Table of Contents
To perform a variance ratio test in Excel, you need to first calculate the variance of your sample data, then calculate the variance of the sample’s moving averages for a certain number of periods. Once you have both of these values, you can use the variance ratio formula to compare them and determine if the sample’s variance is significantly different from the moving average variance. You can then use this information to decide whether or not to reject the null hypothesis that the sample’s variance is equal to the moving average variance.
A variance ratio test is used to test whether or not two population variances are equal.
This test uses the following null and alternative hypotheses:
- H0: The population variances are equal
- HA: The population variances are not equal
To perform this test, we calculate the following test statistic:
F = s12 / s22
where:
- s12: The sample variance of the first group
- s22: The sample variance of the second group
If the that corresponds to this F test-statistic is less than a certain threshold (e.g. 0.05) then we reject the null hypothesis and conclude that the population variance are not equal.
The following step-by-step example shows how to perform a variance ratio test in Excel.
Step 1: Enter the Data
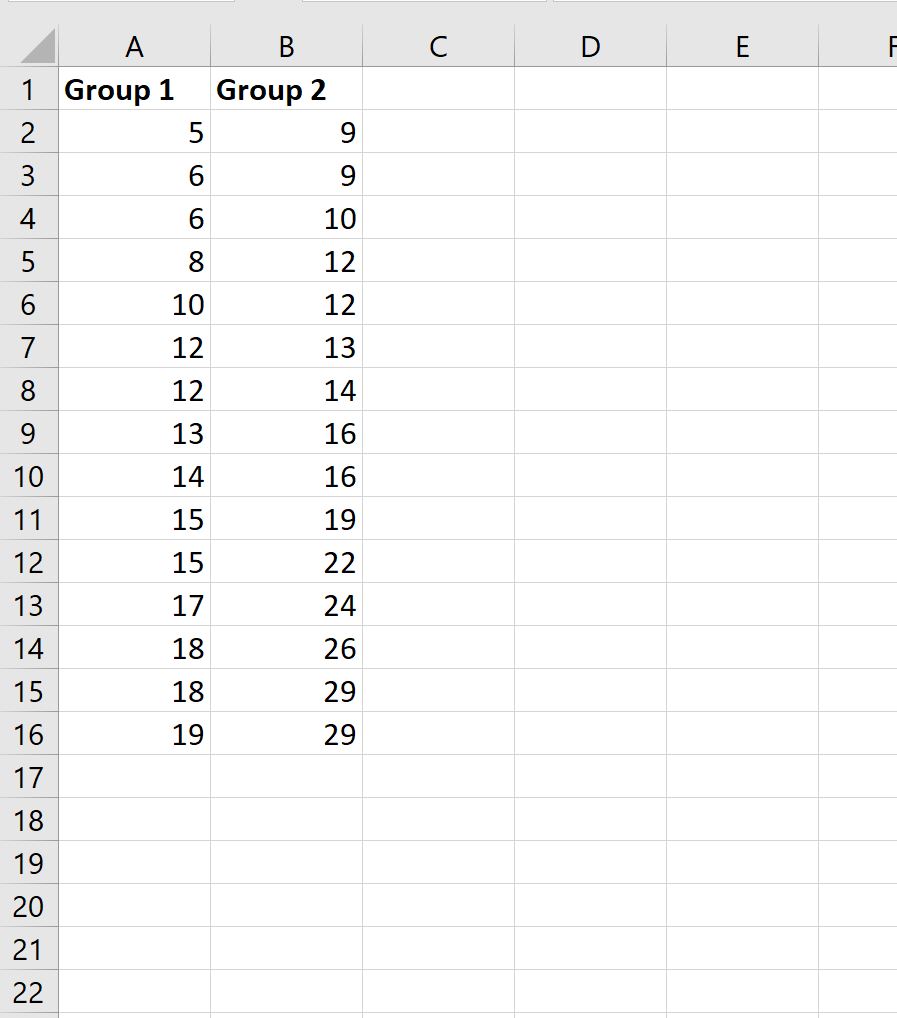
Suppose we want to know if two different species of plants have the same variance in height.
To test this, we collect a simple random sample of 15 plants from each species.
