Table of Contents
Qualitative and quantitative variables are two types of data that are used in research and data analysis. Qualitative variables are descriptive and do not have numerical values, while quantitative variables are numerical and can be measured or counted.
The main difference between the two is that qualitative variables are based on qualities or characteristics, while quantitative variables are based on quantity or numerical values. Qualitative variables are often used to describe and categorize things, such as gender, ethnicity, or occupation. On the other hand, quantitative variables are used to measure and compare data, such as height, weight, or income.
Another key difference is that qualitative variables are often subjective and can be interpreted differently by different individuals, while quantitative variables are more objective and can be measured and compared using statistical methods.
In summary, the main distinction between qualitative and quantitative variables lies in their nature and purpose. Qualitative variables provide descriptive information, while quantitative variables provide numerical data that can be analyzed and used for statistical purposes. Understanding the difference between these two types of variables is crucial in conducting accurate and meaningful research.
Qualitative vs. Quantitative Variables: What’s the Difference?
In statistics, there are two types of variables:
1. Quantitative Variables: Sometimes referred to as “numeric” variables, these are variables that represent a measurable quantity. Examples include:
- Number of students in a class
- Number of square feet in a house
- Population size of a city
- Age of an individual
- Height of an individual
2. Qualitative Variables: Sometimes referred to as “categorical” variables, these are variables that take on names or labels and can fit into categories. Examples include:
- Eye color (e.g. “blue”, “green”, “brown”)
