Table of Contents
To calculate SST, SSR, and SSE in Excel, you need to use the SUM function to calculate the sum of the squares of the differences between the actual values and the mean of the actual values (SST), the sum of the squares of the differences between the predicted values and the mean of the actual values (SSR), and the sum of the squares of the differences between the actual values and the predicted values (SSE). Once you have these sums, you can calculate the SST, SSR, and SSE from these sums.
We often use three different values to measure how well a actually fits a dataset:
1. Sum of Squares Total (SST) – The sum of squared differences between individual data points (yi) and the mean of the response variable (y).
- SST = Σ(yi – y)2
2. Sum of Squares Regression (SSR) – The sum of squared differences between predicted data points (ŷi) and the mean of the response variable(y).
- SSR = Σ(ŷi – y)2
3. Sum of Squares Error (SSE) – The sum of squared differences between predicted data points (ŷi) and observed data points (yi).
- SSE = Σ(ŷi – yi)2
The following step-by-step example shows how to calculate each of these metrics for a given regression model in Excel.
Step 1: Create the Data
First, let’s create a dataset that contains the number of hours studied and exam score received for 20 different students at a certain school:

Step 2: Fit a Regression Model
Along the top ribbon in Excel, click the Data tab and click on Data Analysis. If you don’t see this option, then you need to first .

Once you click on Data Analysis, a new window will pop up. Select Regression and click OK.
In the new window that appears, fill in the following information:


Step 3: Analyze the Output
The three sum of squares metrics – SST, SSR, and SSE – can be seen in the SS column of the ANOVA table:
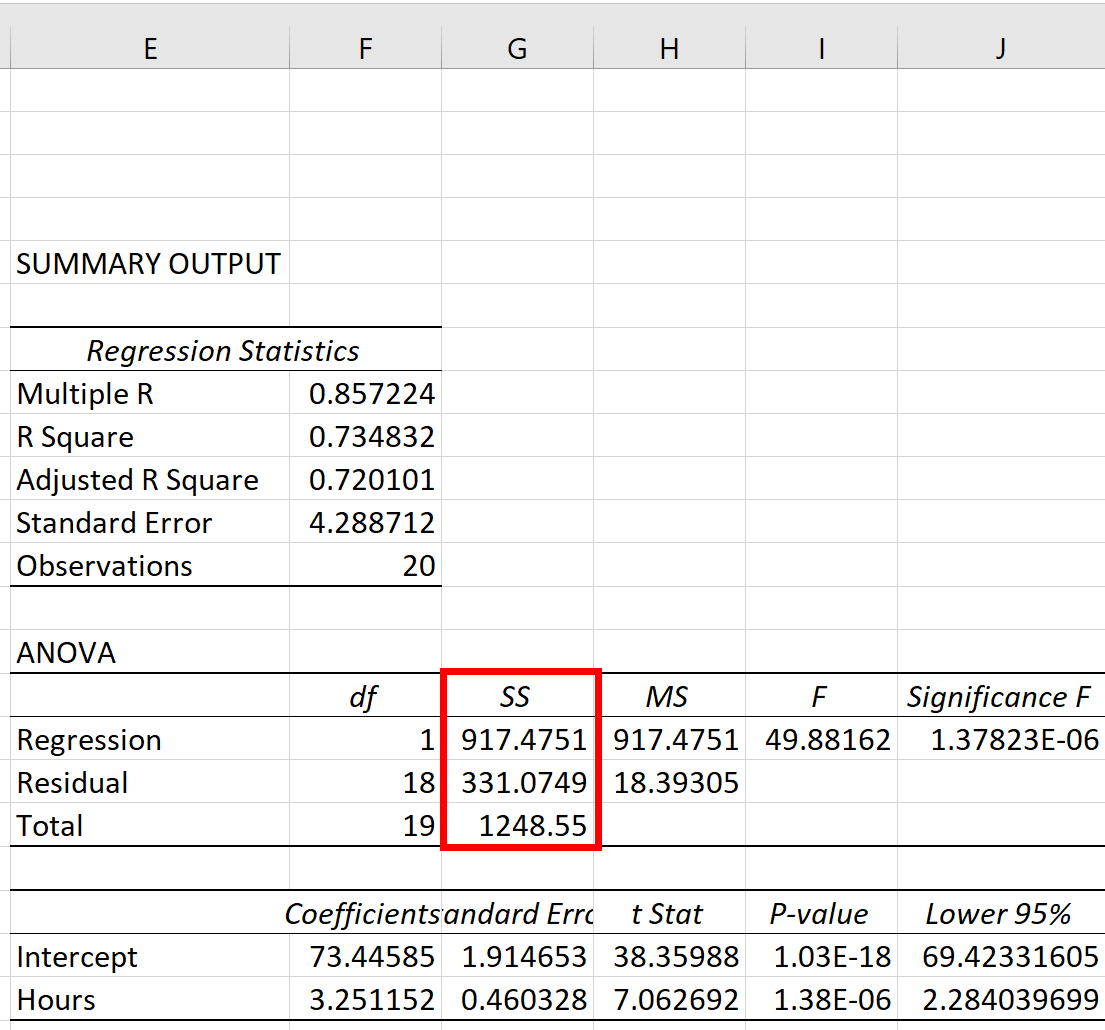
The metrics turn out to be:
- Sum of Squares Total (SST): 1248.55
- Sum of Squares Regression (SSR): 917.4751
- Sum of Squares Error (SSE): 331.0749
We can verify that SST = SSR + SSE:
- SST = SSR + SSE
- 1248.55 = 917.4751 + 331.0749
We can also manually calculate the of the regression model:
- R-squared = SSR / SST
- R-squared = 917.4751 / 1248.55
- R-squared = 0.7348
This tells us that 73.48% of the variation in exam scores can be explained by the number of hours studied.