First, we’ll enter the heights for each species:
Step 2: Calculate the F Test Statistic
Next, we’ll type the following formula into cell E1 to calculate the F test-statistic:
=VAR.S(A2:A16)/VAR.S(B2:B16)
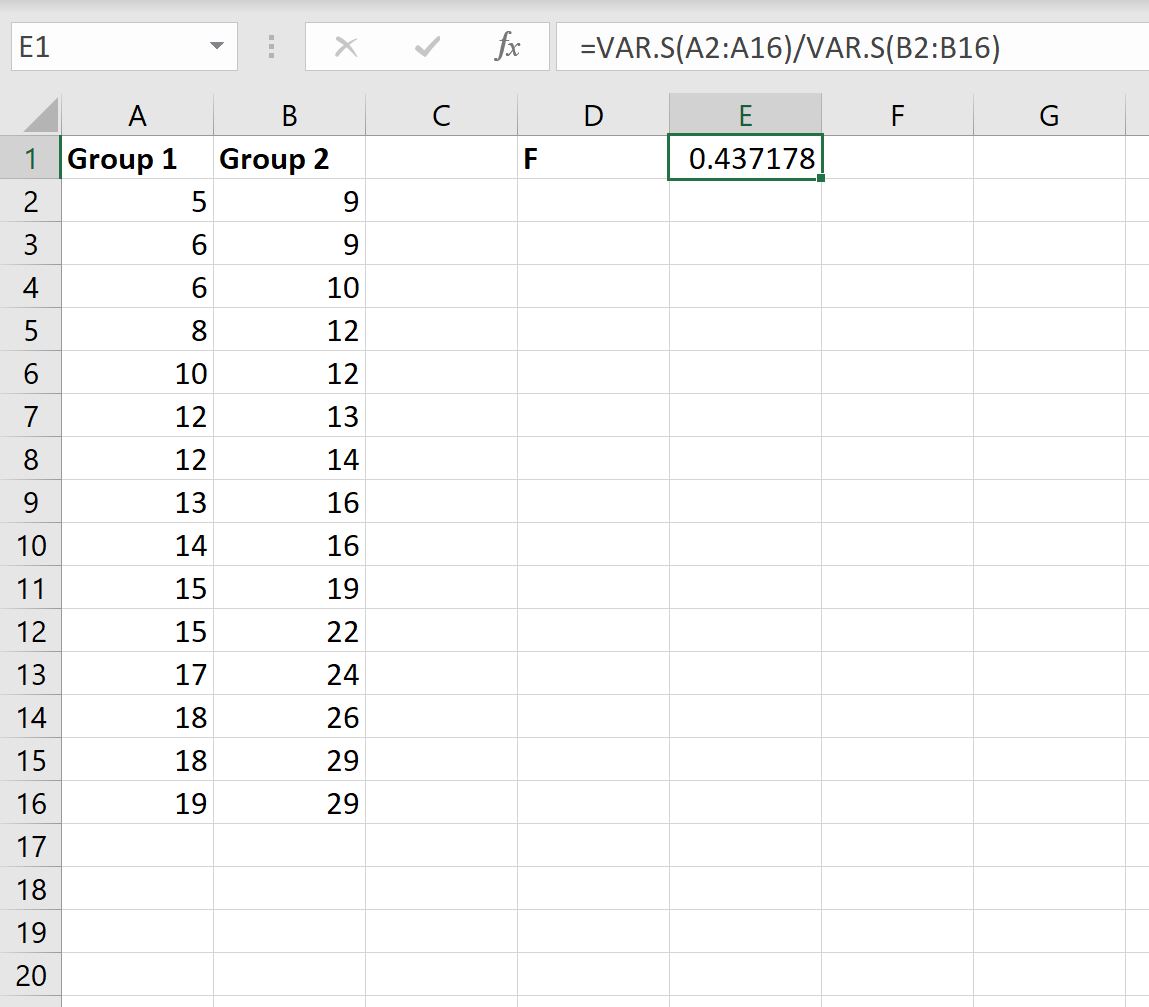
The F test-statistic turns out to be 0.437178.
