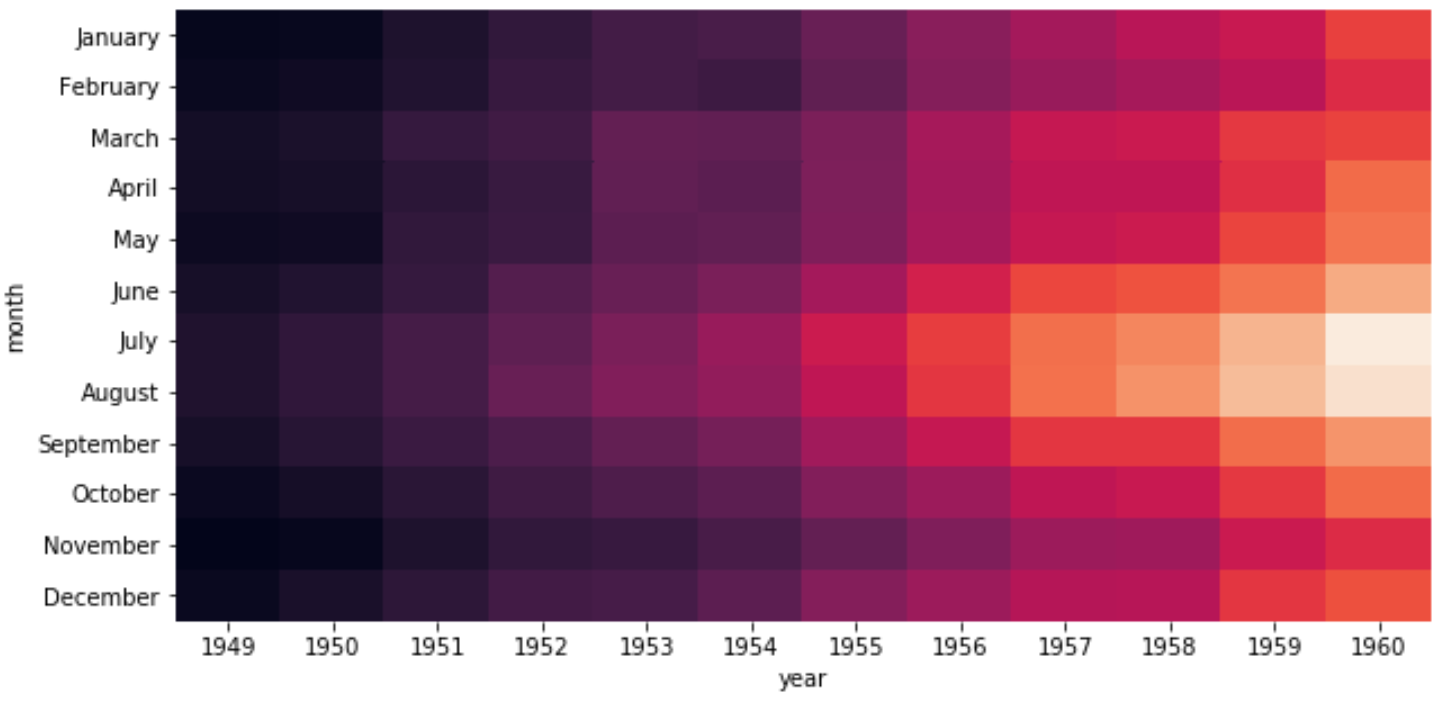
Lastly, we can turn the colorbar off if we’d like using the cbar argument:
sns.heatmap(data, cbar=False)
Find more Seaborn tutorials on .
