Table of Contents
The indicated area under the standard normal curve refers to the portion of the curve that lies between a specific set of values on the horizontal axis. This area represents the probability of a random variable falling within that range of values. It is commonly used in statistics to calculate the likelihood of an event occurring within a certain range of a normal distribution. The standard normal curve is a bell-shaped curve with a mean of 0 and a standard deviation of 1, and the indicated area is often represented by the shaded region under the curve. This concept is important in understanding the probabilities associated with different values in a normal distribution.
Find the Indicated Area Under the Standard Normal Curve
One of the most common questions in elementary statistics is:
“Find the indicated area under the standard normal curve.”
These types of questions can be answered by using values found in the z table. This tutorial explains how to use the z table to answer the following four types of these questions:
- Find the area under the curve less than some value.
- Find the area under the curve greater than some value.
- Find the area under the curve between two values.
- Find the area under the curve outside of two values.
Example 1: Find the Indicated Area Less Than Some Value
Question: Find the area under the standard normal curve to the left of z = 1.26.
Solution: To answer this question, we simply need to look up the value in the z table that corresponds to 1.26:
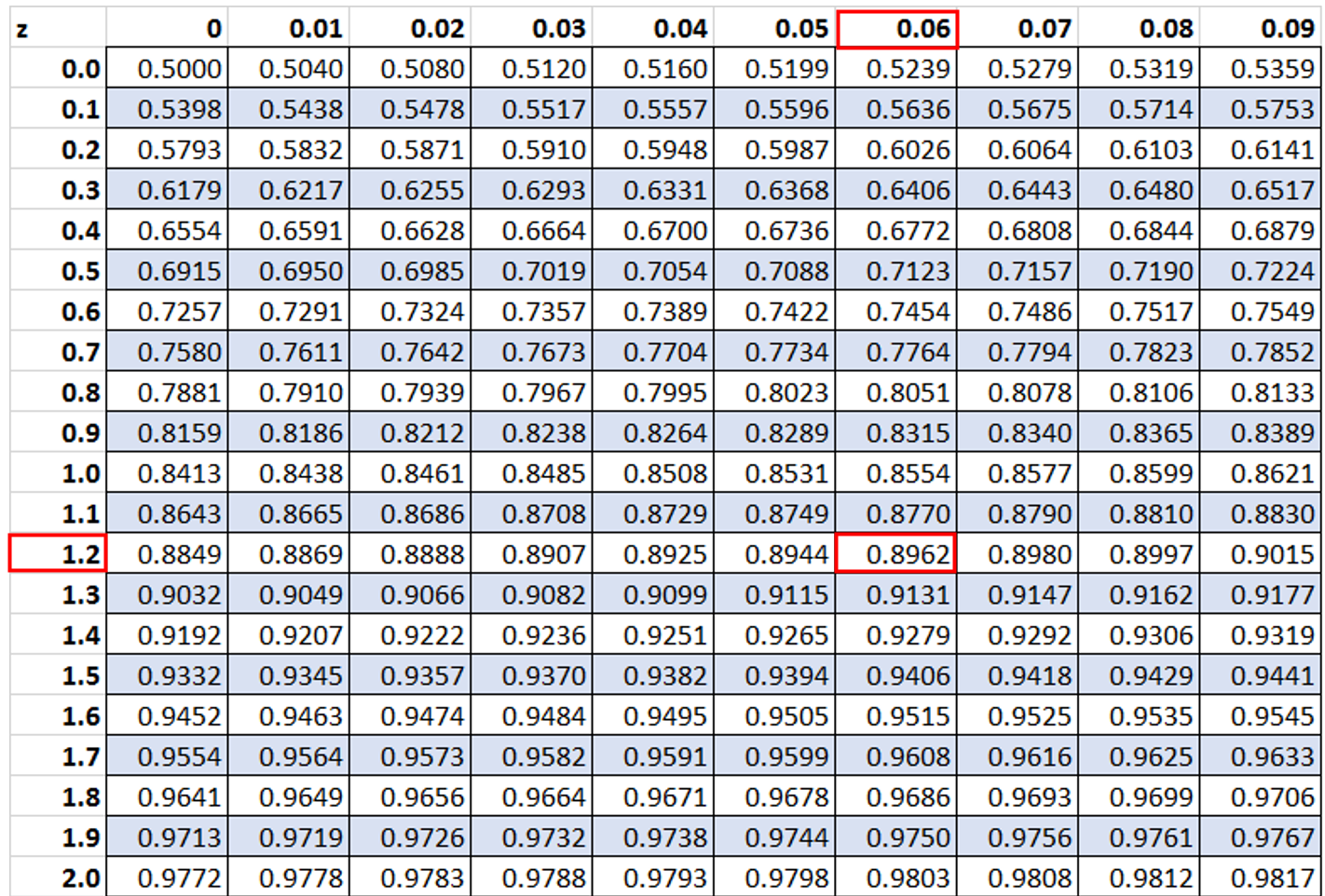
The area under the standard normal curve to the left of z = 1.26 is 0.8962.
Example 2: Find the Indicated Area Greater Than Some Value
Question: Find the area under the standard normal curve to the right of z = -1.81.
Solution: To answer this question, we simply need to look up the value in the z table that corresponds to -1.81 and subtract it from 1:

The area under the standard normal curve to the right of z = -1.81 is 1 – .0351 – 0.9649.
Example 3: Find the Indicated Area Between Two Values
Question: Find the area under the standard normal curve between z = -1.81 and z = 1.26
Solution: To answer this question, we simply need to subtract the area to the left of z = -1.81 from the area to the left of 1.26.
Thus, the area under the standard normal curve between z = -1.81 and z = 1.26 is .8962 – .0351 = 0.8611.
Example 4: Find the Indicated Area Outside of Two Values
Question: Find the area under the standard normal curve outside of z = -1.81 and z = 1.26
Solution: To answer this question, we need to add up the area to the left of z = -1.81 and the area to the right of z = 1.26.
The area to the left of z = -1.81 is .0351 and the area to the right of z = 1.26 is 1-.8962 = .1038.
Thus, the area between z = -1.81 and z = 1.26 is .0351 + .1038 = .1389.
Bonus: The Standard Normal Curve Area Calculator
You can use this calculator to automatically find the area under the standard normal curve between two values.