Step 3: Calculate the P-Value
Next, we’ll type the following formula into cell E2 to calculate the p-value that corresponds to the F test-statistic:
=F.DIST(E1, COUNT(A2:A16)-1, COUNT(B2:B16)-1, TRUE)*2
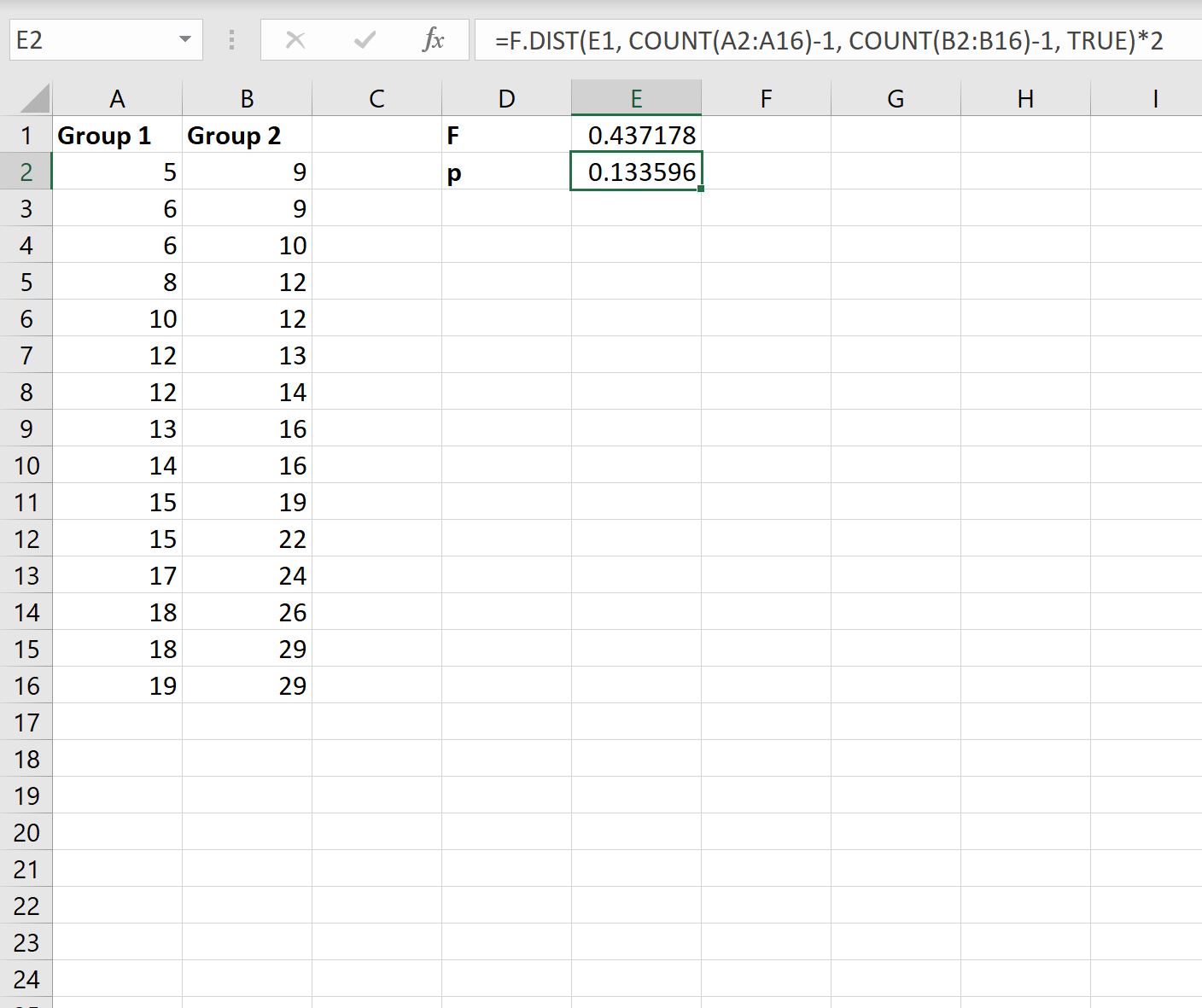
Note: In the formula, we multiplied by 2 at the end to produce a two-tailed p-value.
The p-value turns out to be 0.133596.
Recall the null and alternative hypotheses for this test:
- H0: The population variances are equal
- HA: The population variances are not equal
Because the p-value of our test (.133596) is not less than 0.05, we fail to reject the null hypothesis.
This means we do not have sufficient evidence to conclude that the variance in plant height between the two species is unequal.
