Table of Contents
A correlation matrix is a way to visualize the relationship between different variables in a dataset. To create a correlation matrix in Google Sheets, you must first enter the data you wish to analyze into columns of the sheet. Then, you can go to the Data menu, select the Correlation option, and select the columns you wish to analyze. The matrix will then be generated and displayed in the sheet. This is a great tool for quickly identifying relationships between variables in a dataset.
One way to quantify the relationship between two variables is to use the Pearson correlation coefficient, which is a measure of the linear association between two variables. It has a value between -1 and 1 where:
- -1 indicates a perfectly negative linear correlation between two variables
- 0 indicates no linear correlation between two variables
- 1 indicates a perfectly positive linear correlation between two variables
The further away the correlation coefficient is from zero, the stronger the relationship between the two variables.
But in some cases we want to understand the correlation between more than just one pair of variables. In these cases, we can create a correlation matrix, which is a square table that shows the the correlation coefficients between several pairwise combination of variables.
This tutorial explains how to create and interpret a correlation matrix in Google Sheets.
How to Create a Correlation Matrix in Google Sheets
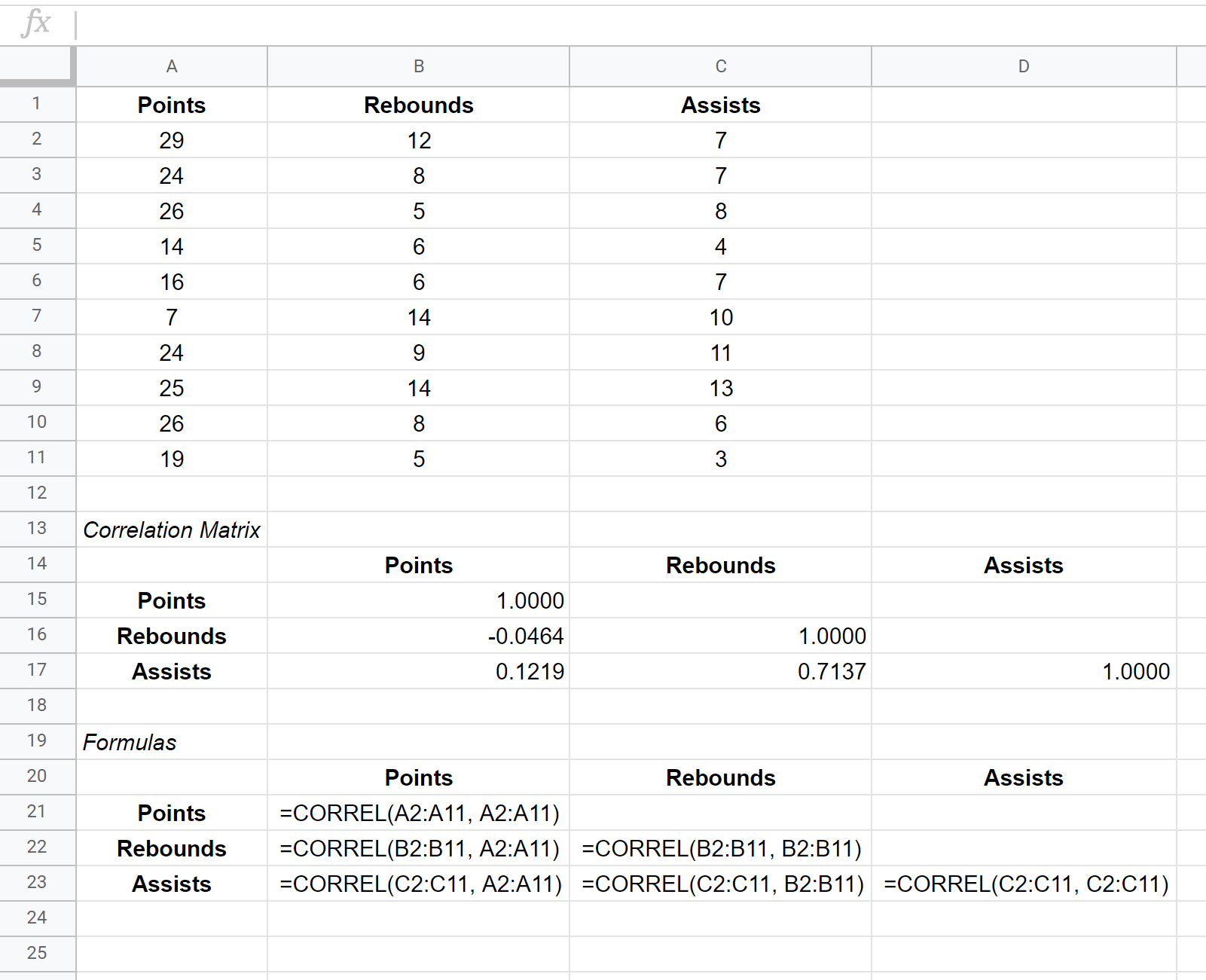
Suppose we have the following dataset that shows the average numbers of points, rebounds, and assists for 10 basketball players:
To create a correlation matrix for this dataset, we can use the CORREL() function with the following syntax:
COVAR(data_y, data_x)
The covariance matrix for this dataset is shown in cells B15:D17 while the formulas used to create the covariance matrix are shown in cells B21:D23 below:
How to Interpret a Correlation Matrix
The values in the individual cells of the correlation matrix tell us the Pearson Correlation Coefficient between each pairwise combination of variables. For example:
Correlation between Points and Rebounds: -0.0464. Points and rebounds are slightly negatively correlated, but this value is so close to zero that there isn’t strong evidence for a significant association between these two variables.
Correlation between Points and Assists: 0.1219. Points and assists are slightly positively correlated, but this value also is fairly close to zero so there isn’t strong evidence for a significant association between these two variables.
Correlation between Rebounds and Assists: 0.7137. Rebounds and assists are strongly positively correlated. That is, players who have more rebounds also tend to have more assists.
Notice that the diagonal values in the correlation matrix are all equal to 1 because the correlation between a variable and itself is always 1. In practice, this number isn’t useful to interpret.
How to Read a Correlation Matrix
How to Create a Correlation Matrix in Excel
