Table of Contents
Creating a correlation matrix in Python involves using the built-in functions and libraries such as NumPy and Pandas. Firstly, the data needs to be imported and organized into a dataframe. Then, the correlation method can be applied to the dataframe to generate a matrix of correlation values between the variables. This can be further customized by specifying the type of correlation coefficient to be used. The resulting matrix can be visualized using various plotting libraries. Overall, creating a correlation matrix in Python allows for a quick and efficient way to analyze the relationships between variables in a dataset.
Create a Correlation Matrix in Python
One way to quantify the relationship between two variables is to use the , which is a measure of the linear association between two variables.
It takes on a value between -1 and 1 where:
- -1 indicates a perfectly negative linear correlation.
- 0 indicates no linear correlation.
- 1 indicates a perfectly positive linear correlation.
The further away the correlation coefficient is from zero, the stronger the relationship between the two variables.
But in some cases we want to understand the correlation between more than just one pair of variables. In these cases, we can create a , which is a square table that shows the the correlation coefficients between several pairwise combination of variables.
This tutorial explains how to create and interpret a correlation matrix in Python.
How to Create a Correlation Matrix in Python
Use the following steps to create a correlation matrix in Python.
Step 1: Create the dataset.
import pandas as pd data = {'assists': [4, 5, 5, 6, 7, 8, 8, 10], 'rebounds': [12, 14, 13, 7, 8, 8, 9, 13], 'points': [22, 24, 26, 26, 29, 32, 20, 14] } df = pd.DataFrame(data, columns=['assists','rebounds','points']) df assist rebounds points 0 4 12 22 1 5 14 24 2 5 13 26 3 6 7 26 4 7 8 29 5 8 8 32 6 8 9 20 7 10 13 14
Step 2: Create the correlation matrix.
#create correlation matrix df.corr() assists rebounds points assists 1.000000 -0.244861 -0.329573 rebounds -0.244861 1.000000 -0.522092 points -0.329573 -0.522092 1.000000 #create same correlation matrix with coefficients rounded to 3 decimals df.corr().round(3) assists rebounds points assists 1.000 -0.245 -0.330 rebounds -0.245 1.000 -0.522 points -0.330 -0.522 1.000
Step 3: Interpret the correlation matrix.
The correlation coefficients along the diagonal of the table are all equal to 1 because each variable is perfectly correlated with itself.
All of the other correlation coefficients indicate the correlation between different pairwise combinations of variables. For example:
- The correlation coefficient between assists and rebounds is -0.245.
- The correlation coefficient between assists and points is -0.330.
- The correlation coefficient between rebounds and points is -0.522.
Step 4: Visualize the correlation matrix (optional).
corr = df.corr() corr.style.background_gradient(cmap='coolwarm')

You can also change the argument of cmap to produce a correlation matrix with different colors.
corr = df.corr() corr.style.background_gradient(cmap='RdYlGn')
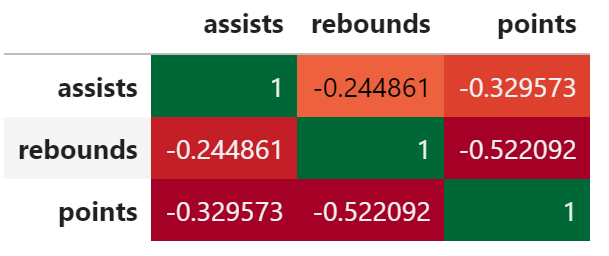
corr = df.corr() corr.style.background_gradient(cmap='bwr')
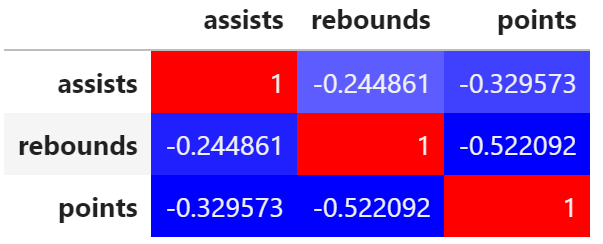
corr = df.corr() corr.style.background_gradient(cmap='PuOr')
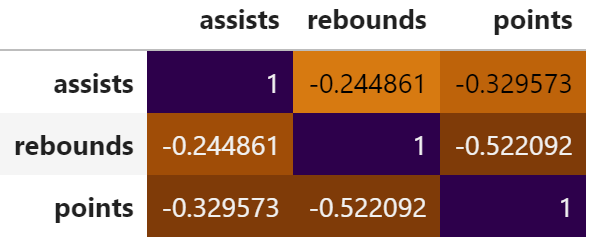
Note: For a complete list of cmap arguments, refer to the .
