Table of Contents
A prediction interval in Excel is a range of values that can be used to predict future values of a variable. It is constructed by combining a point estimate of the mean of the variable with an estimated standard deviation. This can be done by using the FORECAST and CONFIDENCE functions in Excel. The FORECAST function predicts a future value of a variable, while the CONFIDENCE function calculates the standard deviation of the prediction. The prediction interval can then be calculated by adding and subtracting the standard deviation from the point estimate of the mean.
In statistics, is a technique we can use to quantify the relationship between a predictor variable, x, and a response variable, y.
When we conduct a simple linear regression, we obtain a “line of best fit” that describes the relationship between x and y, which can be written as:
ŷ = b0 + b1x
where:
- ŷ is the predicted value of the response variable
- b0 is the y-intercept
- b1 is the regression coefficient
- x is the value of the predictor variable
Sometimes we’re interested in using this line of best fit to construct a prediction interval for a given value of x0, which is an interval around the predicted value ŷ0 such that there is a 95% probability that the real value of y in the population corresponding to x0 is within this interval.
The formula to calculate the prediction interval for a given value x0 is written as:
ŷ0 +/- tα/2,df=n-2 * s.e.
where:
s.e. = Syx√(1 + 1/n + (x0 – x)2/SSx)
The formula might look a bit intimidating, but it’s actually straightforward to calculate in Excel. Next, we’ll walk through an example of how to use this formula to calculate a prediction interval for a given value in Excel.
Example: How to Construct a Prediction Interval in Excel
The following dataset shows the number of hours studied along with the exam score received by 15 different students:
Suppose we would like to create a 95% prediction interval for the value x0 = 3. That is, we want to create an interval such that there is a 95% probability that the exam score is within this interval for a student who studies for 3 hours.
The following screenshot shows how to calculate all of the necessary values to obtain this prediction interval.
Note: The formulas in column F show how the values in column E were calculated.
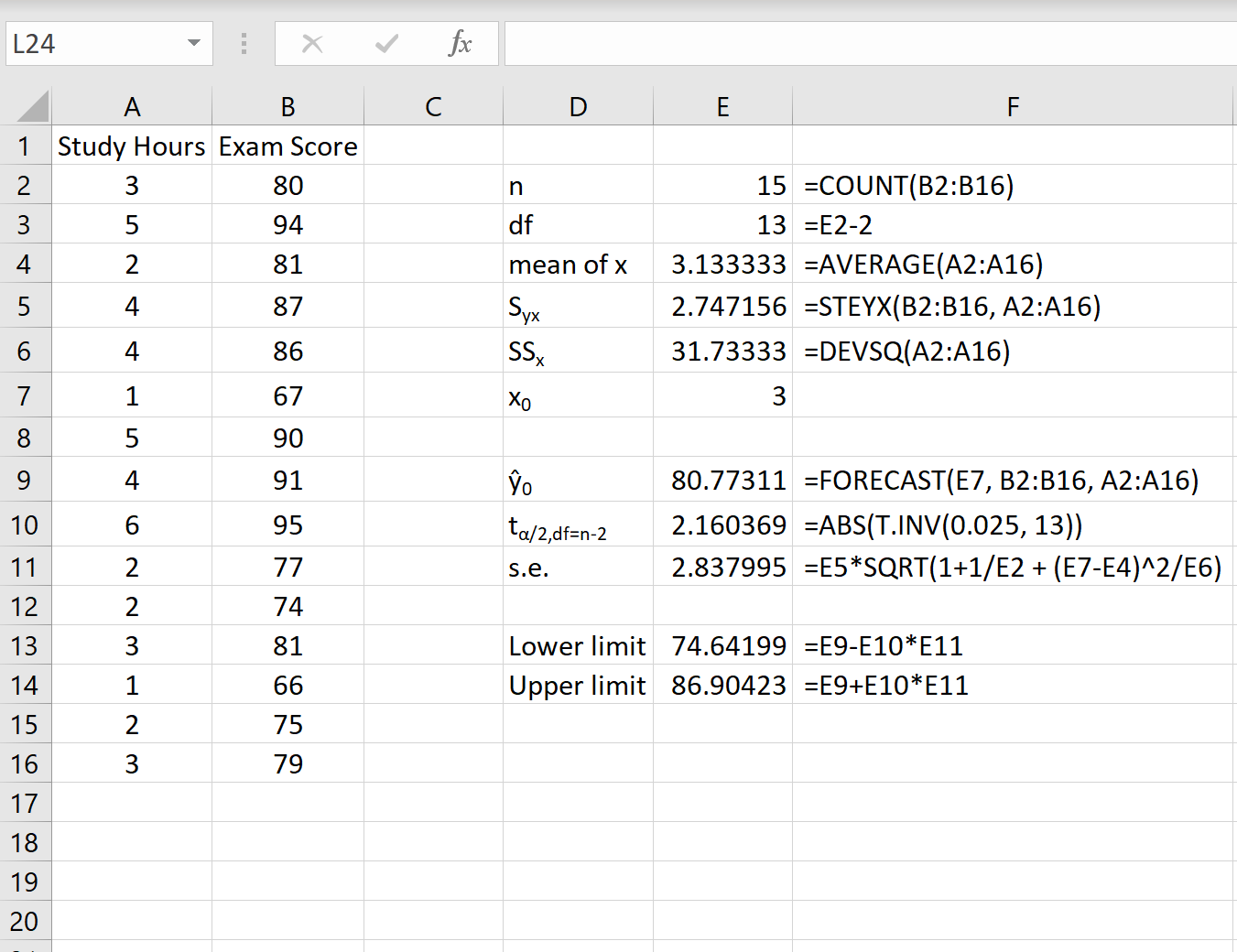
The 95% prediction interval for a value of x0 = 3 is (74.64, 86.90). That is, we predict with 95% probability that a student who studies for 3 hours will earn a score between 74.64 and 86.90.
A couple notes on the calculations used:
- To calculate the t-critical value of tα/2,df=n-2 we used α/2 = .05/2 = 0.25 since we wanted a 95% prediction interval. Note that higher prediction intervals (e.g. 99% prediction interval) will lead to wider intervals. Conversely, a lower prediction interval (e.g. 90% prediction interval) will lead to a more narrow interval.
- We used the formula =FORECAST() to obtain the predicted value for ŷ0 but the formula =FORECAST.LINEAR() will return the exact same value.
