Table of Contents
To import an Excel file into SAS, you must first save the Excel file as a CSV (Comma Separated Value) file. Then, you can use the IMPORT procedure in SAS to import the CSV file into a SAS dataset. You can specify the CSV file to be imported, along with various other options such as where the first row of data is located and the delimiter to use. You can also use the IMPORT procedure to import multiple CSV files at once. Once the CSV file is imported, you can use the SAS dataset for further analysis.
You can use proc import to quickly import data from an Excel file into SAS.
This procedure uses the following basic syntax:
/*import data from Excel file called my_data.xlsx*/ proc import out=my_data datafile="/home/u13181/my_data.xlsx" dbms=xlsx replace; getnames=YES; run;
Here’s what each line does:
- out: Name to give dataset once imported into SAS
- datafile: Location of Excel file to import
- dbms: Format of file being imported
- replace: Replace the file if it already exists
- getnames: Use first row as variable names (Set to NO if first row does not contain variable names)
The following example shows how to use this function in practice.
Example: Import Data from Excel File into SAS
Suppose we have the following dataset in Excel:

We can use the following code to import this dataset into SAS and call it new_data:
/*import data from Excel file called my_data.xlsx*/ proc import out=new_data datafile="/home/u13181/my_data.xlsx" dbms=xlsx replace; getnames=YES; run; /*view dataset*/ proc print data=new_data;
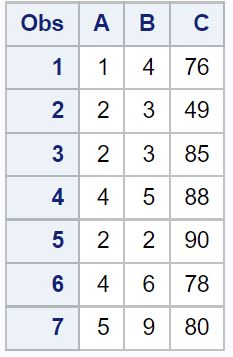
The data shown in the SAS output matches the data shown in the Excel file.
Note: We used getnames=YES when importing the file since the first row of the Excel file contained variable names.
The following tutorials explain how to perform other common tasks in SAS:
