Table of Contents
A case statement in VBA is a type of programming construct that allows you to make decisions based on a range of different values or conditions. The syntax for a case statement typically consists of a Select Case statement followed by Case and End Select clauses. Within the Case clauses you define the conditions that should trigger a certain action. If none of the conditions are met, the default action defined in the Case Else clause will be executed.
A case statement is a type of statement that goes through conditions and returns a value when the first condition is met.
You can use the following basic syntax to write a case statement in VBA:
Sub CaseStatement() Dim i As Integer For i = 2 To 9 Select Case Range("B" & i).Value Case Is >= 30 result = "Great" Case Is >= 20 result = "Good" Case Is >= 15 result = "OK" Case Else result = "Bad" End Select Range("C" & i).Value = result Next i End Sub
This particular example looks at each cell in the range B2:B9 and returns the following values in the range C2:C9:
- “Great” if the value in column B is greater than or equal to 30.
- Else, “Good” if the value in column B is greater than or equal to 20.
- Else, “OK” if the value in column B is greater than or equal to 15.
- Else, “Bad” if none of the previous conditions are met.
The following example shows how to use this syntax in practice.
Example: Writing a Case Statement in VBA
Suppose we have the following dataset in Excel that shows the number of points scored by various basketball players:
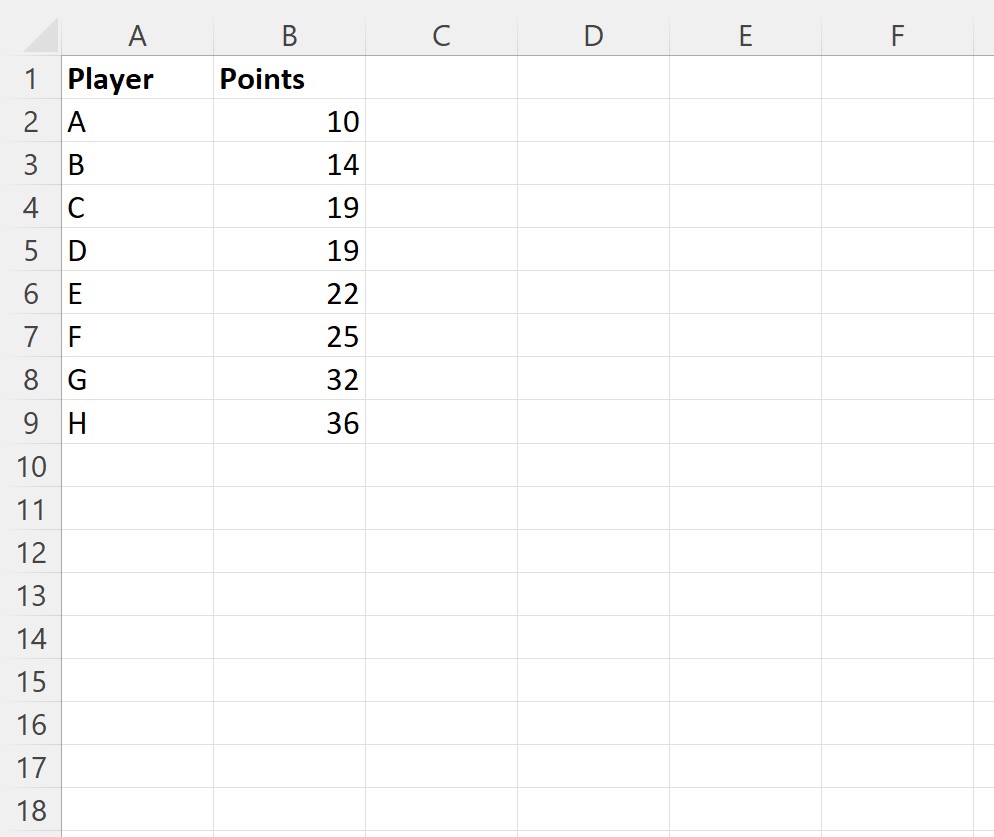
Suppose we would like to write a case statement to assign a value of Great, Good, OK or Bad to each player based on their number of points scored.
We can create the following macro to do so:
Sub CaseStatement() Dim i As Integer For i = 2 To 9 Select Case Range("B" & i).Value Case Is >= 30 result = "Great" Case Is >= 20 result = "Good" Case Is >= 15 result = "OK" Case Else result = "Bad" End Select Range("C" & i).Value = result Next i End Sub
When we run this macro, we receive the following output:
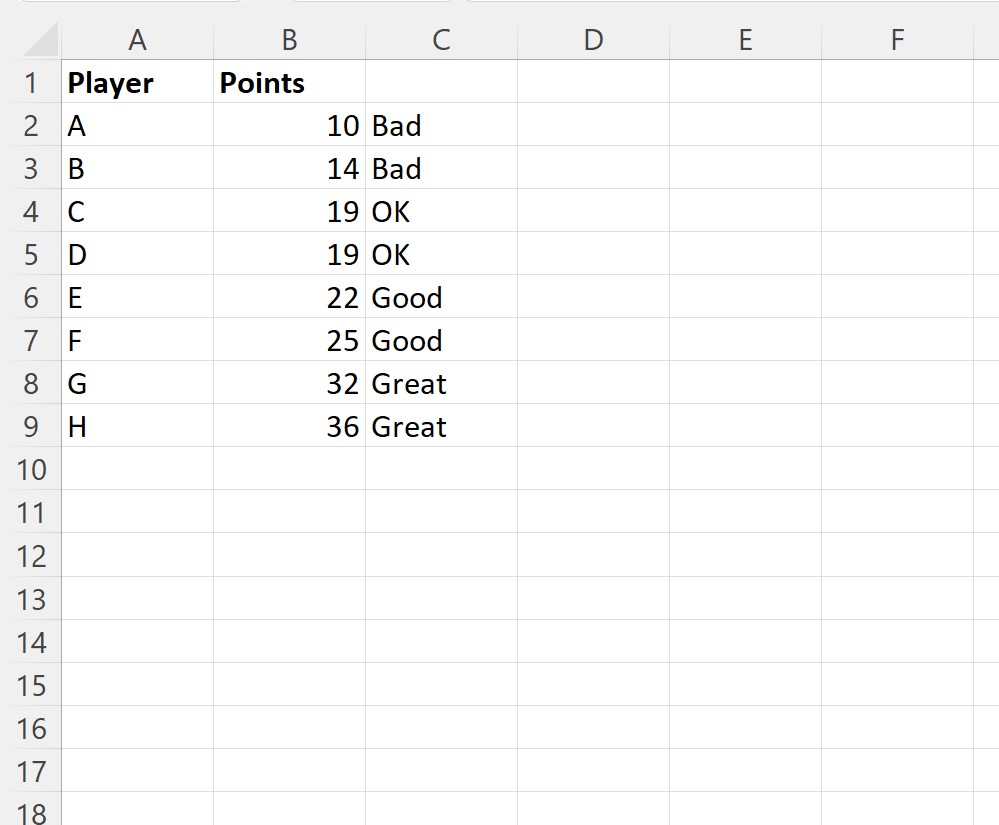
Column C returns a value of Great, Good, OK or Bad based on the corresponding value in column B.
