Table of Contents
Pandas get_dummies is a function used to convert categorical variables into dummy/indicator variables (0 or 1). It takes in a dataframe and a list of columns and separates the values in the columns into different dummy columns with 0 or 1 values. It is a useful tool for transforming categorical data into numerical data that can be used in machine learning algorithms.
Often in statistics, the datasets we’re working with include .
These are variables that take on names or labels. Examples include:
- Marital status (“married”, “single”, “divorced”)
- Smoking status (“smoker”, “non-smoker”)
- Eye color (“blue”, “green”, “hazel”)
- Level of education (e.g. “high school”, “Bachelor’s degree”, “Master’s degree”)
When fitting machine learning algorithms (like , , , etc.), we often convert categorical variables to dummy variables, which are numeric variables that are used to represent categorical data.
For example, suppose we have a dataset that contains the categorical variable Gender. To use this variable as a predictor in a regression model, we would first need to convert it to a dummy variable.
To create this dummy variable, we can choose one of the values (“Male”) to represent 0 and the other value (“Female”) to represent 1:
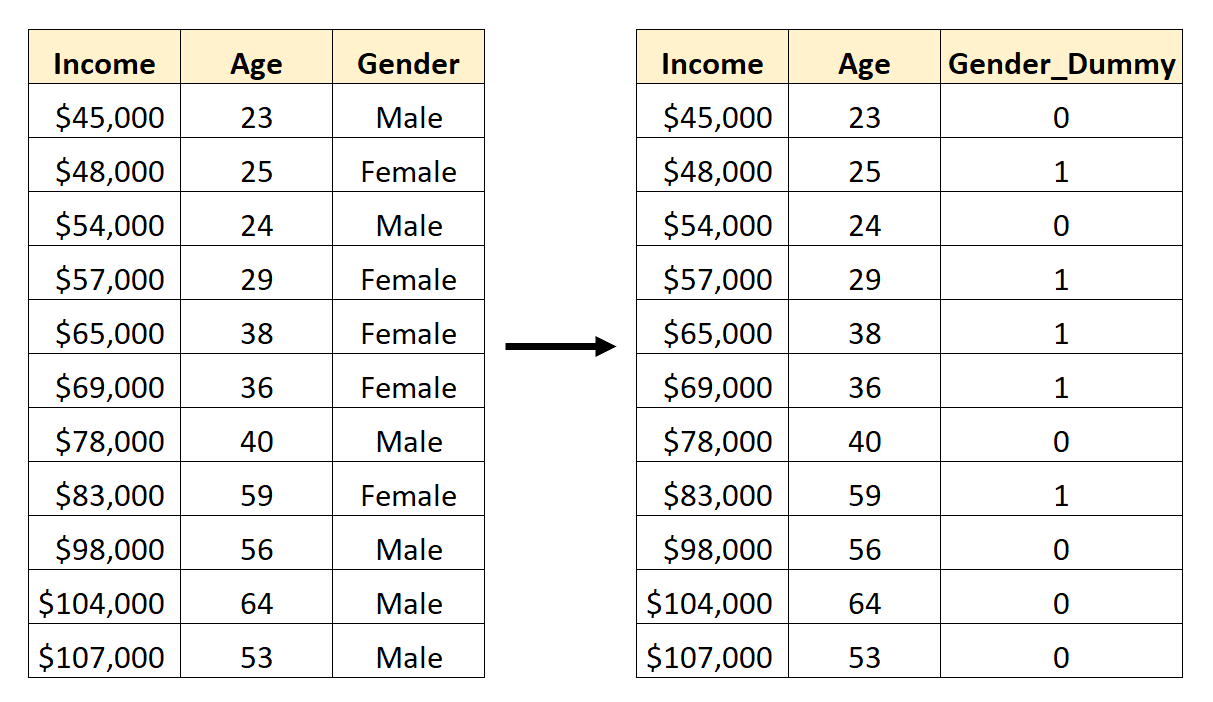
How to Create Dummy Variables in Pandas
To create dummy variables for a variable in a pandas DataFrame, we can use the function, which uses the following basic syntax:
pandas.get_dummies(data, prefix=None, columns=None, drop_first=False)
where:
- data: The name of the pandas DataFrame
- prefix: A string to append to the front of the new dummy variable column
- columns: The name of the column(s) to convert to a dummy variable
- drop_first: Whether or not to drop the first dummy variable column
The following examples show how to use this function in practice.
Example 1: Create a Single Dummy Variable
Suppose we have the following pandas DataFrame:
import pandas as pd #create DataFrame df = pd.DataFrame({'income': [45, 48, 54, 57, 65, 69, 78], 'age': [23, 25, 24, 29, 38, 36, 40], 'gender': ['M', 'F', 'M', 'F', 'F', 'F', 'M']}) #view DataFrame df income age gender 0 45 23 M 1 48 25 F 2 54 24 M 3 57 29 F 4 65 38 F 5 69 36 F 6 78 40 M
We can use the pd.get_dummies() function to turn gender into a dummy variable:
#convert gender to dummy variable pd.get_dummies(df, columns=['gender'], drop_first=True) income age gender_M 0 45 23 1 1 48 25 0 2 54 24 1 3 57 29 0 4 65 38 0 5 69 36 0 6 78 40 1
The gender column is now a dummy variable where:
- A value of 0 represents “Female”
- A value of 1 represents “Male”
Example 2: Create Multiple Dummy Variables
Suppose we have the following pandas DataFrame:
import pandas as pd #create DataFrame df = pd.DataFrame({'income': [45, 48, 54, 57, 65, 69, 78], 'age': [23, 25, 24, 29, 38, 36, 40], 'gender': ['M', 'F', 'M', 'F', 'F', 'F', 'M'], 'college': ['Y', 'N', 'N', 'N', 'Y', 'Y', 'Y']}) #view DataFrame df income age gender college 0 45 23 M Y 1 48 25 F N 2 54 24 M N 3 57 29 F N 4 65 38 F Y 5 69 36 F Y 6 78 40 M Y
We can use the pd.get_dummies() function to convert gender and college both into dummy variables:
#convert gender to dummy variable pd.get_dummies(df, columns=['gender', 'college'], drop_first=True) income age gender_M college_Y 0 45 23 1 1 1 48 25 0 0 2 54 24 1 0 3 57 29 0 0 4 65 38 0 1 5 69 36 0 1 6 78 40 1 1
The gender column is now a dummy variable where:
- A value of 0 represents “Female”
- A value of 1 represents “Male”
And the college column is now a dummy variable where:
- A value of 0 represents “No” college
- A value of 1 represents “Yes” college