- Gender (e.g. “male”, “female”)
- Breed of dog (e.g. “lab”, “bulldog”, “poodle”)
- Level of education (e.g. “high school”, “Associate’s degree”, “Bachelor’s degree”)
- Marital status (e.g. “married”, “single”, “divorced”)
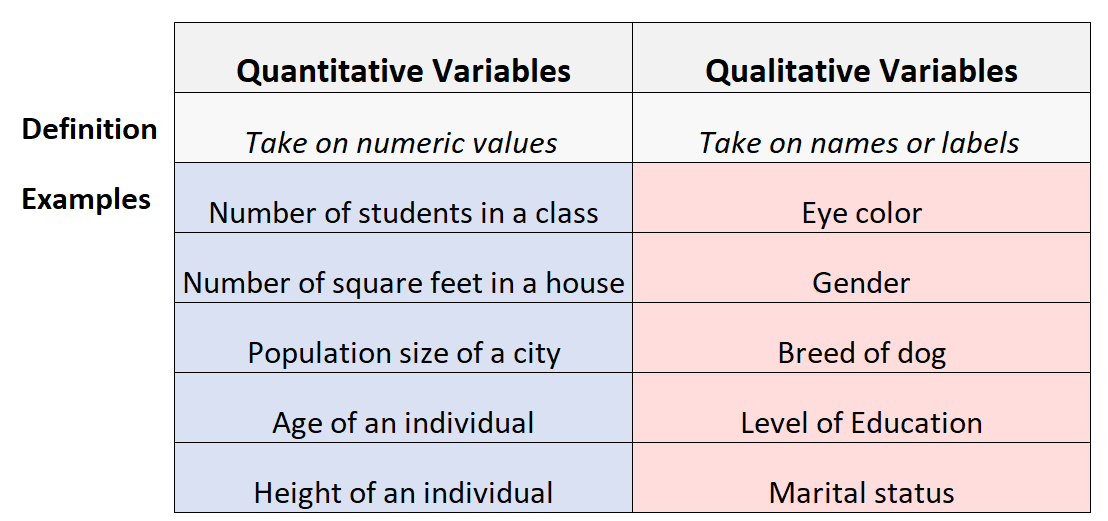
Every single variable you will ever encounter in statistics can be classified as either quantitative or qualitative.
Example: Classifying Quantitative & Qualitative Variables
Consider the following dataset with information about 10 different basketball players:
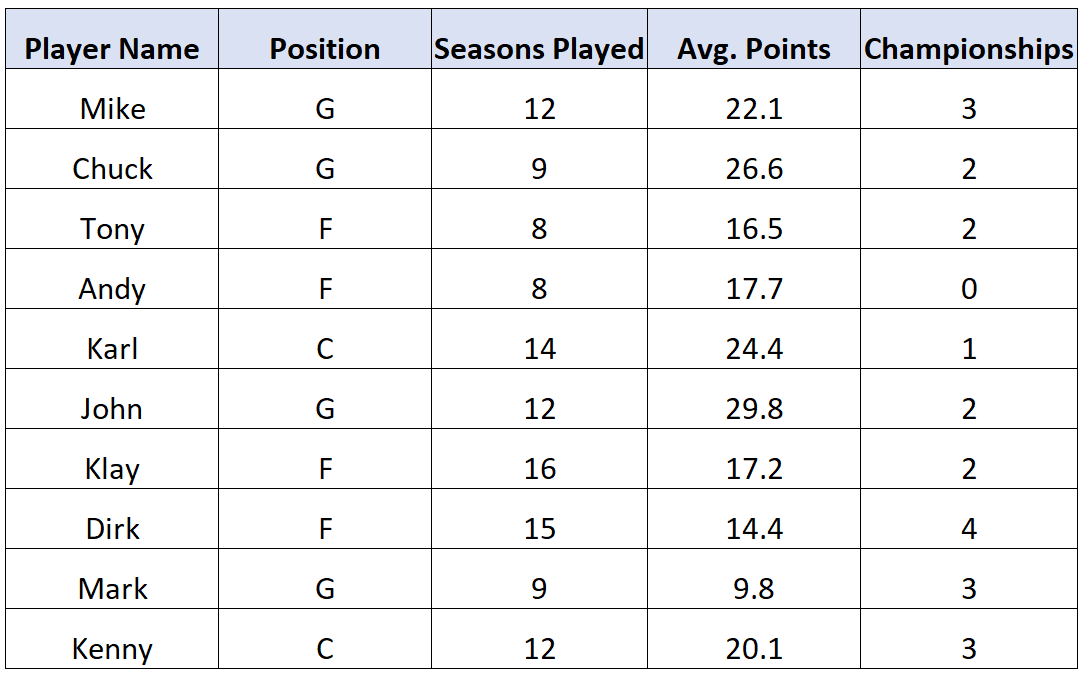
There are five total variables in this dataset. Two of them are qualitative variables and three of them are quantitative variables:
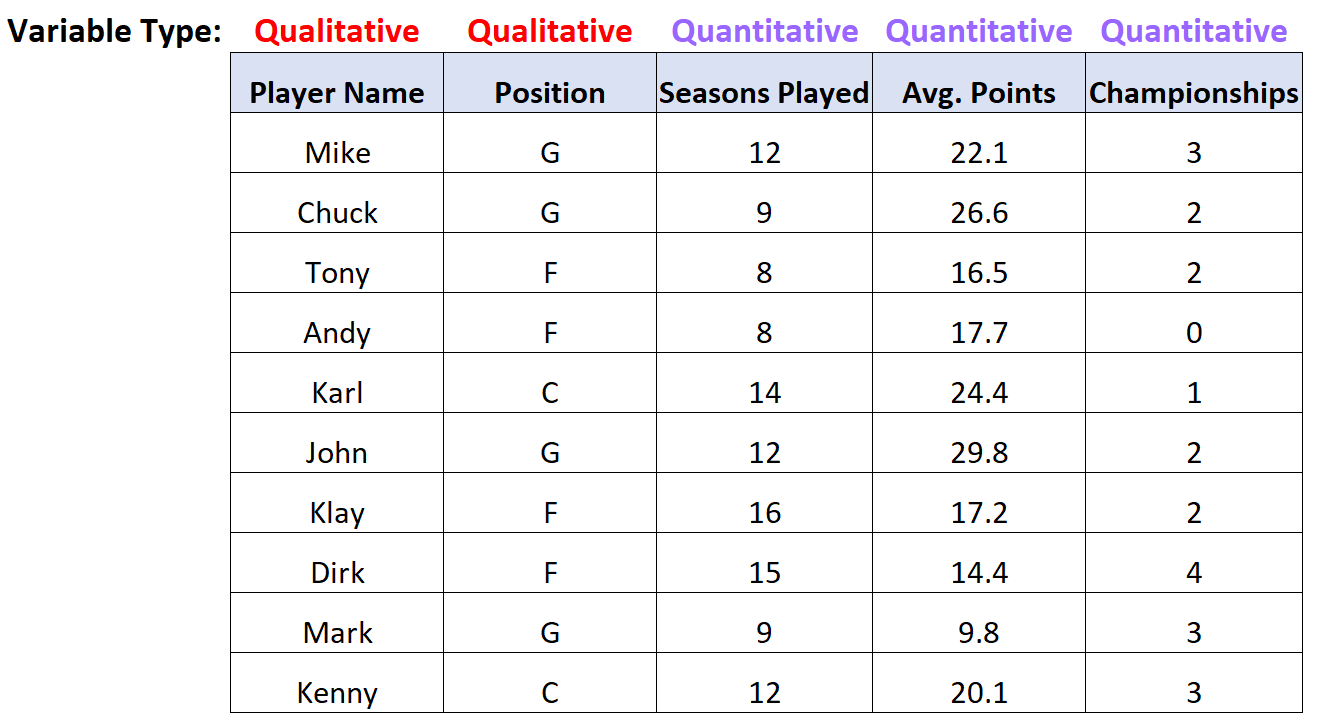
Summarizing Quantitative & Qualitative Variables
We can use many different metrics to summarize quantitative variables, including:
- Measures of central tendency like the mean, median, and mode.
- Measures of dispersion like the range, interquartile range, and standard deviation.
However, we can only use frequency tables and relative frequency tables to summarize qualitative variables.
To illustrate this, let’s once again consider the dataset from the previous example:

For the quantiative variable Seasons Played, we can calculate the following metrics:
- Mean: 11.5
- Median: 12
- Mode: 12
- Range: 8
- Interquartile Range: 4.5
- Standard Deviation: 2.915
These metrics give us a good idea of where the center value is located as well as how spread out the values are for this variable.
And for the qualitative variable Position, we can create a frequency table to describe how often different values occur:
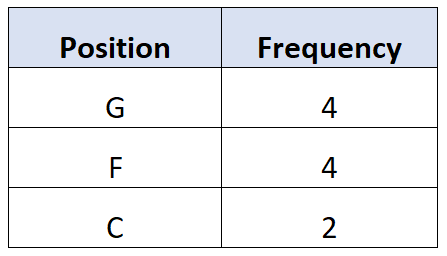
This table lets us quickly see how frequently each position (G=guard, F=forward, C=center) occurred in the dataset.
Additional Resources
Descriptive vs. Inferential Statistics
Statistic vs. Parameter
Levels of Measurement: Nominal, Ordinal, Interval and Ratio
