Table of Contents
The NOT EQUAL operator in SAS is an operator that is used to check if two values are not equal to each other. It is indicated by the “<>” symbol and it is used in an IF statement to evaluate if the condition is false.
There are two ways to use a NOT EQUAL operator in SAS:
- ne
- ^=
The following examples show how to use each operator in practice with the following dataset in SAS that contains information about various basketball players:
/*create dataset*/
data my_data;
input team $ position $ points assists;
datalines;
A Guard 14 4
A Guard 22 22
A Guard 24 9
A Forward 13 13
A Forward 13 9
A Forward 10 10
B Guard 24 4
B Guard 10 6
B Forward 34 2
B Forward 15 5
B Forward 23 23
B Forward 10 4
;
run;
/*view dataset*/
proc print data=my_data;
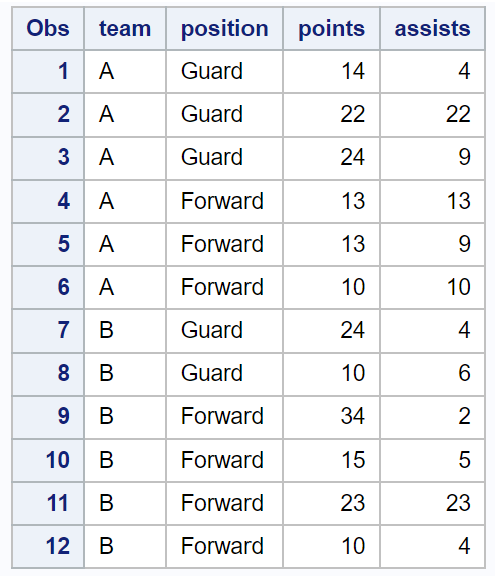
Example 1: Using ne as “NOT EQUAL” in SAS
The following code shows how to create a new dataset in SAS and use the ne operator to check if the values in the points and assists columns in each row are not equal:
/*create new dataset*/
data new_data;
set my_data;
if points ne assists then points_vs_assists = 'not equal';
else points_vs_assists = 'equal';
run;
/*view dataset*/
proc print data=new_data;
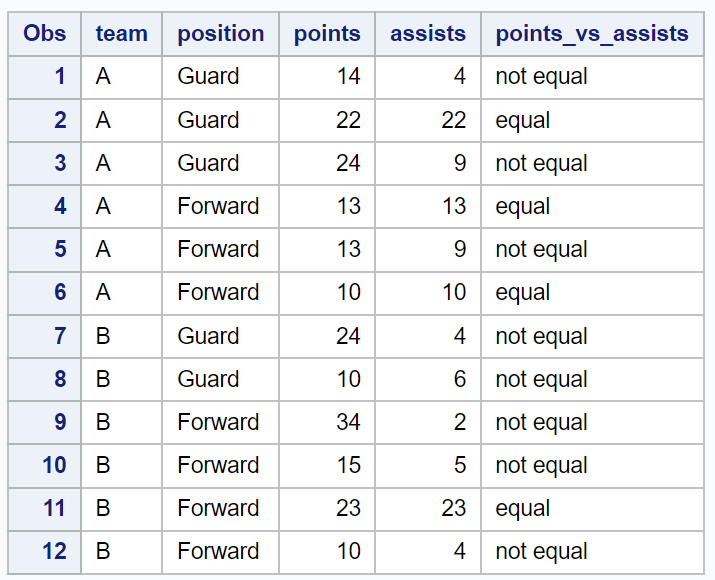
Notice that the new column called points_vs_assists has a value of “not equal” if the values in the points and assists columns are not equal or a value of “equal” if the values in the two columns are equal.
Example 2: Using ^= as “NOT EQUAL” in SAS
The following code shows how to create a new dataset in SAS and use the ^= operator to check if the values in the points and assists columns in each row are not equal:
/*create new dataset*/
data new_data;
set my_data;
if points ^= assists then points_vs_assists = 'not equal';
else points_vs_assists = 'equal';
run;
/*view dataset*/
proc print data=new_data;

Notice that the values in the points_vs_assists column match the values from the previous example.
The following tutorials explain how to perform other common tasks in SAS:
